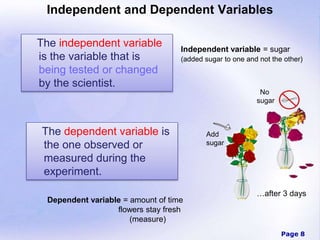
Science is the organized study of the world through observation and experimentation. Scientists propose explanations and use the scientific method to test them, gathering evidence. The scientific method involves asking a question, forming a hypothesis, designing an experiment to test the hypothesis, recording and analyzing the experimental data, and drawing a conclusion about whether the hypothesis was confirmed or not based on the evidence.