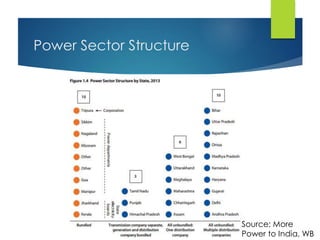
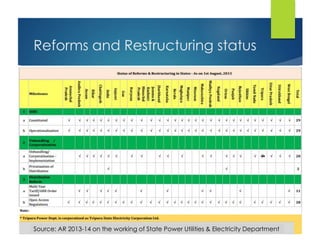
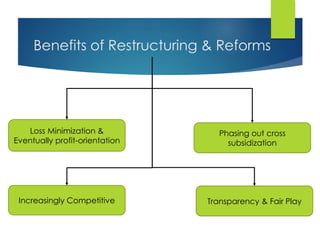
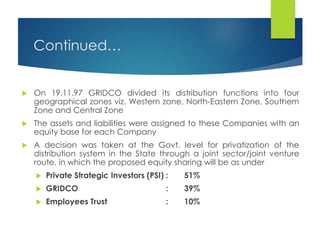
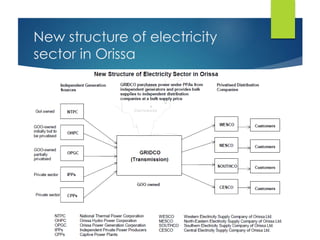
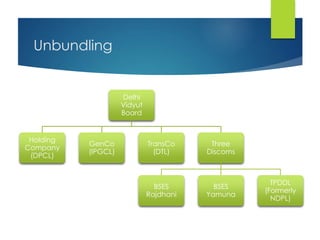
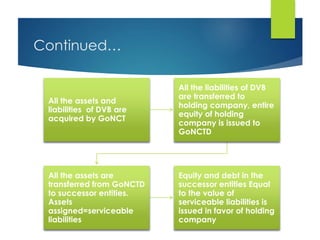
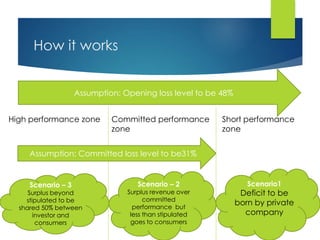
Here are the key points against privatization of the power sector:
- Access and affordability: Privatization may reduce access to power for low-income households who cannot afford higher tariffs set by private companies. Fulfilling universal service obligations may not be a priority for profit-driven private players.
- Remote areas: Private companies may have little incentive to expand networks and supply power to remote, low-density or less profitable areas due to high costs.
- Cartelization: There is a risk of cartelization or non-competitive behavior if the market is not properly regulated. Private players could collude to keep prices high and hamper consumer interests in a non-regulated or self-regulated market.