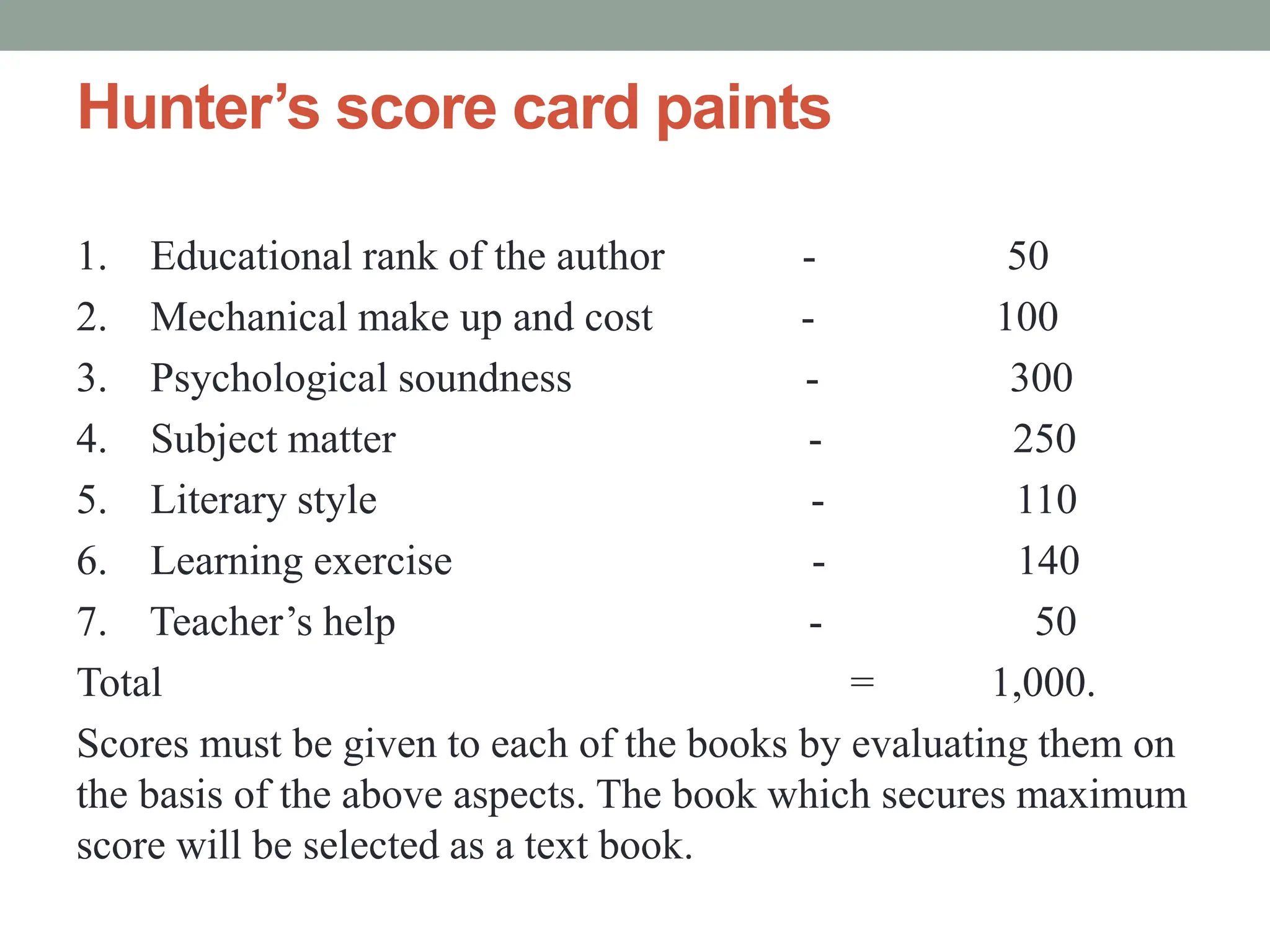
The document discusses the importance and characteristics of science textbooks, outlining their role in the teaching-learning process and criteria for selecting high-quality materials. It emphasizes the need for textbooks that are organized, appropriate in content, accessible in literary style, visually appealing, and backed by expert authors. The document also highlights the significance of textbooks in supporting both teachers and students in grasping fundamental scientific concepts and encourages the development of self-study habits.