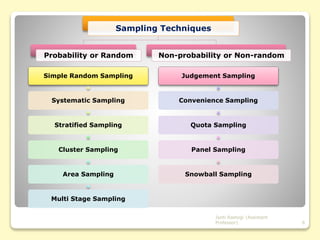
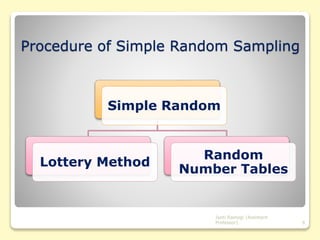
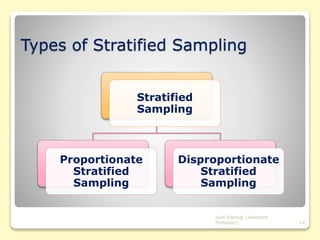
This document discusses sampling and sample design. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of individuals from a larger population for statistical analysis. There are different sample design techniques, including probability and non-probability sampling methods. Probability methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling allow researchers to precisely determine the relationship between the sample and population. Effective sample design considers the population, sample units, sampling frame, sampling technique, sample size, and execution of the sampling process. The document provides details on various sampling techniques and their advantages and disadvantages.