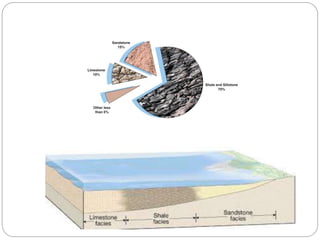
This document summarizes key information about sedimentary rocks, including their formation processes (mechanical, organic, chemical), structural features (stratification, lamination, cross-bedding), and common types (limestone, sandstone, shale, laterite). Sedimentary rocks form from the deposition and consolidation of sediments and make up 70-80% of the Earth's surface. Their formation involves compaction, cementation, and crystallization. Structural features provide clues to depositional environments. Common types are described along with their compositions and uses.