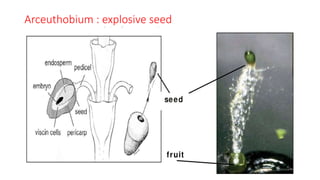
The document defines seed dispersal as the movement of seeds away from their parent plant and outlines its importance in reducing competition and increasing progeny variety. It describes various methods of seed dispersal including by wind (anemochory), water (hydrochory), animals (zoochory), and explosive mechanisms (autochory). Each method has specific characteristics and examples that illustrate how seeds can travel long distances and establish in new environments.