EEG basics for Mental Health Professionals provides an overview of EEG (electroencephalography). Some key points covered include:
- Hans Berger invented EEG in 1924 to study how the brain and mind interact with the outside world.
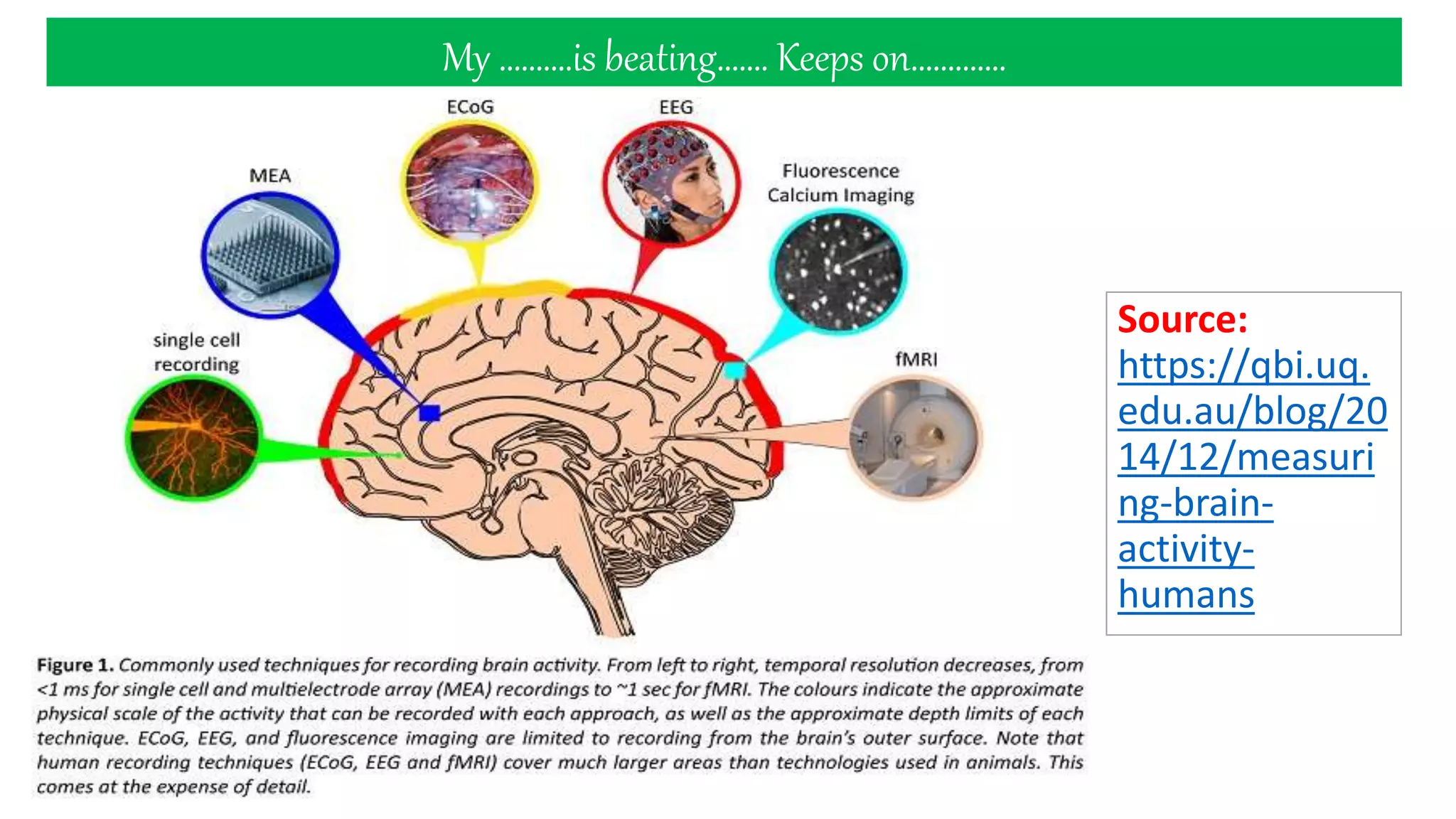
