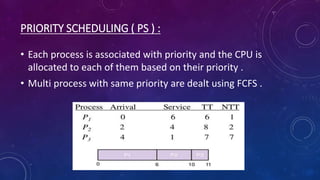
This document summarizes several CPU scheduling algorithms used in operating systems. It discusses the process states of ready, running, and waiting. The key scheduling algorithms covered are first come first serve (FCFS), shortest job first (SJF), priority scheduling, and round robin. For each algorithm, it describes the approach, advantages, and disadvantages. It analyzes and compares the algorithms based on average turnaround time, waiting time, and CPU utilization. FCFS is found to have the highest CPU utilization while SJF has the lowest average turnaround and waiting times.