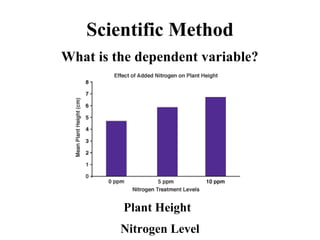
The document discusses the scientific method, which is a set of procedures scientists follow to solve problems. It involves 7 key steps: 1) defining the problem, 2) collecting data, 3) drawing a hypothesis, 4) planning and performing an experiment, 5) collecting and recording observations, 6) drawing a conclusion, and 7) communicating findings. The document provides examples and explanations of each step, including defining variables, designing valid experiments, and types of measurements and data.