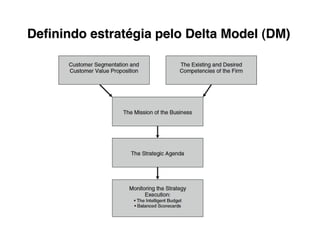
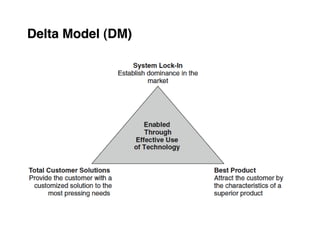
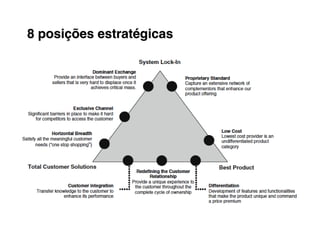
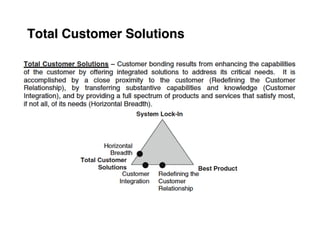
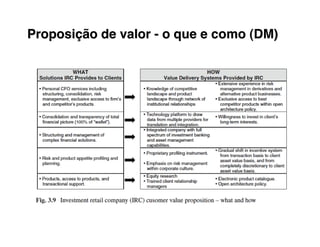
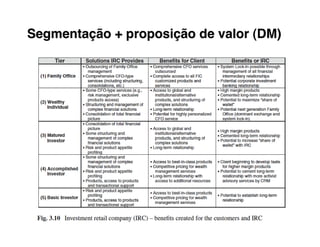
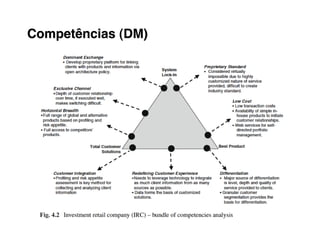
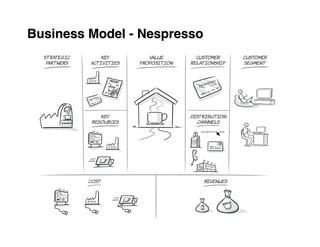
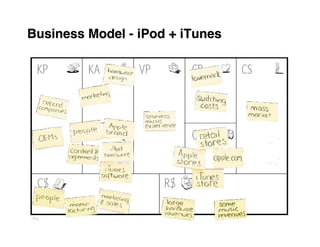
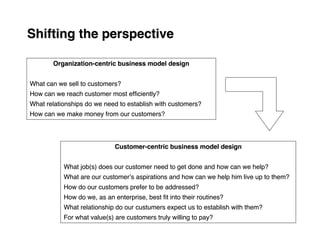
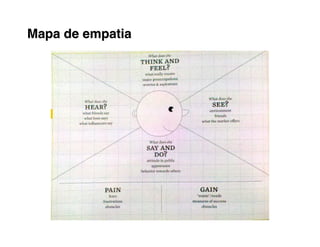
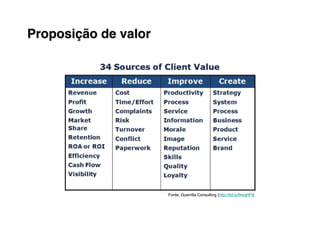
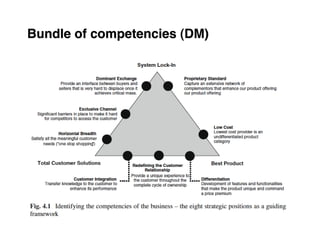
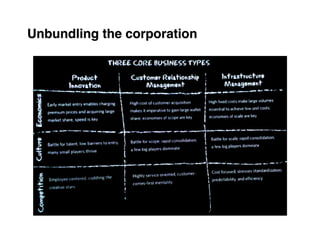
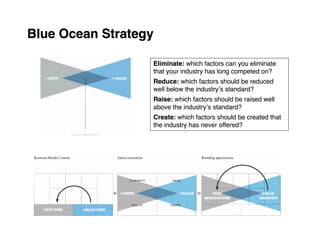
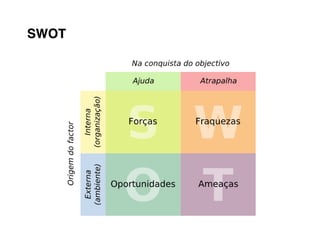
Here are the key steps to developing a strategy using the Delta Model approach:
