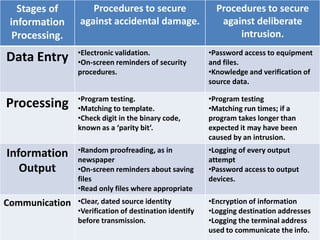
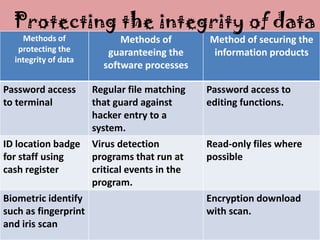
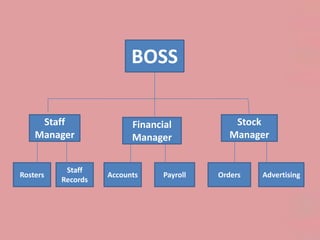
The document outlines various procedures for securing information within an organization, including:
1) Implementing password protections, regular backups, and access restrictions to safeguard data from accidental loss or deliberate intrusion.
2) Using techniques like encryption and activity logging when information is transmitted externally.
3) Restricting access privileges to files based on employee roles to prevent unauthorized viewing or editing of sensitive data.