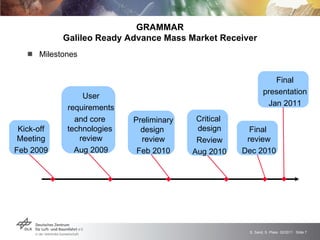
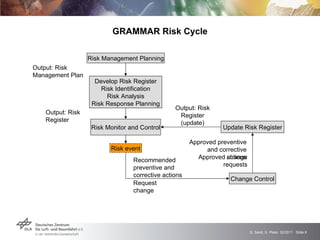
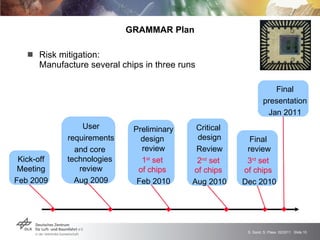
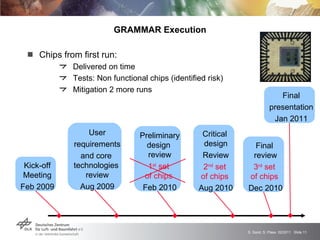
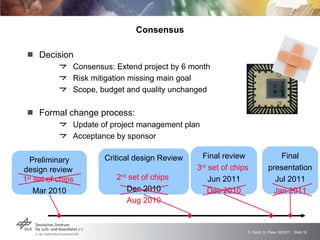
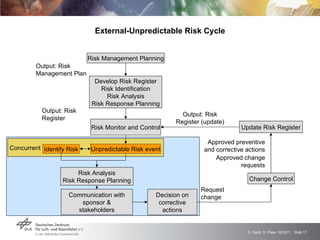
The GRAMMAR project faced challenges from external unpredictable risks. The initial risk plan addressed manufacturing issues but not the concurrent financial crisis affecting the chip producer. This caused delays receiving functioning chips, jeopardizing the main project goal. After impact analysis and risk register updates, the solution was a six month extension to allow time for additional chip production runs and achieve the goal. The experience highlighted the need to consider broader economic risks and risk interactions in plans, with open communication to stakeholders.