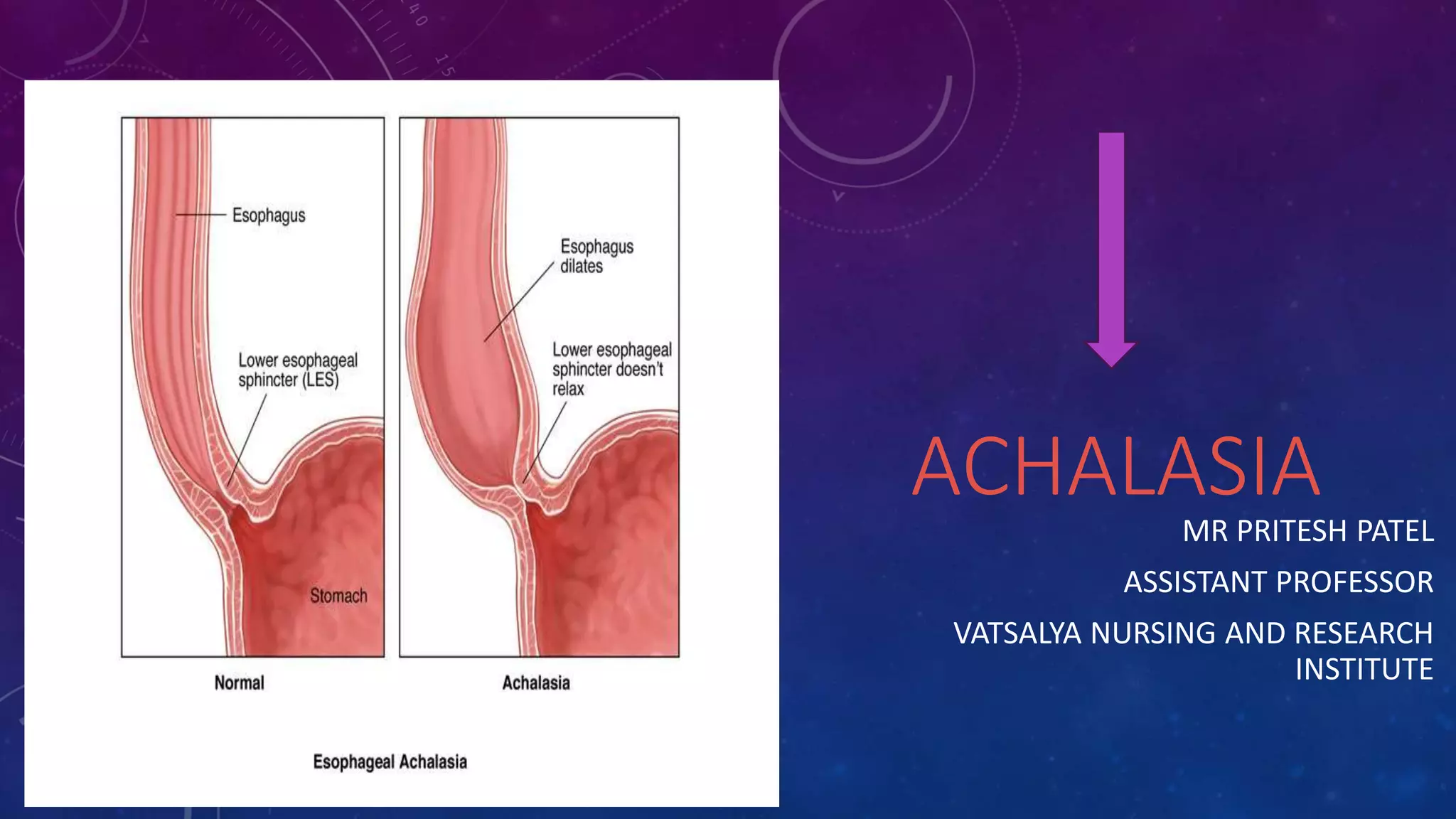
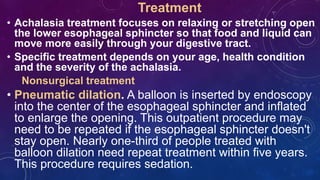
Achalasia is a rare disorder where the esophagus becomes dilated and loses the ability to squeeze food into the stomach, making swallowing difficult. It occurs when nerves in the esophagus become damaged and the cause is poorly understood, though viral infection or autoimmune responses have been suspected. Treatment focuses on relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter through nonsurgical methods like balloon dilation or Botox injections, or through surgery to cut the sphincter muscles.