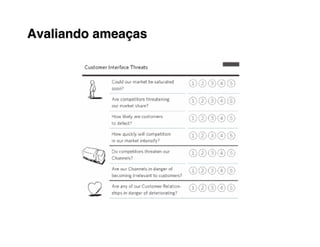
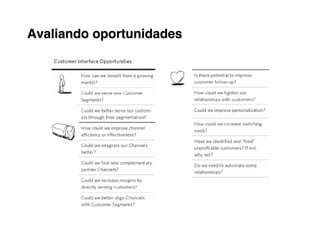
1. Understand your customers deeply through segmentation and profiling their needs/pains.
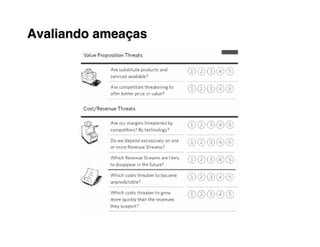
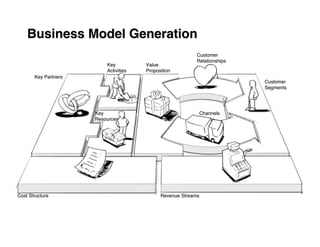
2. Define value propositions for each customer segment based on fulfilling their unique jobs, pains and gains.
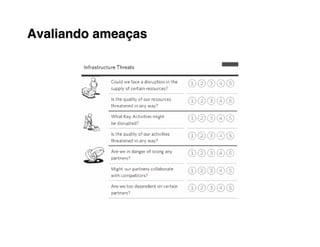
3. Assess your company's existing competencies and resources and any gaps versus what's needed to deliver those value propositions.
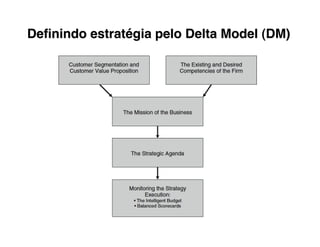
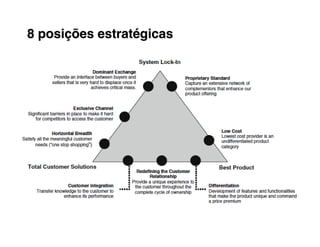
4. Position your value propositions within the Delta Model framework - where do you want to compete?
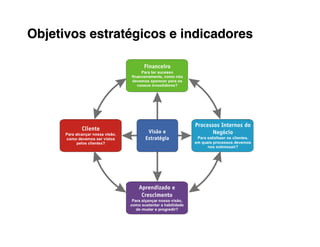
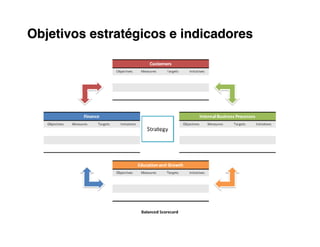
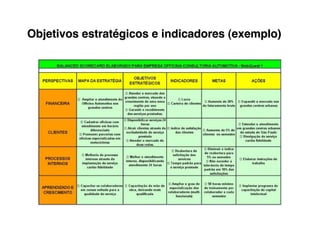
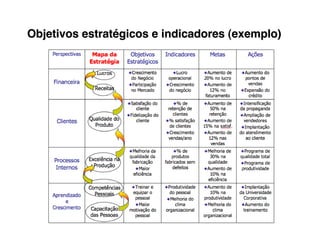
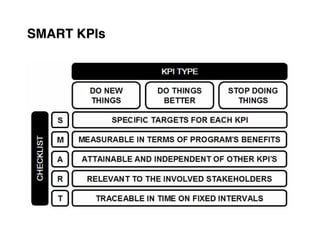
5. Develop objectives and KPIs to track progress in building the needed competencies and delivering on your value propositions.
6. Create an action plan to strengthen competencies, address gaps and