1. Simple machines include the lever, pulley, wheel and axle, inclined plane, wedge, and screw. They make work easier by reducing the amount of force needed.
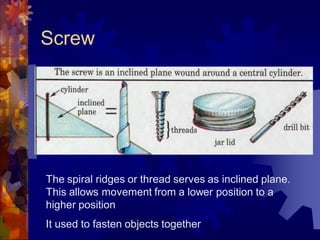
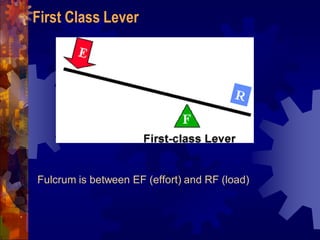
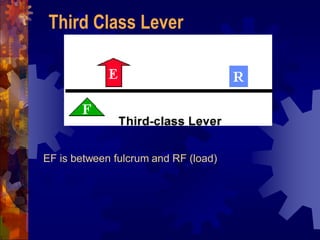
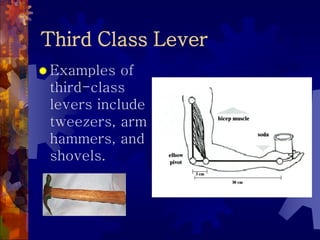
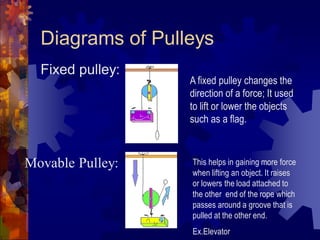
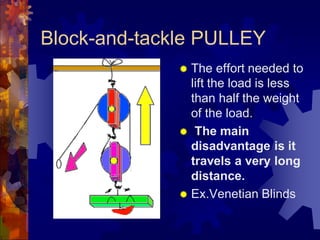
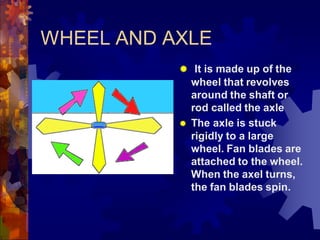
2. The six simple machines are described in detail. A lever has a fulcrum and uses effort to lift a load. Pulleys use wheels and ropes or belts to change the direction or magnitude of force. Wedges, screws, and inclined planes lift or push objects using their sloped surfaces.
3. As an example, the Egyptians used inclined planes and wheels to move heavy stones when building the pyramids. Rube Goldberg machines demonstrate how complex machines are combinations of simple ones. Students are assigned a project to