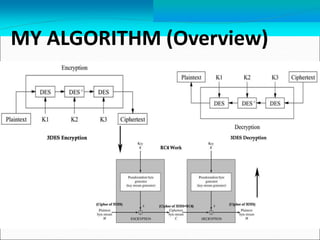
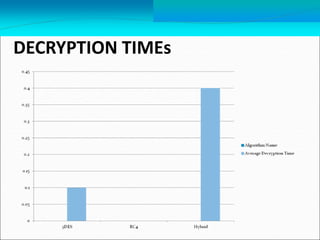
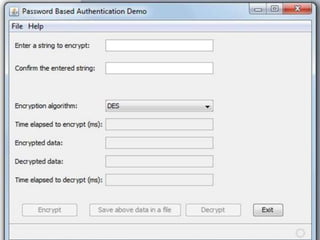
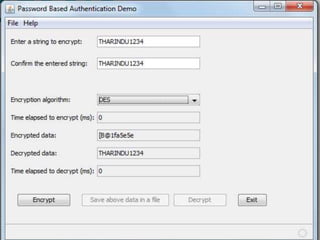
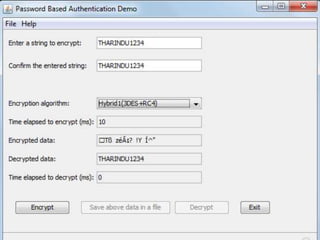
This document describes Tharindu Weerasinghe's MSc research project on developing a hybrid cipher by combining a block cipher and a stream cipher. It summarizes the background on block ciphers like DES and stream ciphers like RC4. It then describes the researcher's algorithm that first encrypts plaintext using 3DES (a block cipher) and then RC4 (a stream cipher), and decrypts in the reverse order. The document discusses the benefits of combining ciphers and addresses some vulnerabilities of using block and stream ciphers individually. It also mentions the researcher implemented the algorithm in Java and measured encryption/decryption times.