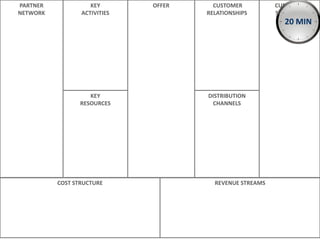
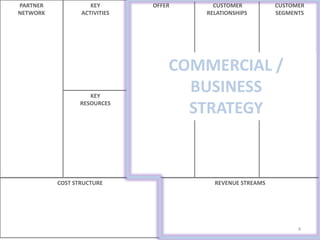
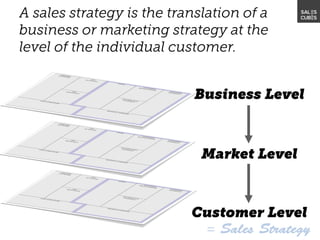
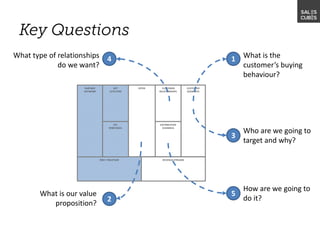
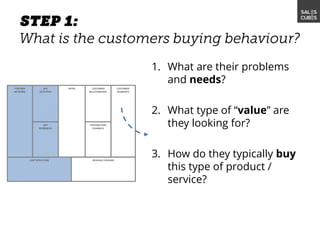
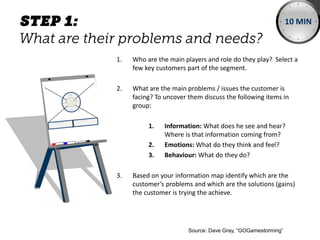
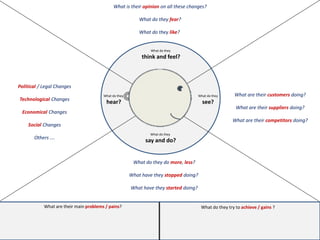
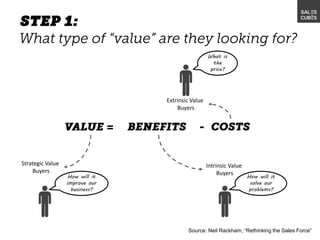
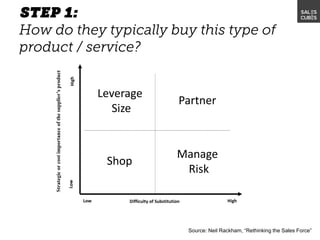
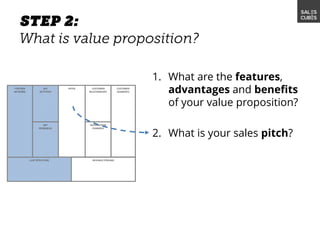
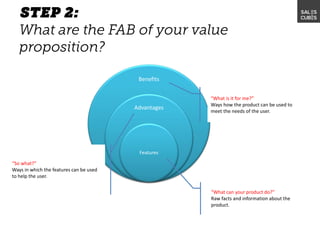
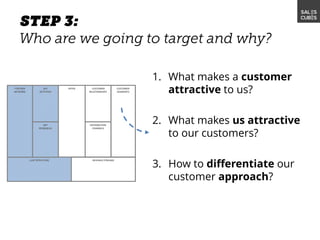
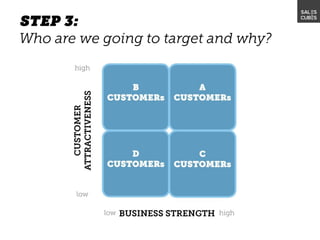
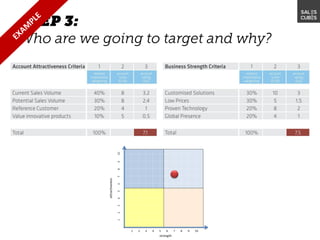
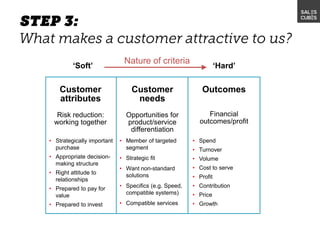
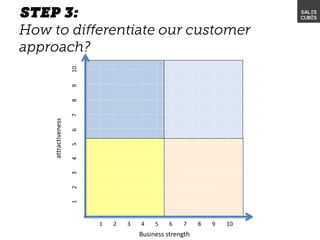
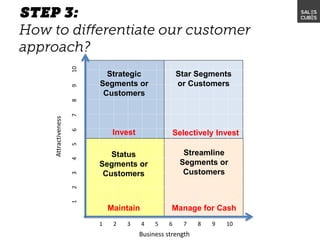
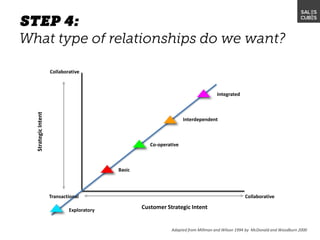
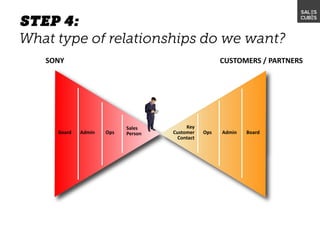
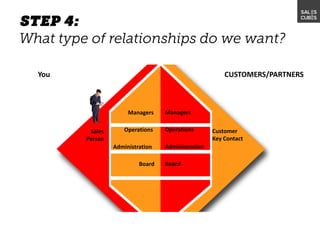
