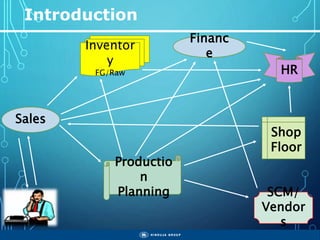
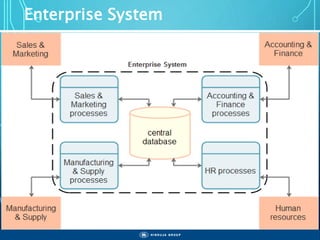
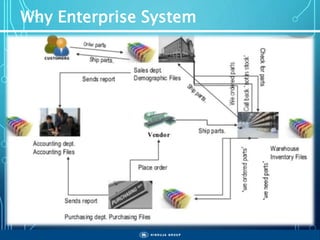
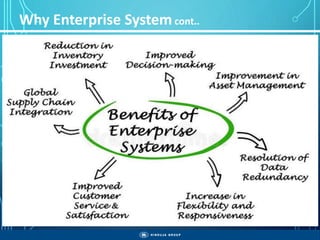
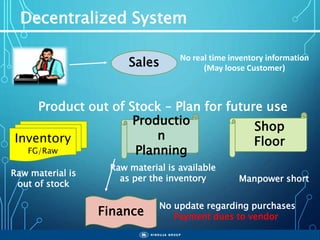
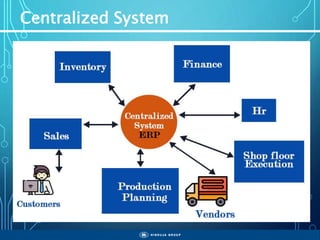
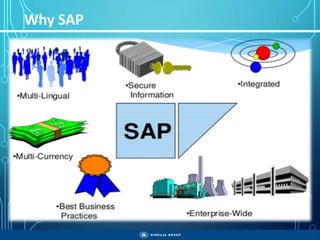
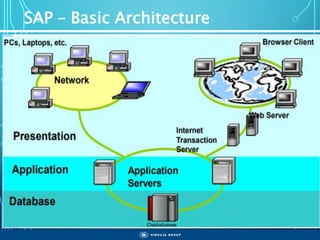
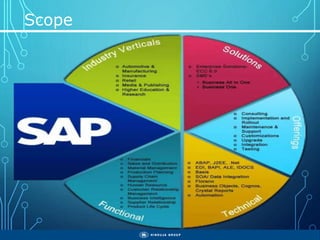
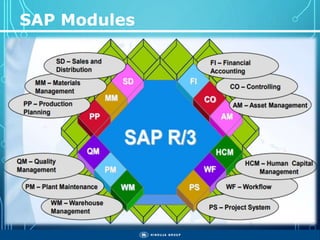
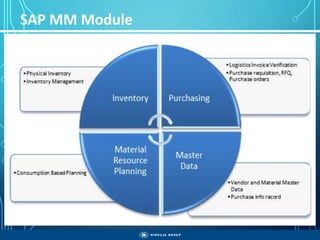
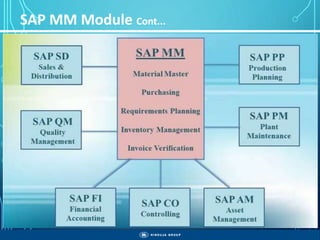
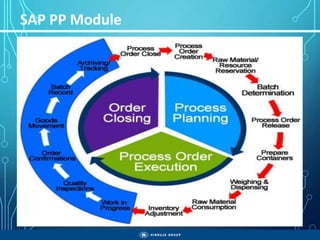
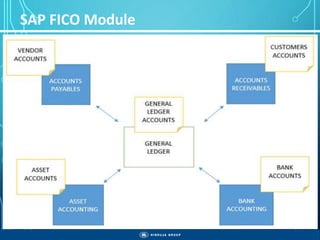
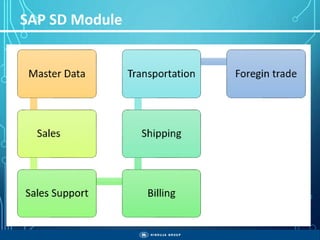
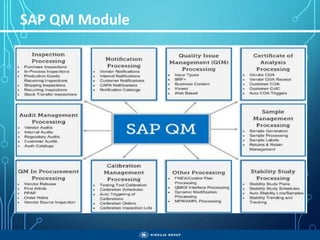
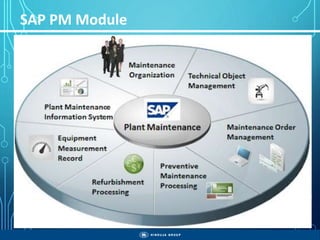
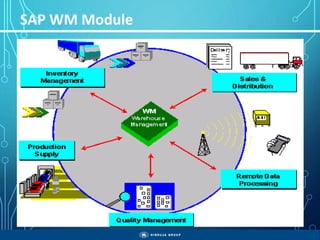
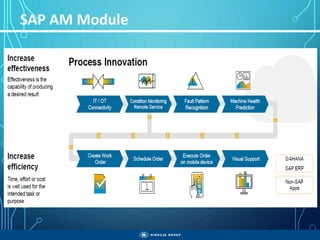
The document outlines the objectives, importance, and classifications of enterprise systems, specifically focusing on SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) software. It contrasts decentralized and centralized systems, highlighting the benefits of centralized systems in improving data management, customer service, and reducing costs. Additionally, the document provides a brief history of SAP's development, its architecture, and an overview of its various modules.