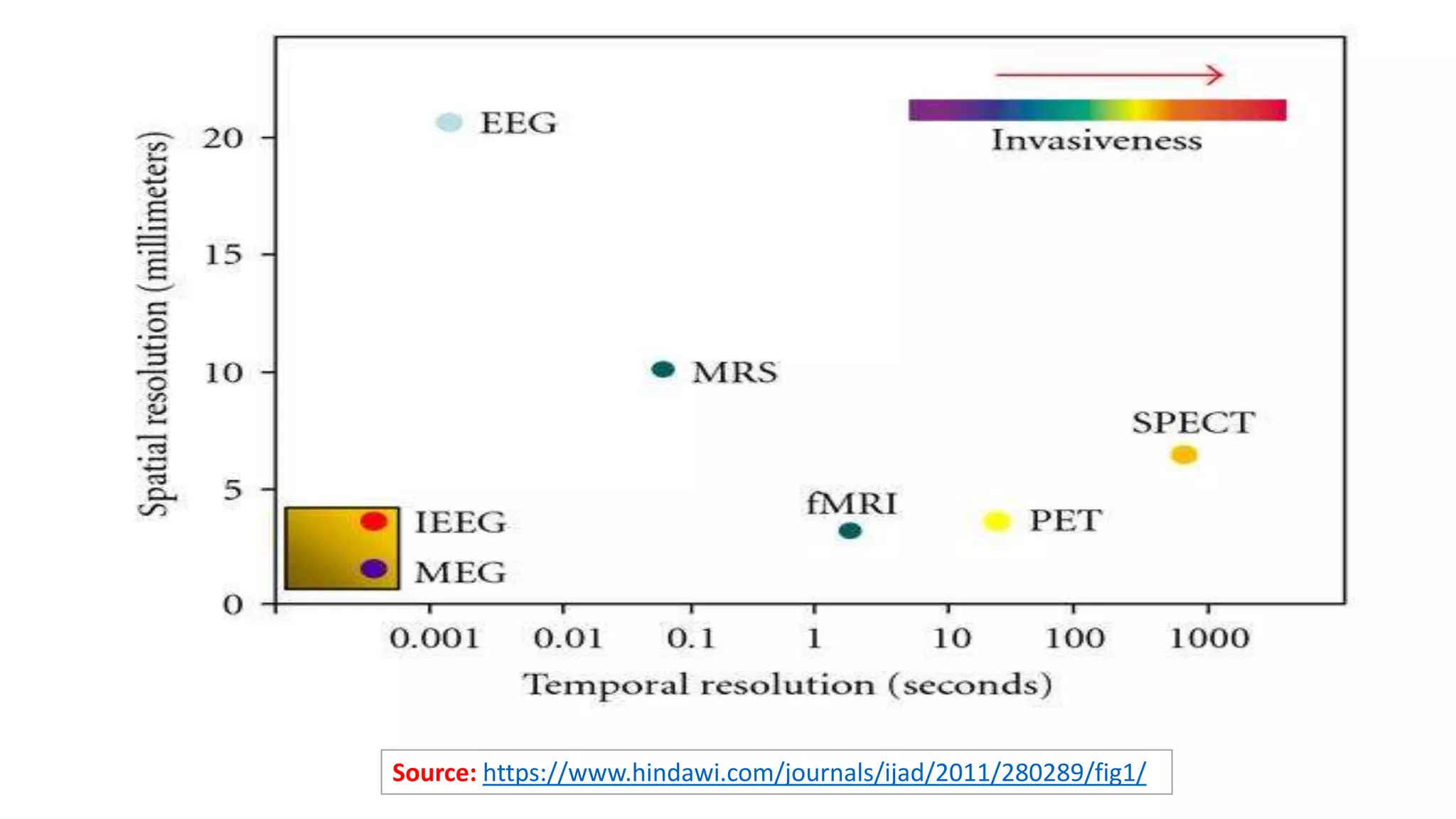
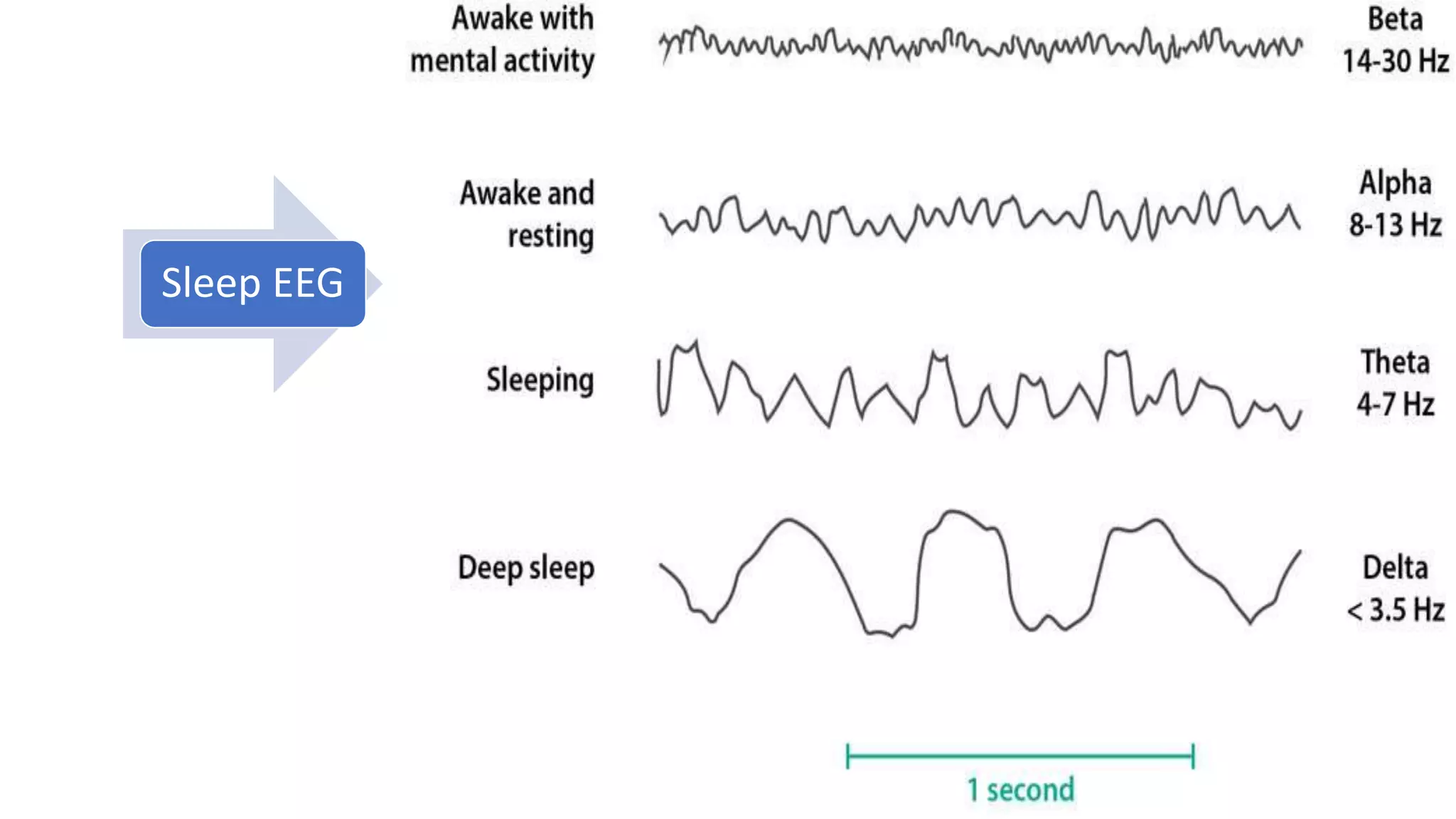
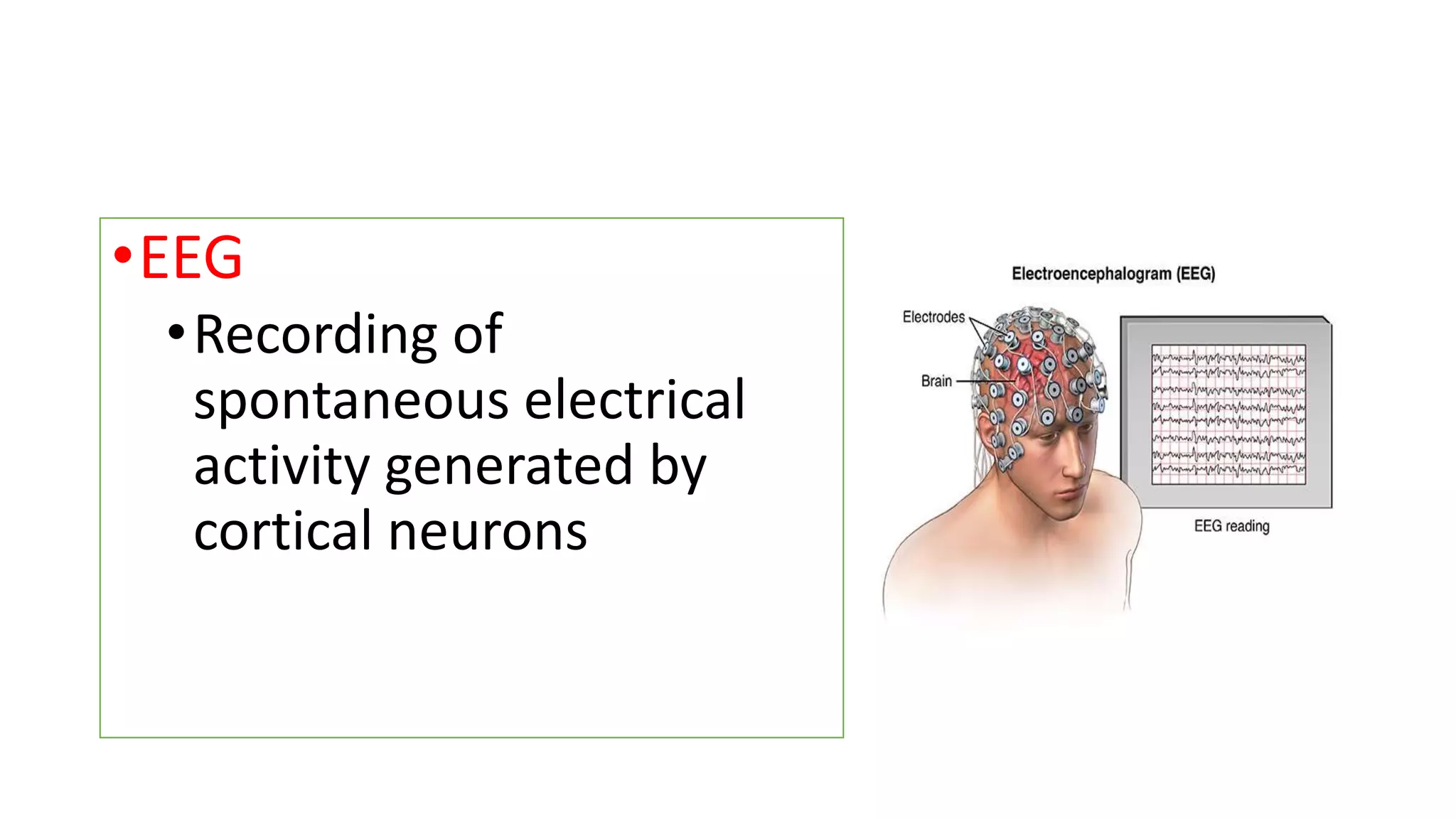
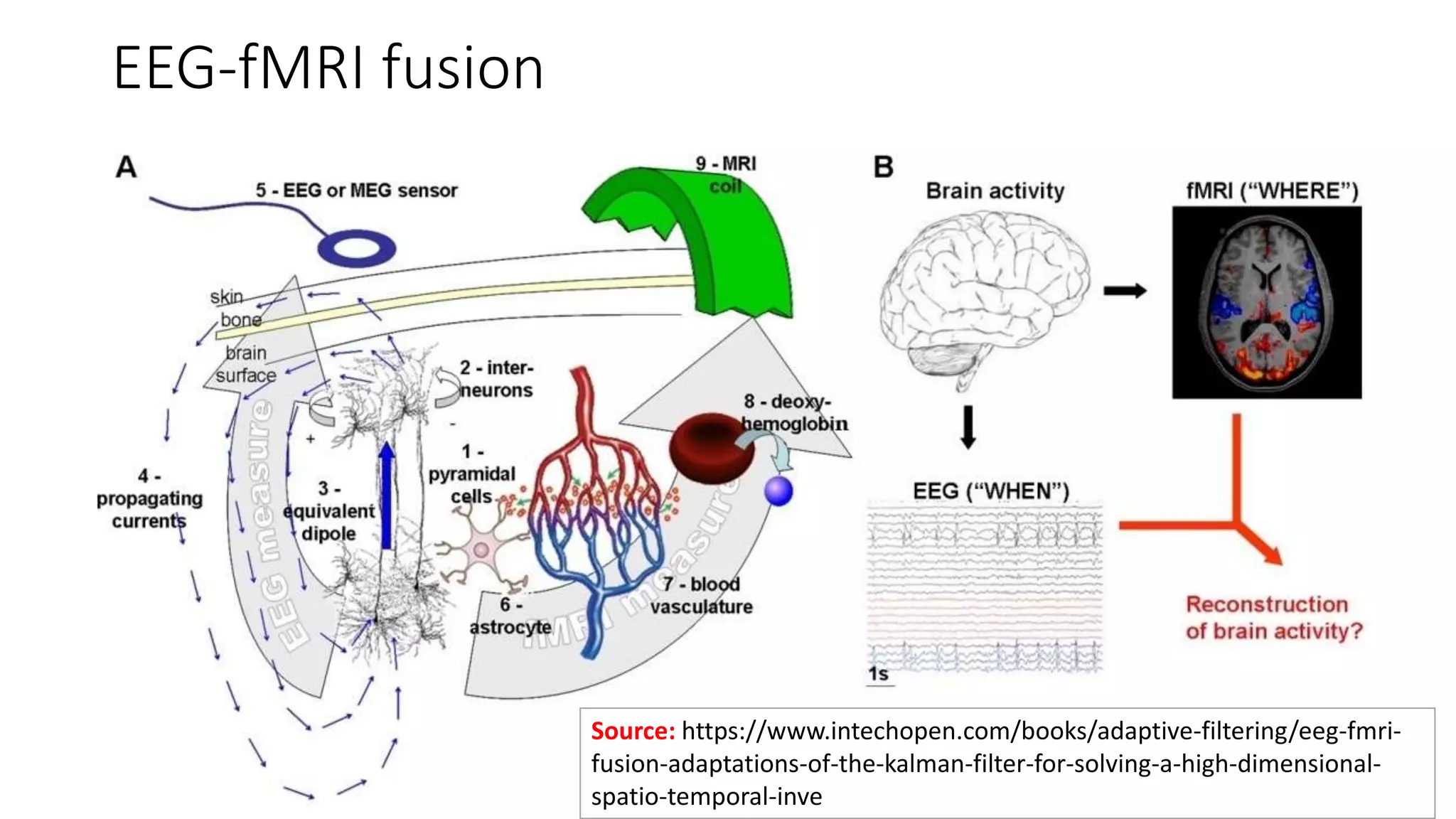
