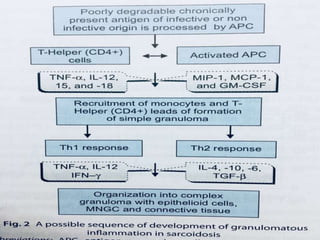
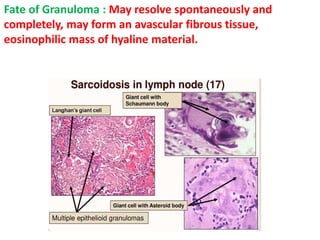
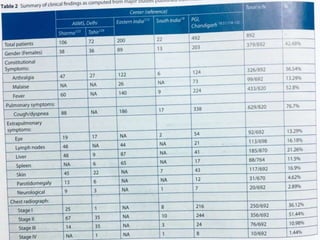
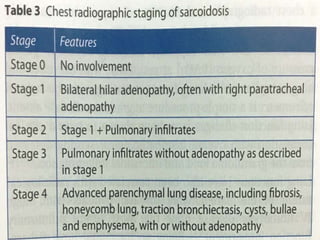
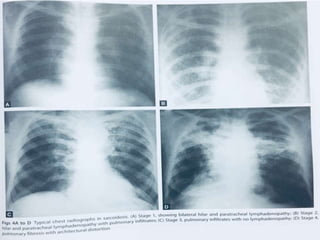
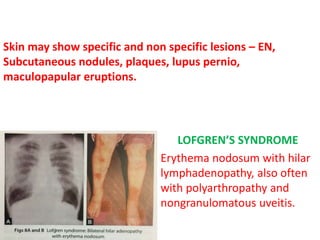
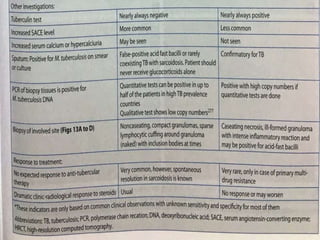
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disorder of unknown origin characterized by non-caseating granulomas. It most commonly affects the lungs, skin and eyes of young adults. The cause is believed to be an abnormal immune response triggered by an environmental antigen in genetically susceptible individuals. Diagnosis involves compatible clinical features and histological evidence of non-caseating granulomas. Treatment focuses on suppressing granuloma formation and inflammation, with corticosteroids being the mainstay. Other immunosuppressants may be used for resistant or severe disease.