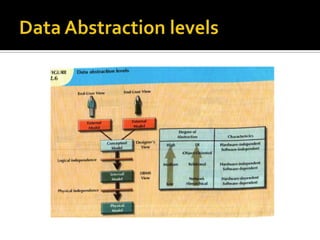
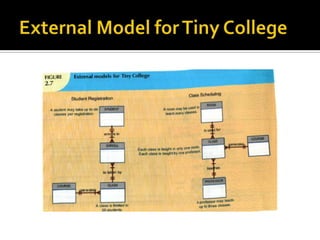
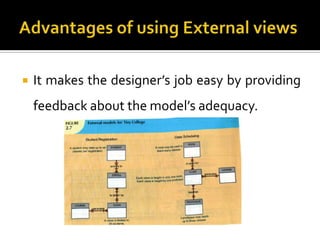
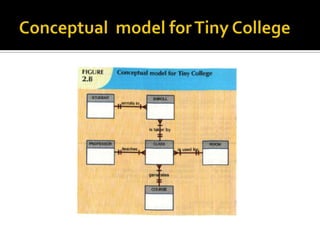
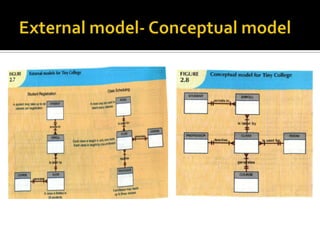
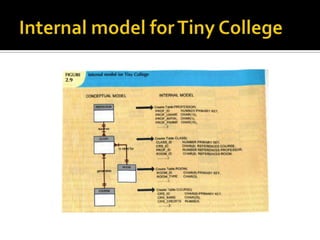
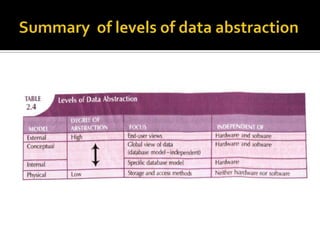
The document discusses three levels of data abstraction defined by ANSI - the external, conceptual, and internal levels. The external level represents the end user's view, the conceptual level provides a global view of the data independent of software and hardware, and the internal level maps the conceptual model to a specific DBMS in a software-dependent way. These levels of abstraction provide organization and flexibility in data modeling.