- EEG involves recording the spontaneous electrical activity generated by cortical neurons via electrodes placed on the scalp. These detect extracellular electrical fields from action potentials and synaptic activity.
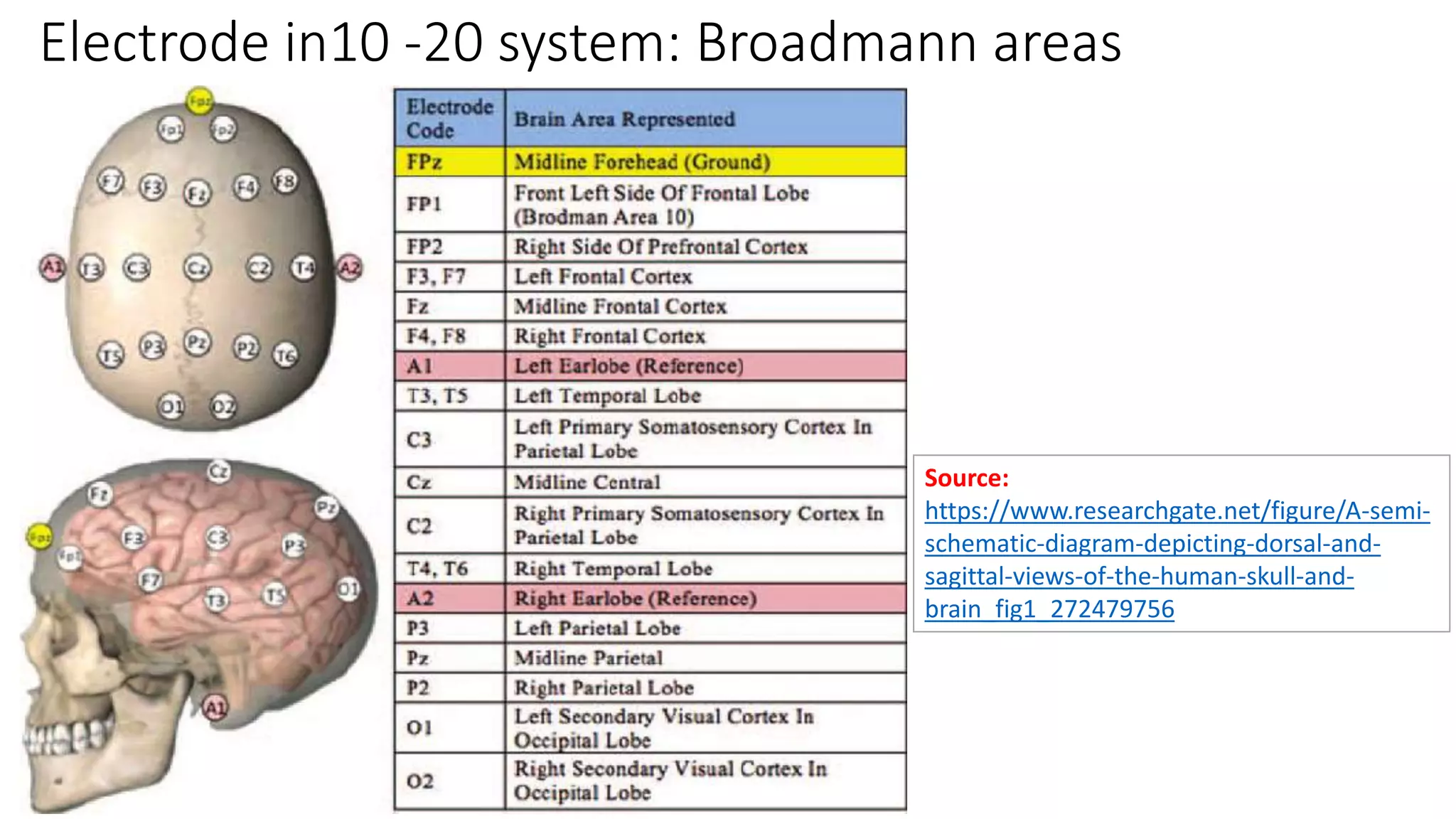
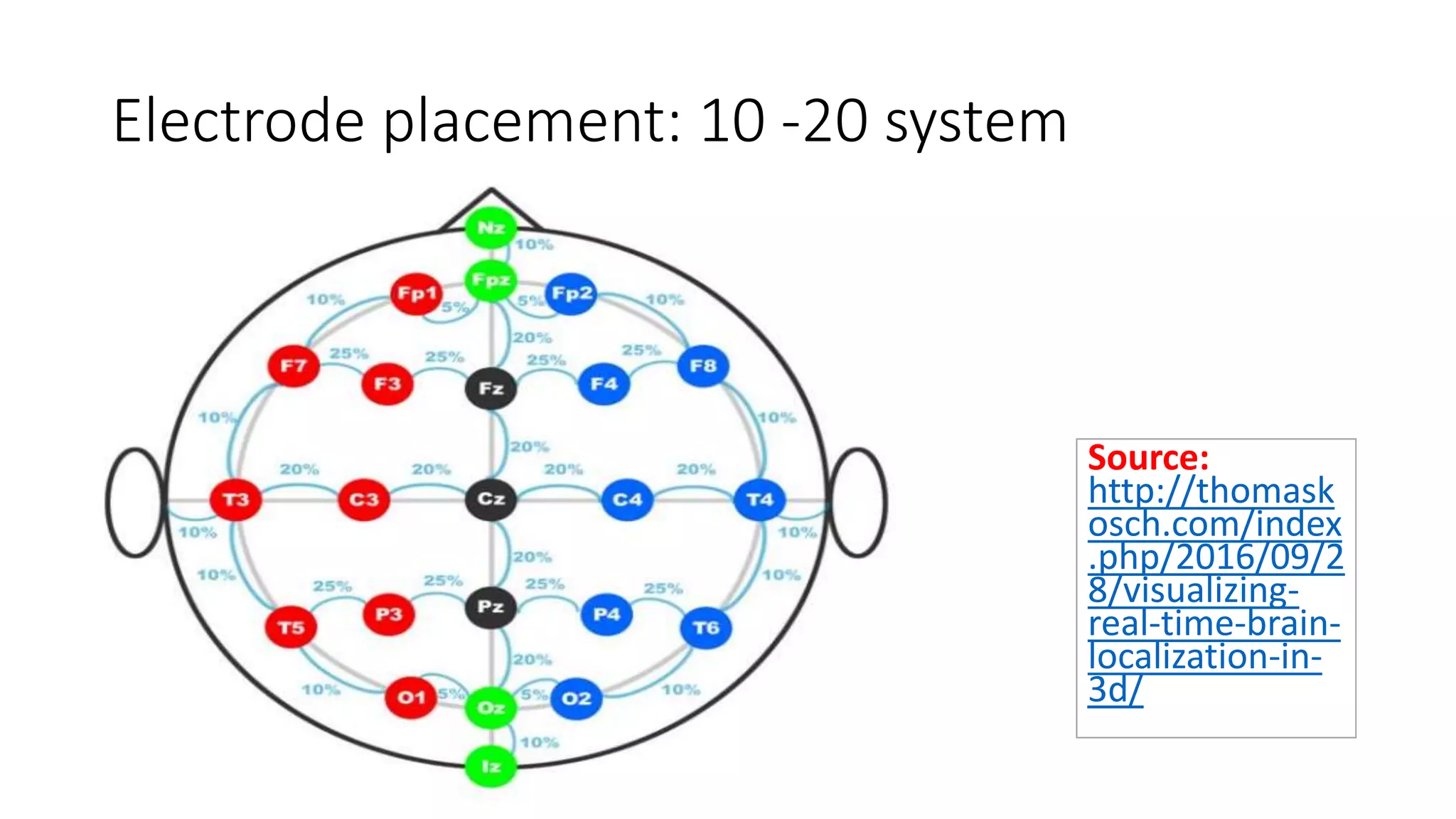
- The international 10-20 system is commonly used for electrode placement. It allows recording of brain activity from different regions.
