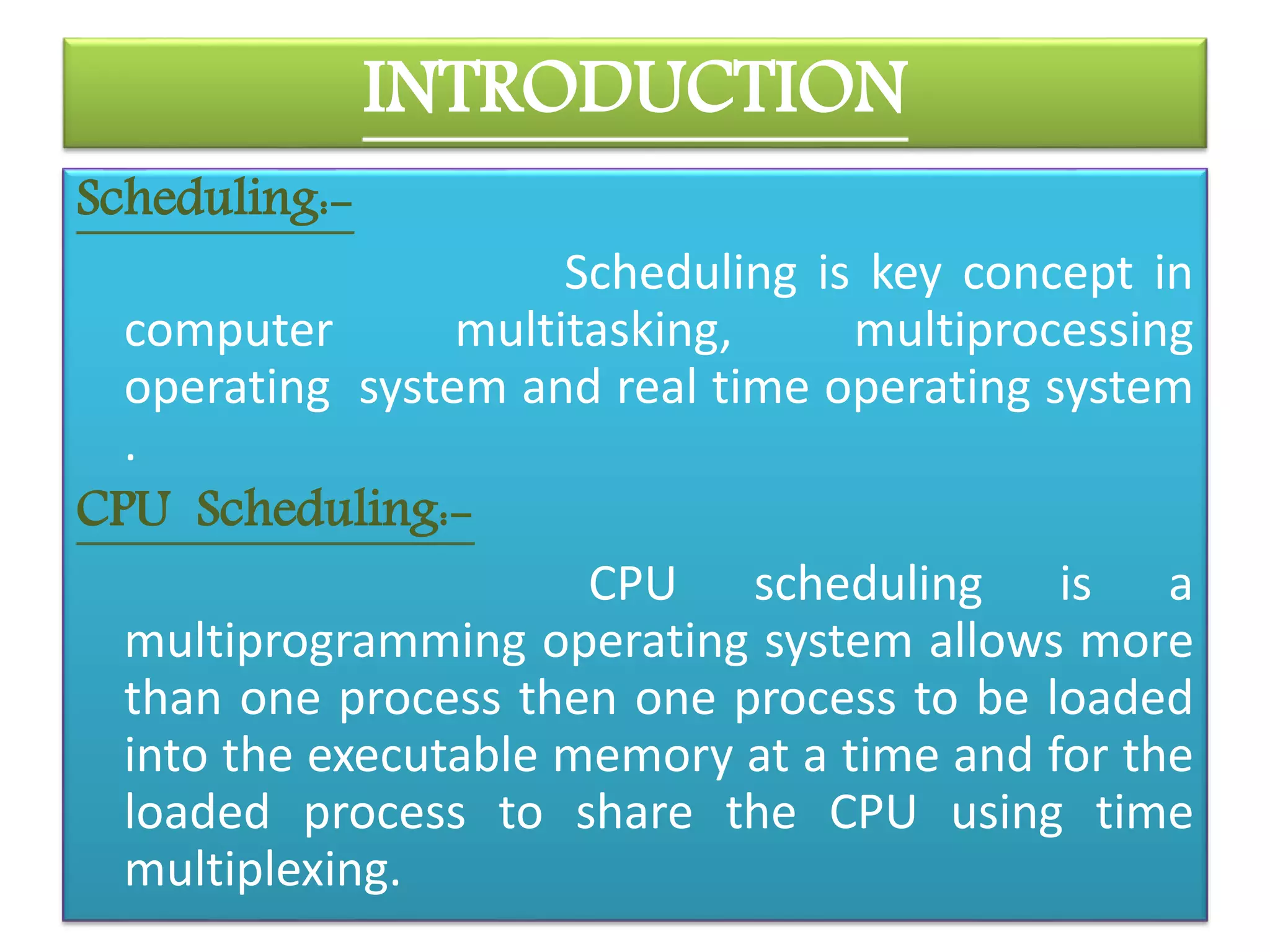
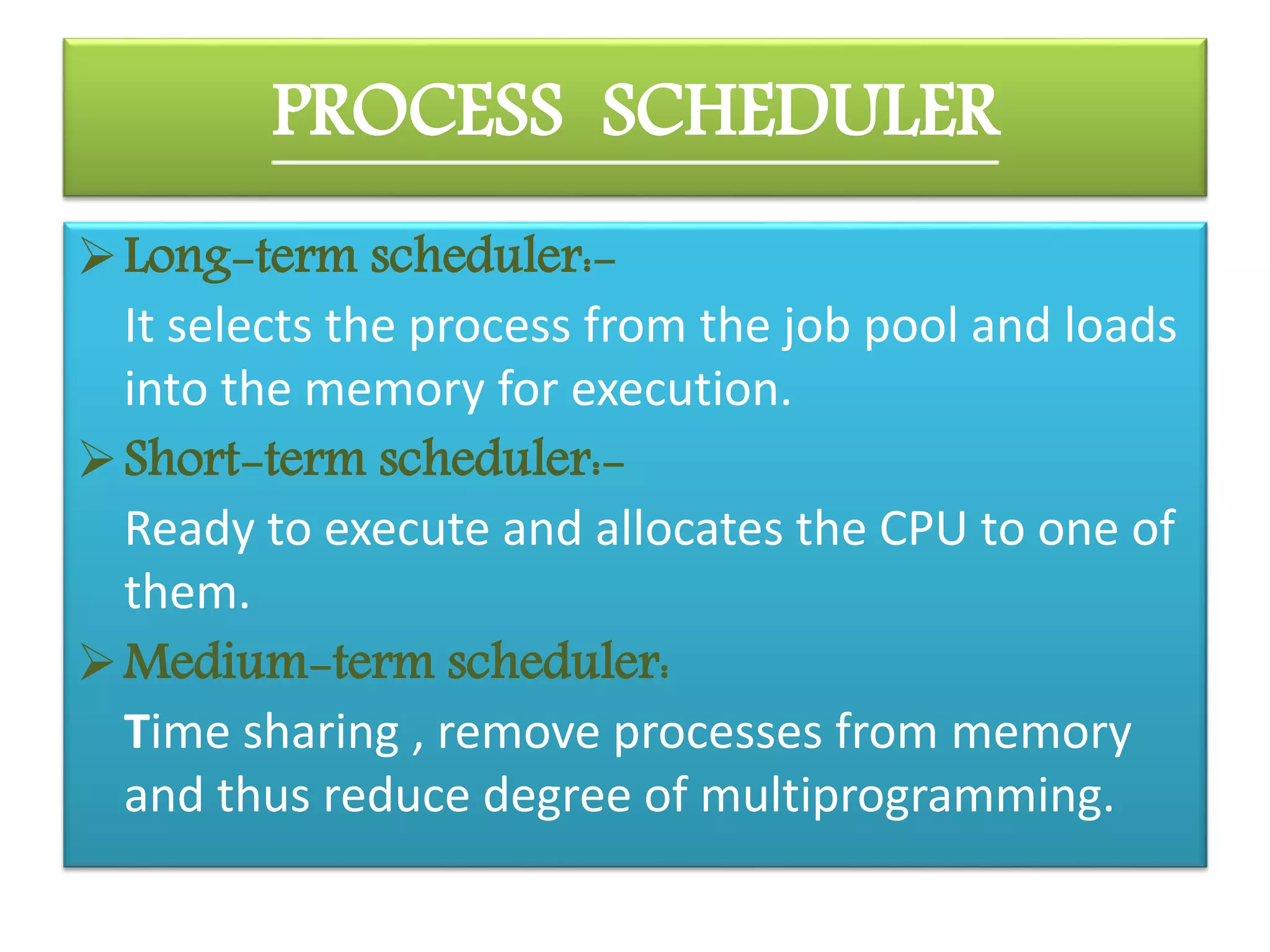
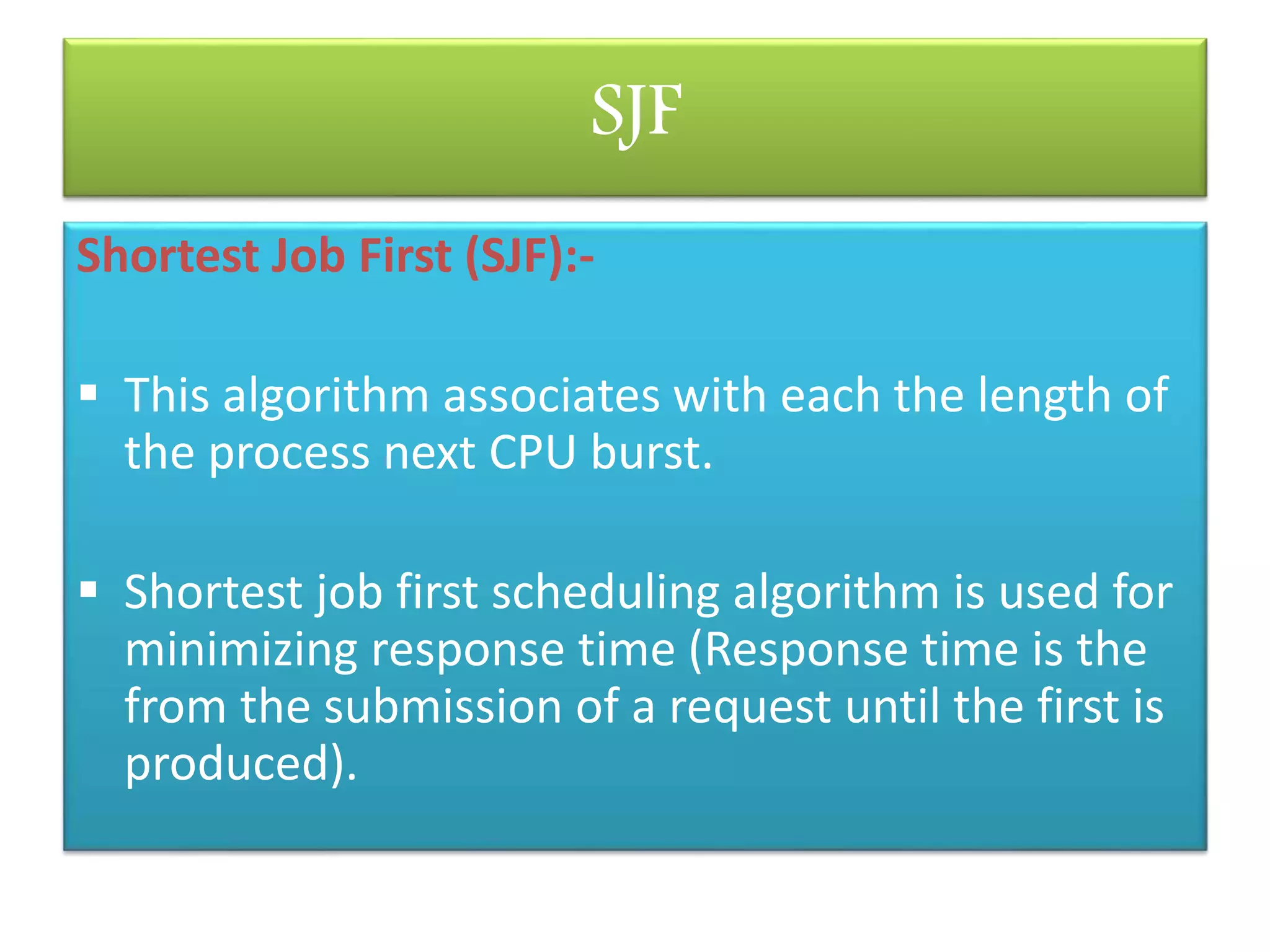
CPU scheduling allows multiple processes to share the CPU using time multiplexing. There are three main types of schedulers: long-term, short-term, and medium-term. Scheduling algorithms can be preemptive or non-preemptive. Common algorithms include first-come, first-served (FCFS), shortest job first (SJF), and round robin scheduling (RRS). FCFS uses a FIFO queue, SJF aims to minimize response time, and RRS provides fair time sharing between processes.