1. The document discusses supervised learning methods for link recommendation in co-authorship networks.
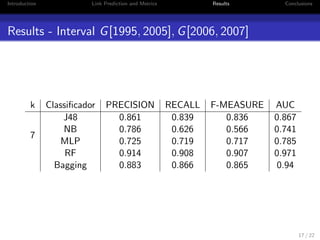
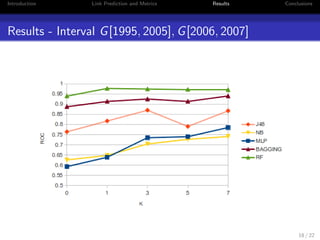
2. It compares algorithms like decision trees, naive Bayes, neural networks, random forests and bagging using metrics like AUC, precision, recall and F1-measure.
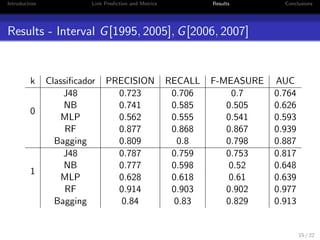
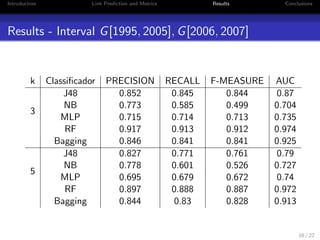
3. The experiments show that random forests and bagging outperform other methods, particularly when dealing with redundant features. The core size parameter k and time intervals also impact recommendation quality.