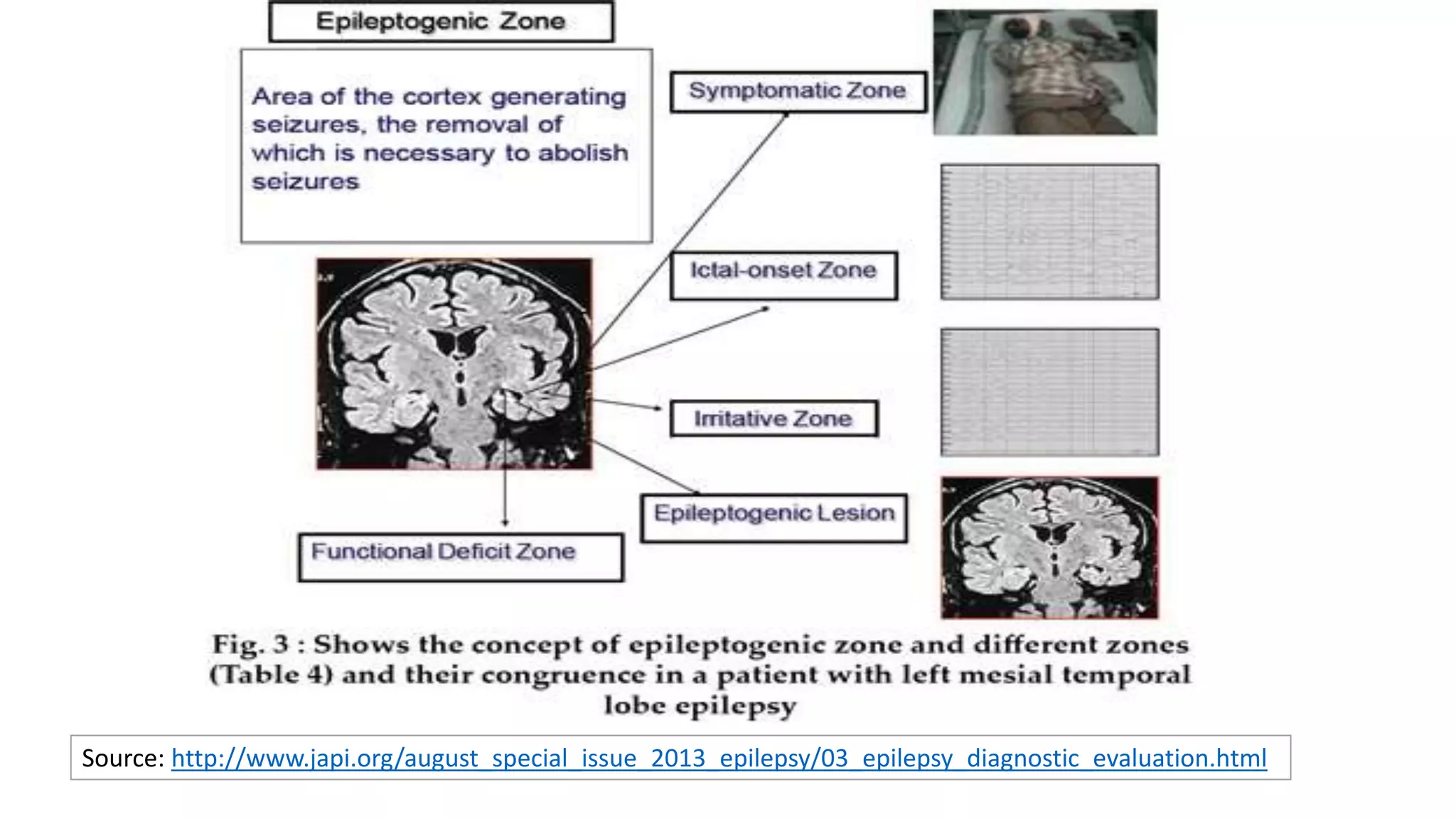
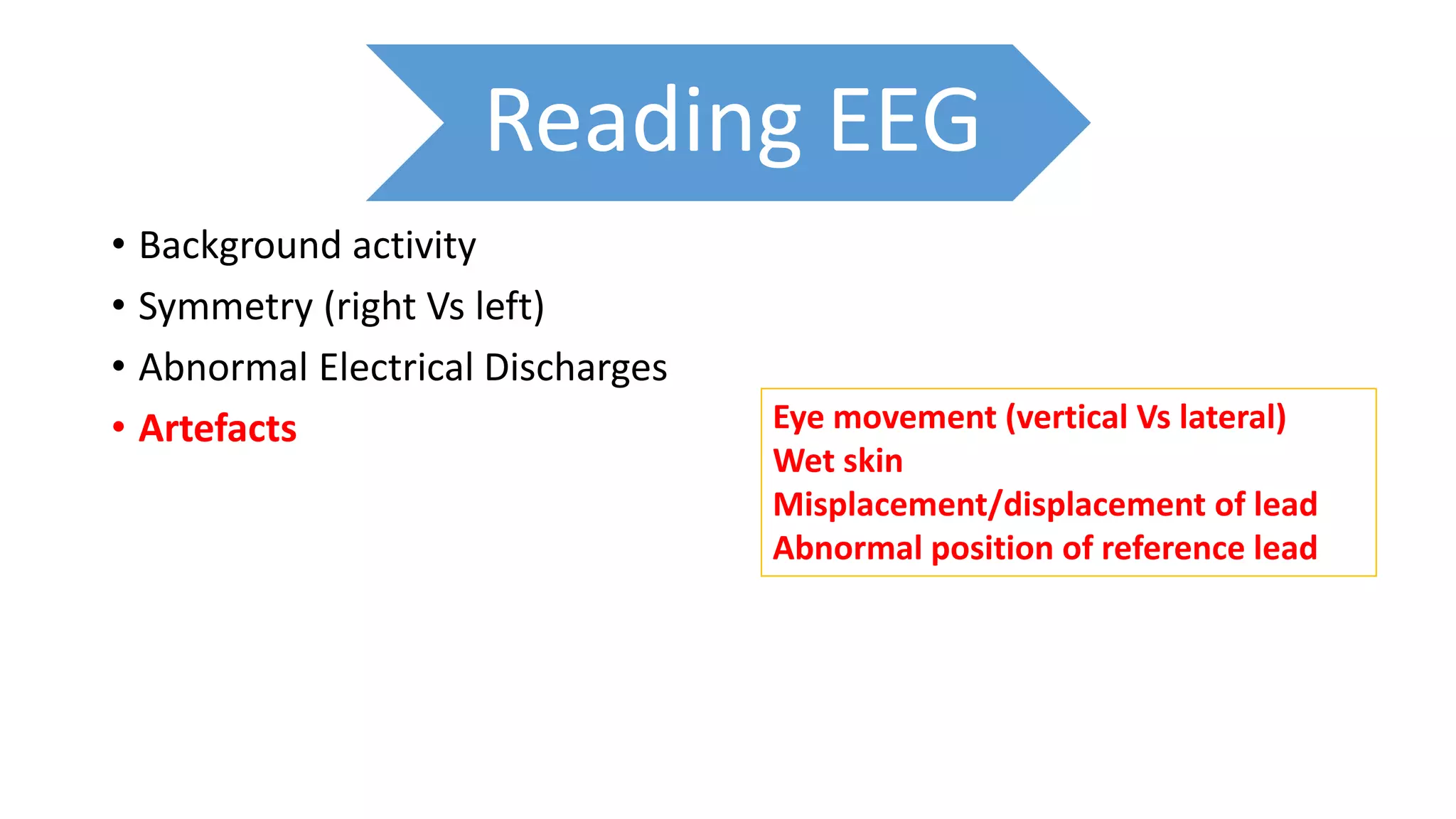
- EEG is used to examine background brainwave activity, symmetry between brain hemispheres, abnormal electrical discharges, and artifacts. This can provide information relevant to conditions like epilepsy,