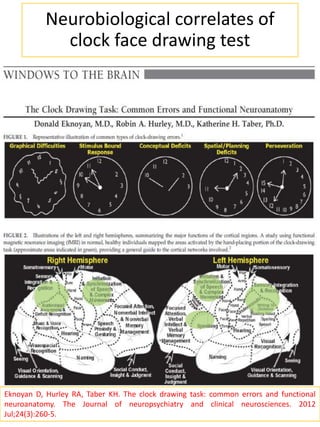
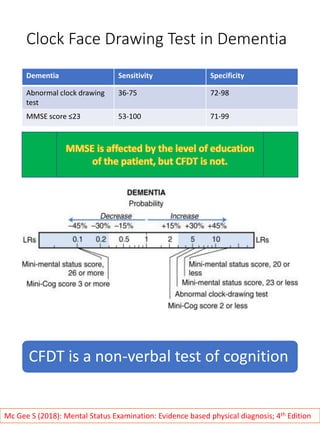
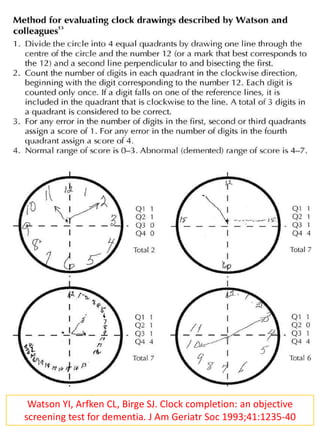
The document discusses the clock face drawing test, which was originally developed in the early 1900s to evaluate soldiers with head injuries. It requires skills such as following directions, language comprehension, visualizing orientation, motor coordination, conceptualization, and number sequencing. Abnormal results on the clock drawing test can indicate issues with fronto-temporo-parietal functioning and constructional apraxia. It is also useful as an early screening test for cognitive impairment and dementia, as sensitivity and specificity rates for detecting dementia range from 36-75% and 72-98%, respectively. There are various scoring systems that can be used to evaluate clock drawings.