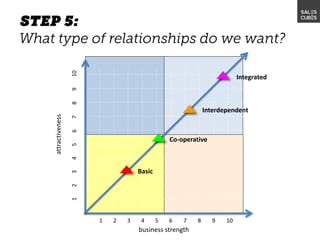
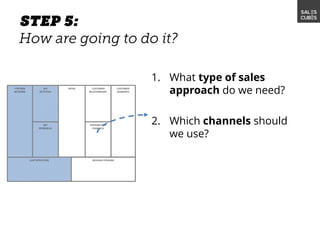
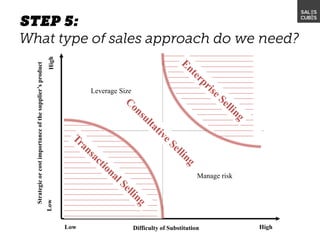
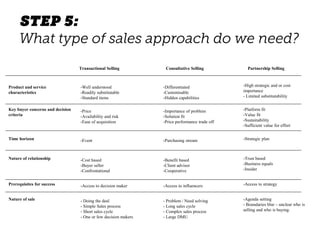
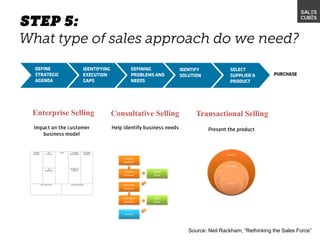
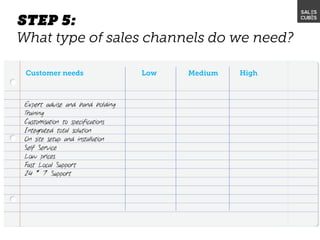
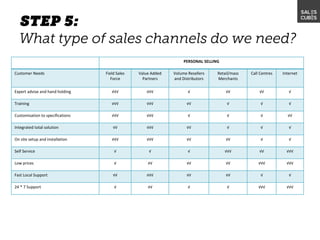
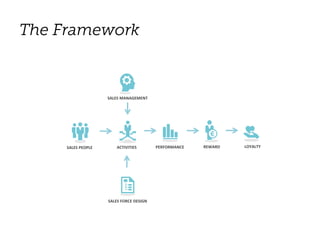
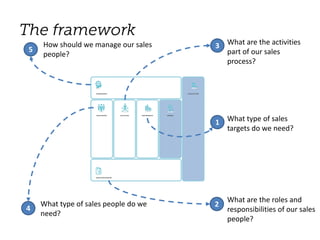
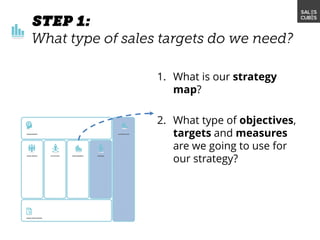
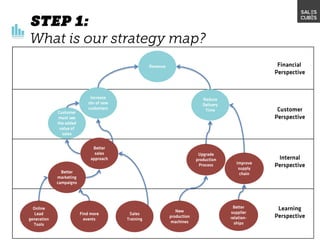
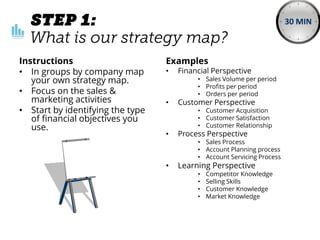
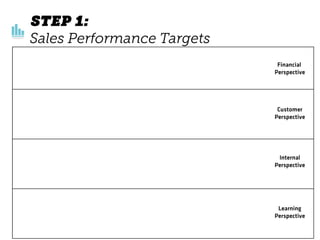
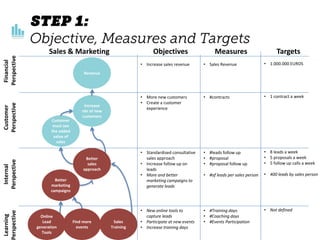
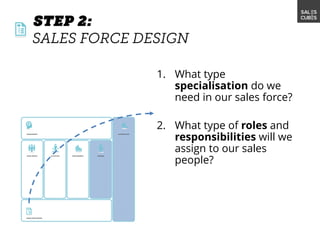
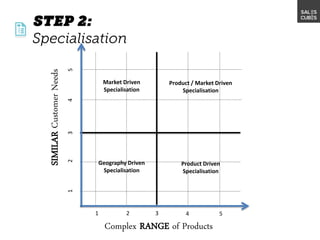
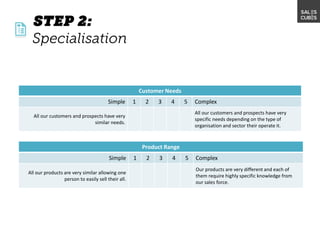
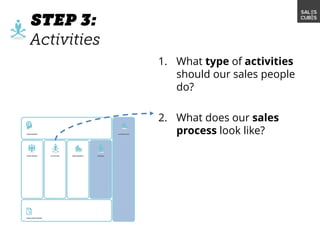
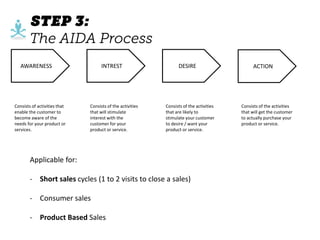
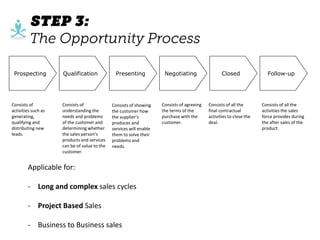
