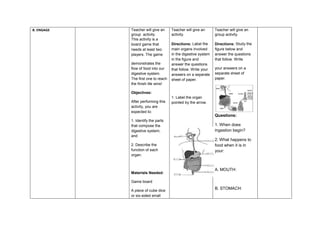
The document outlines a daily lesson log for Grade 8 Science at Tambongon National High School, focusing on the digestive system and its interaction with other body systems. It includes objectives, content standards, performance standards, and various procedures and activities to engage students in learning about digestion, absorption, and the role of different organs. Additionally, it emphasizes assessment strategies and the need for reflective teaching practices to address student progress and identify areas for improvement.