Embed presentation
Downloaded 354 times

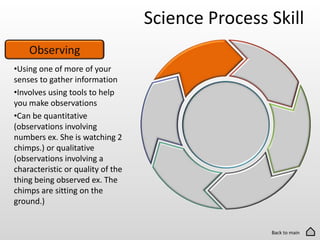
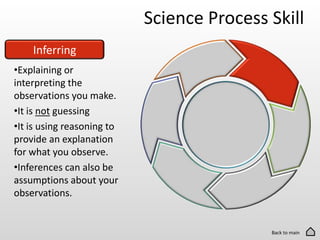
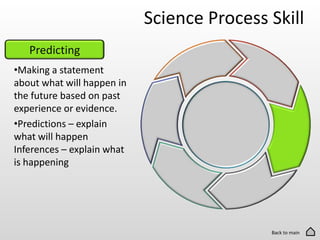
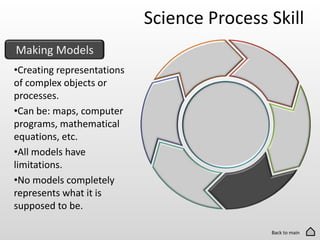
The document discusses the 6 basic science process skills needed to be successful in science classes. These skills are observing, inferring, predicting, making models, classifying, and evaluating. Each skill is defined in 1-2 sentences. Observing involves using senses to gather information. Inferring is explaining observations using reasoning. Predicting is making statements about future events based on evidence. Making models creates representations of complex objects. Classifying groups items based on shared characteristics. Evaluating compares data to reach conclusions.






