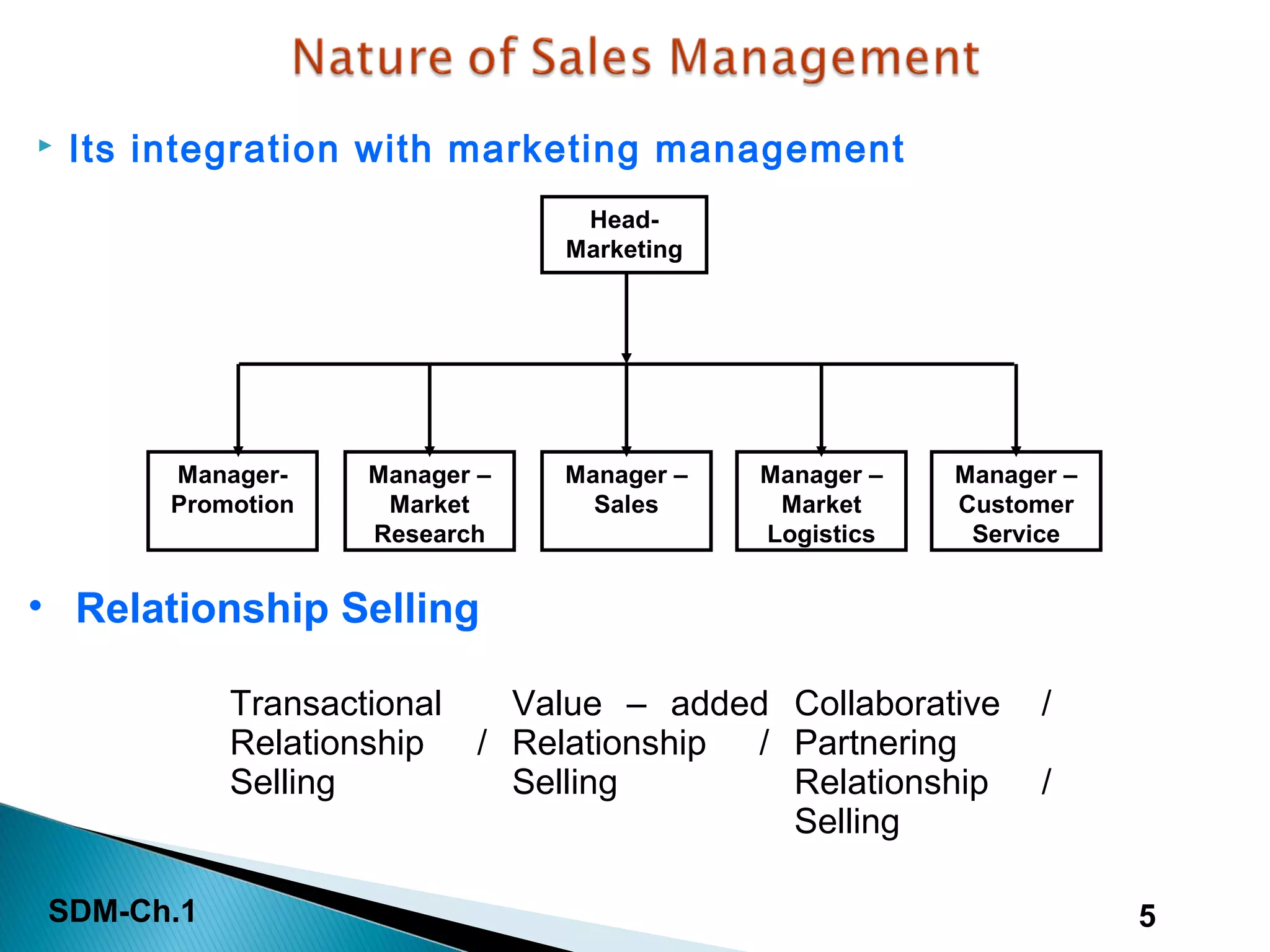
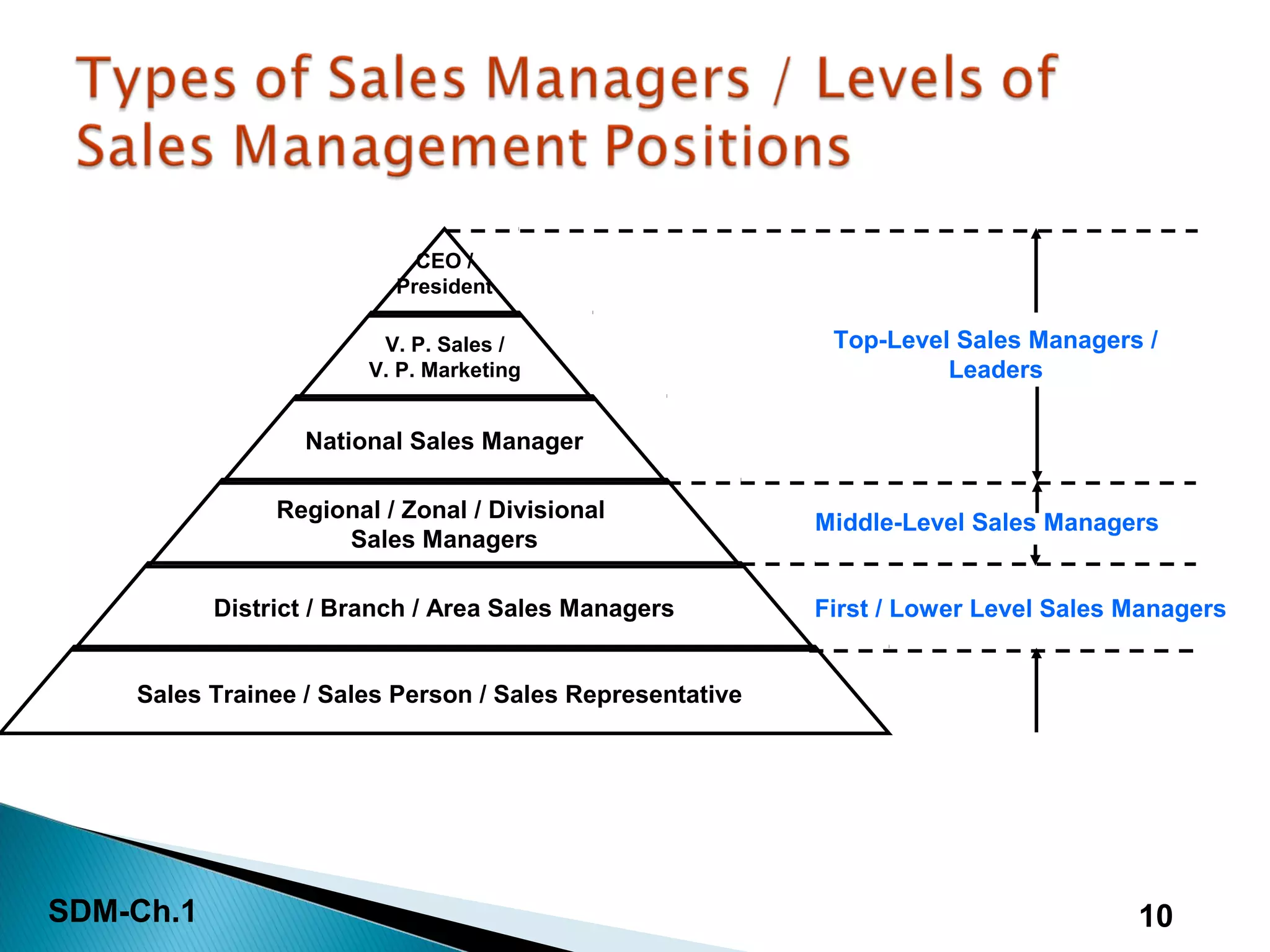
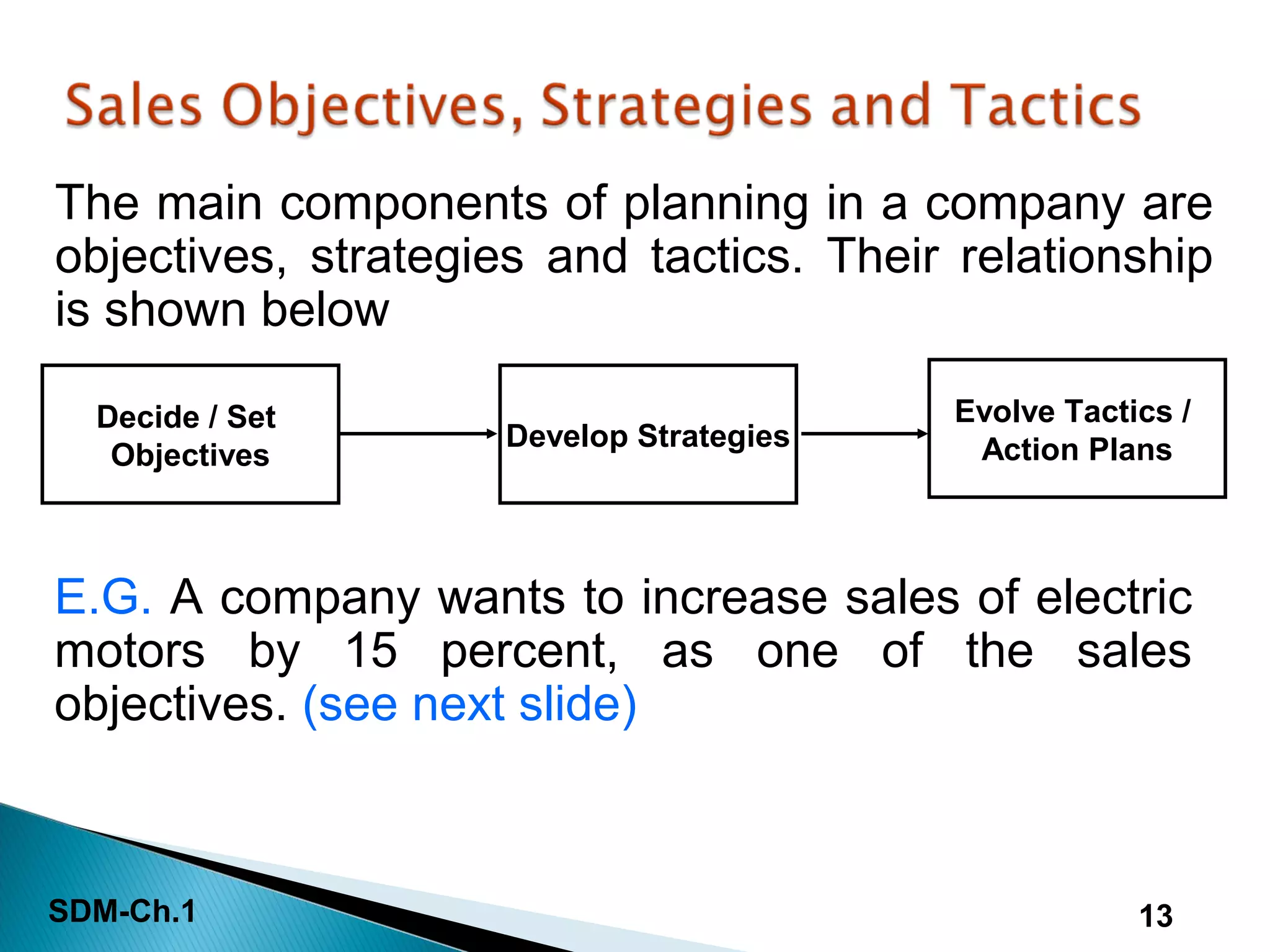
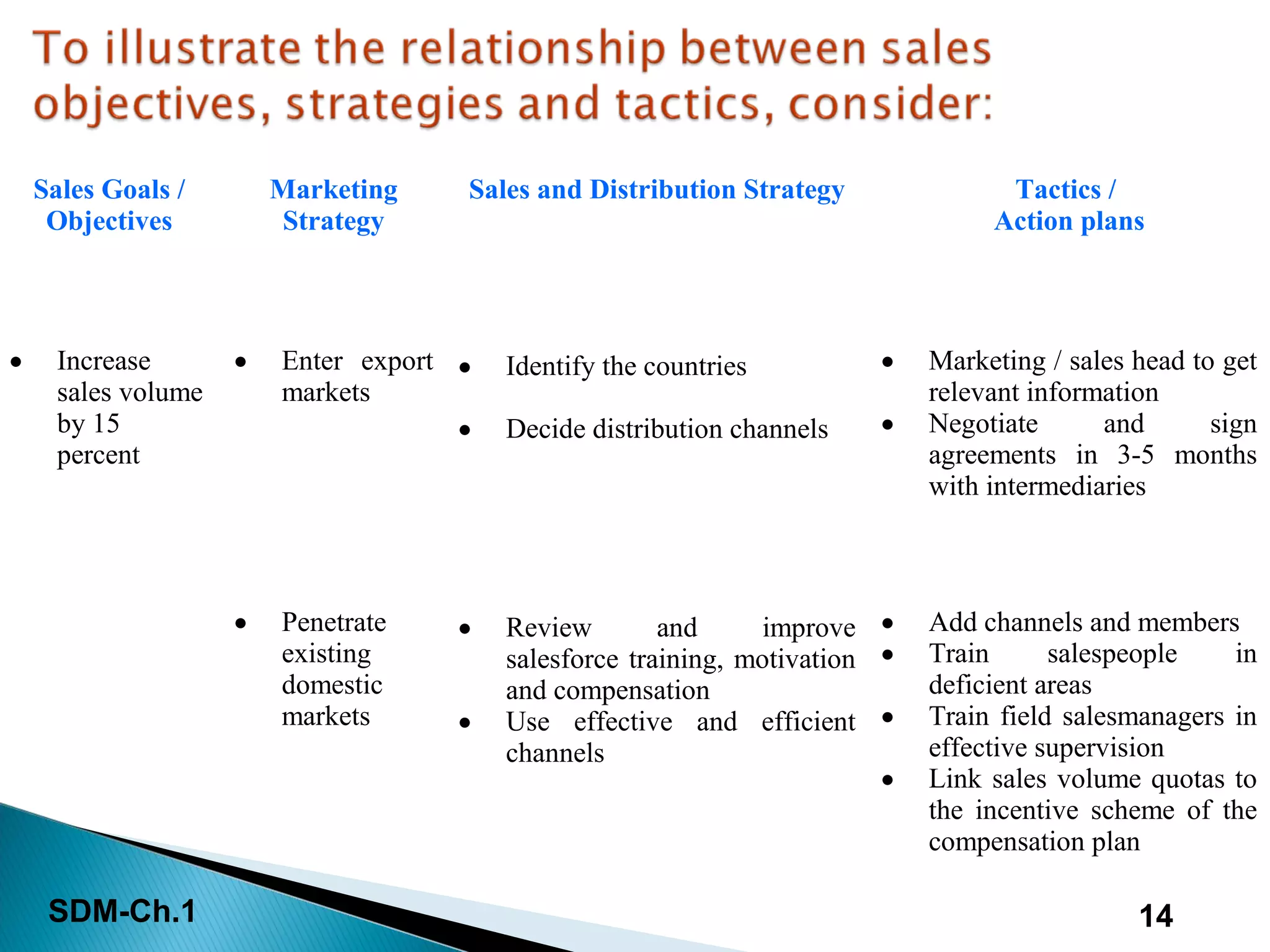
This document discusses the introduction to sales and distribution management. It defines sales management and outlines the key roles and skills of sales managers. The document also describes the evolution of sales management, different types of sales positions, and the importance of sales planning and its relationship to distribution management. Sales and distribution management must work together to achieve sales objectives and execute strategies.