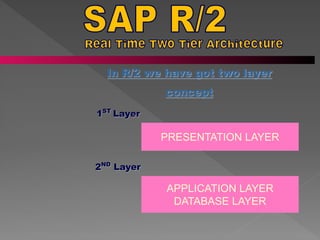
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business functions like planning, manufacturing, sales, and marketing. SAP is the number one vendor of ERP software worldwide, with over 90,000 customers using its R/3 system. SAP R/3 features a three-tier architecture with presentation, application, and database layers to provide a flexible, customizable solution for companies of all sizes. Common SAP modules include finance, logistics, human resources, and customer relationship management.