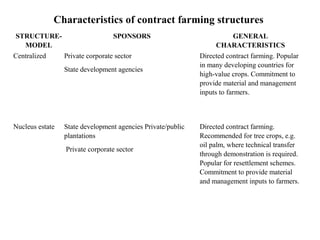
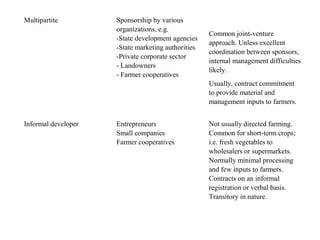
Contract farming involves agricultural production carried out according to a prior agreement between farmers and buyers. There are several models of contract farming including centralized, nucleus estate, multipartite, informal, and intermediary models. Contract farming can provide benefits like higher incomes, access to markets and inputs, and risk reduction. However, it also presents some risks if farmers become overly dependent on a single buyer. Breach of contract by buyers or lack of alternative livelihoods for farmers can threaten rural livelihoods. Overall, contract farming impacts capitals like social, human, physical and financial capital in both positive and negative ways for rural households.