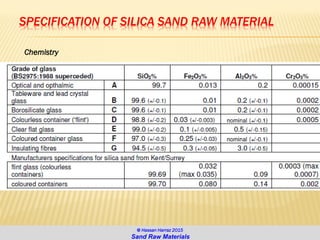
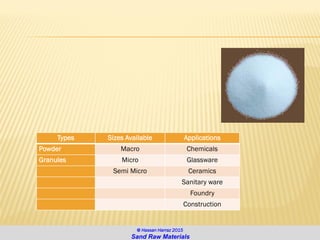
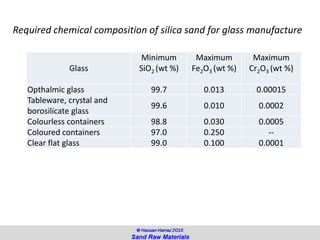
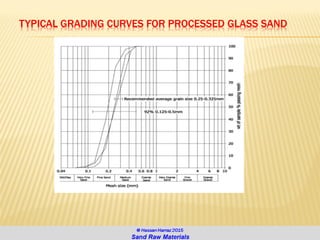
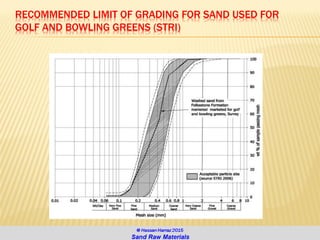
The document discusses the composition and importance of sand, particularly silica sand, which is a key raw material for various industries including glass making and foundry casting. It describes the processes of extraction, types of mineral sands, and the different applications of silica in modern technology and construction. Additionally, it highlights the demand and geographical distribution of silica sand resources, along with its specifications for industrial usage.