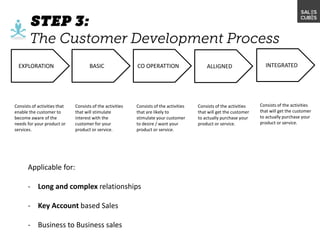
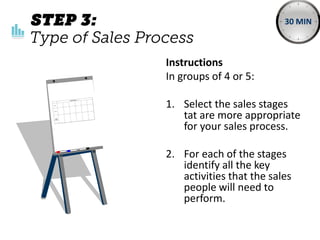
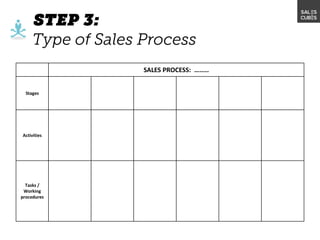
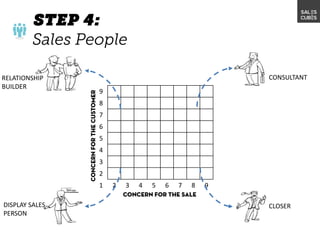
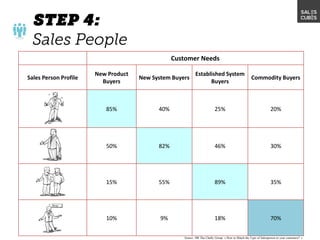
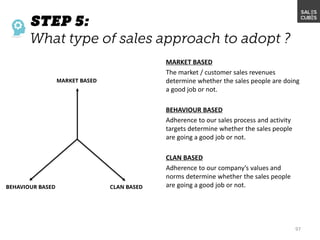
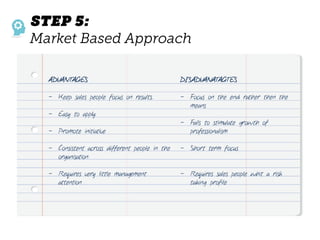
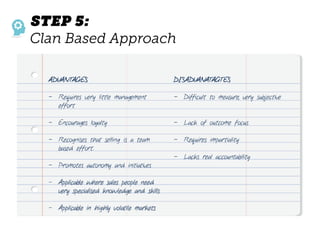
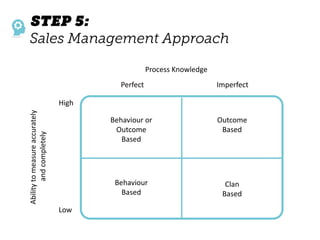
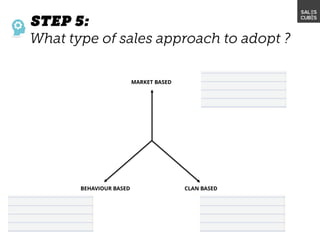
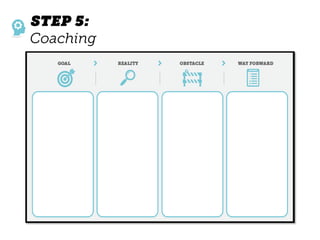
The document outlines elements of a business model canvas, including key parts of a business such as value propositions, distribution channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, and more. It provides discussion questions to help define each part of the model for a particular business. Examples are given to illustrate different business model patterns and strategies.