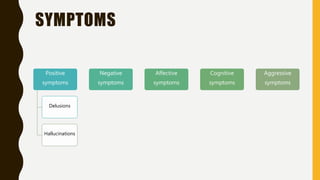
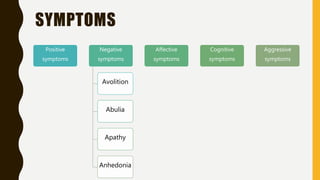
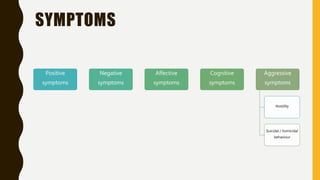
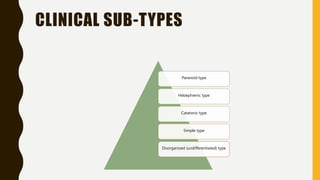
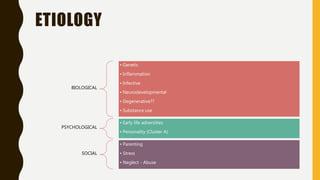
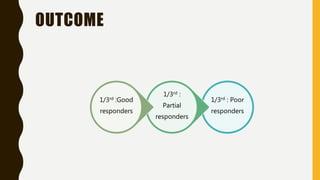
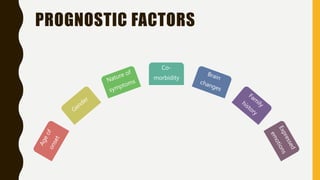
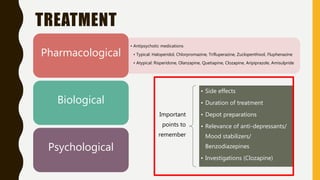
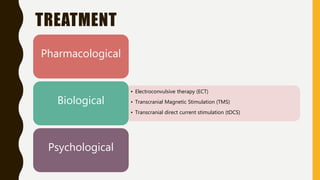
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder characterized by positive symptoms like delusions and hallucinations, negative symptoms like apathy and anhedonia, as well as cognitive and affective symptoms. It has a prevalence of around 1% globally and typically onset is in young adulthood. Treatment involves pharmacological interventions like antipsychotic medications and biological therapies combined with psychological interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy and social skills training. Prognosis depends on factors like comorbidities, with about a third of people experiencing a good response to treatment.