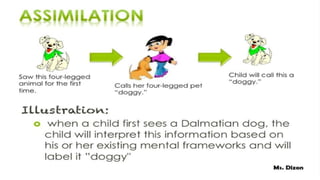
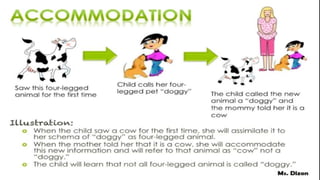
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who pioneered the study of child development and introduced the concept of cognitive schemas. Schema theory describes how knowledge is acquired, processed, and organized through mental representations called schemas. Schemas allow people to understand new information based on prior knowledge and experiences. According to Piaget, cognitive development involves two processes: assimilation, where new information is incorporated into existing schemas, and accommodation, where schemas change to fit new information. Through assimilation and accommodation over time, schemas adapt and become better organized, allowing individuals to make sense of their environment.