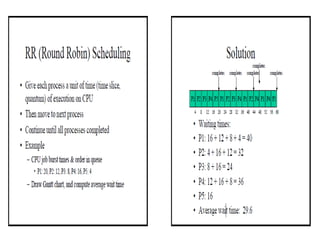
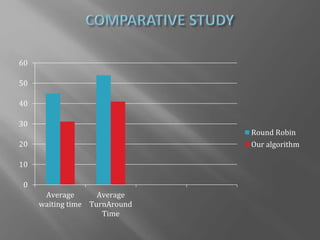
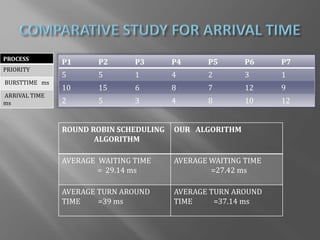
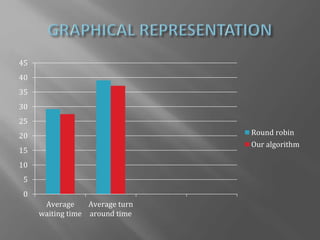
The document presents a design for an improved round robin CPU scheduling algorithm that incorporates process priorities to optimize waiting and turnaround times. It describes traditional CPU scheduling concepts, the performance and limitations of round robin scheduling, and introduces a system where processes are prioritized across multiple queues. The proposed algorithm shows better efficiency with high-priority processes while maintaining the original round robin structure when all processes share the same priority.