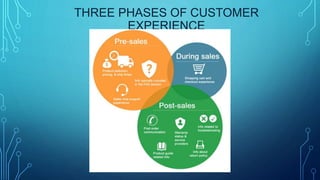
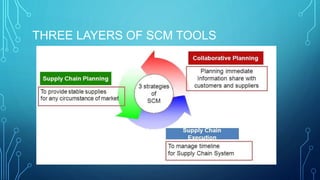
This document discusses supply chain management (SCM), customer relationship management (CRM), and the integration of SCM and CRM (ISCRM). SCM involves planning and executing the flow of goods from raw materials to the customer. CRM uses technology to organize sales, marketing, and customer service to acquire, retain, and increase sales to customers. Integrating SCM and CRM allows companies to improve financial and operational metrics by providing customers with optimized product delivery and service. The document outlines the components, benefits, and types of CRM systems as well as a SWOT analysis of CRM.