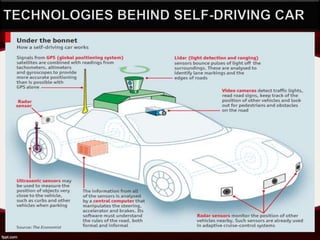
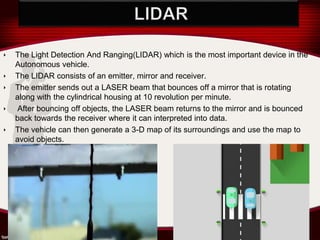
The document discusses Google's self-driving car. It describes the key technologies that enable the car to drive autonomously such as LIDAR sensors to map surroundings, radar sensors to detect distant objects, GPS for positioning, and computer vision. The car's central computer analyzes sensor data to understand road rules and control steering, braking, and acceleration without human input. Benefits are reduced accidents from human error and increased road capacity, while disadvantages could include potential hacking risks.