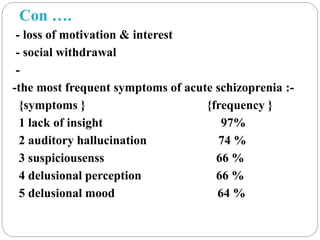
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder characterized by disordered thoughts, abnormal behaviors, and difficulties perceiving reality. It is prevalent worldwide and genetic and environmental factors likely contribute to its development. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech and behavior, negative symptoms like apathy, and impaired social and occupational functioning. Treatment involves antipsychotic medications and psychotherapy. Nurses monitor symptoms, assess functioning, and aim to promote health, self-care, and appropriate thought processes through therapeutic interventions.






![B ]. Psychosocial factor s:
1 impaired ego functioning :
reality testing and judgement is affected .the intensity
of schizophrenia will depend up on the intense
impairment of ego function .
2 pathological communication :
it has a significant role to play in a child whether to
withdraw from the communication
for example. In double bound communication the child
is not able to discriminate the short of message is ,”Go
out and play ,but see that you don’t fight with anyone
“](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schizophreniapriteshmhn-201215103304/85/Schizophrenia-pritesh-mhn-7-320.jpg)

![CON ..
c] social cultural factors : person who live
in low socio –economic families are suffer
to schizophrenia . exp :A child at a very
young age goes for work .
D] organic theory : theorists believe that
schizophrenia is caused due to infection
,poison ,trauma or metabolic disorders.
E] a patient with vitamin B1 ,B6,B12
vitamin c deficiency may become
schizophrenic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schizophreniapriteshmhn-201215103304/85/Schizophrenia-pritesh-mhn-9-320.jpg)