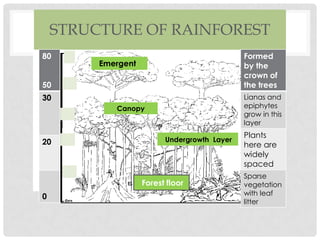
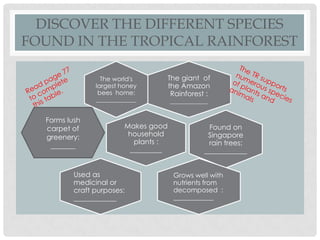
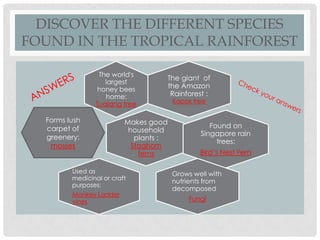
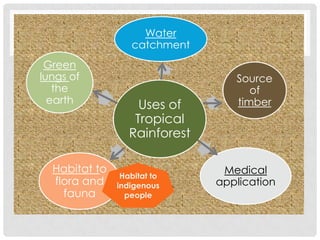
Tropical rainforests once covered 14% of the Earth's land but now only cover 6%, and experts say the last remaining forests could be destroyed within 40 years. Tropical rainforests are characterized by year-round high temperatures and rainfall. They have several distinct layers including an emergent layer with the tallest trees reaching 50-80 meters, a canopy layer from 20-30 meters, and an undergrowth layer with sparse vegetation. Rainforests provide many benefits such as being habitats for biodiversity, sources of medicines and timber, and helping regulate the Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide. However, they are being destroyed for agriculture, logging and other human activities.