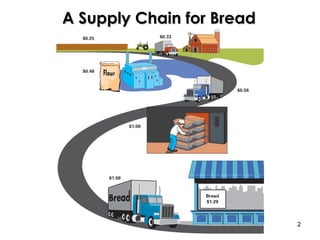
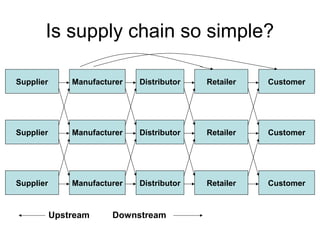
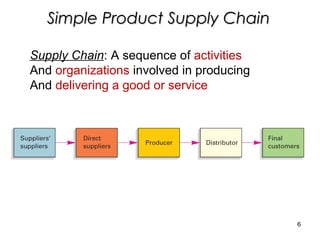
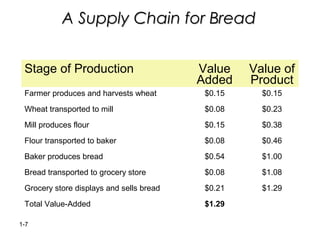
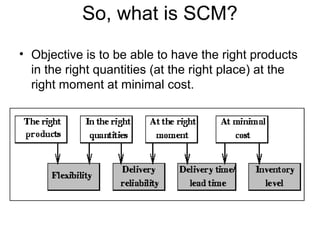
Supply chain management involves coordinating all parties involved in fulfilling customer requests, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers. The objective is to maximize overall profit by generating revenue from customers that exceeds costs incurred along the entire supply chain. An effective supply chain manages product, information, and fund flows to have the right products in the right quantities available at the minimal cost. A simple example supply chain for bread shows the value added at each stage from farmer to grocery store. Logistics is the management of the flow of goods, information, and resources between the point of origin and consumption, integrating transportation, inventory, and warehousing to add time and place value.