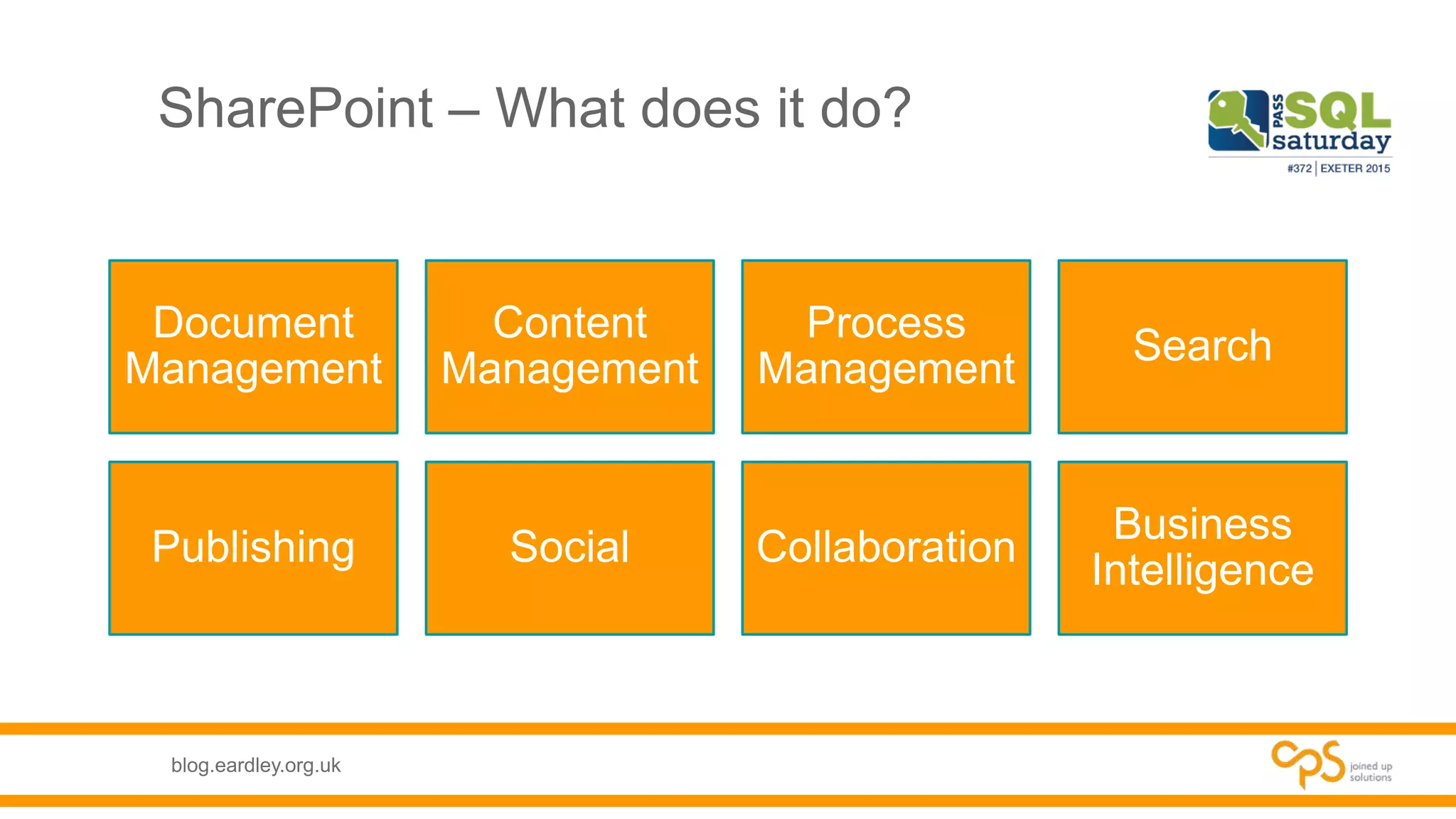
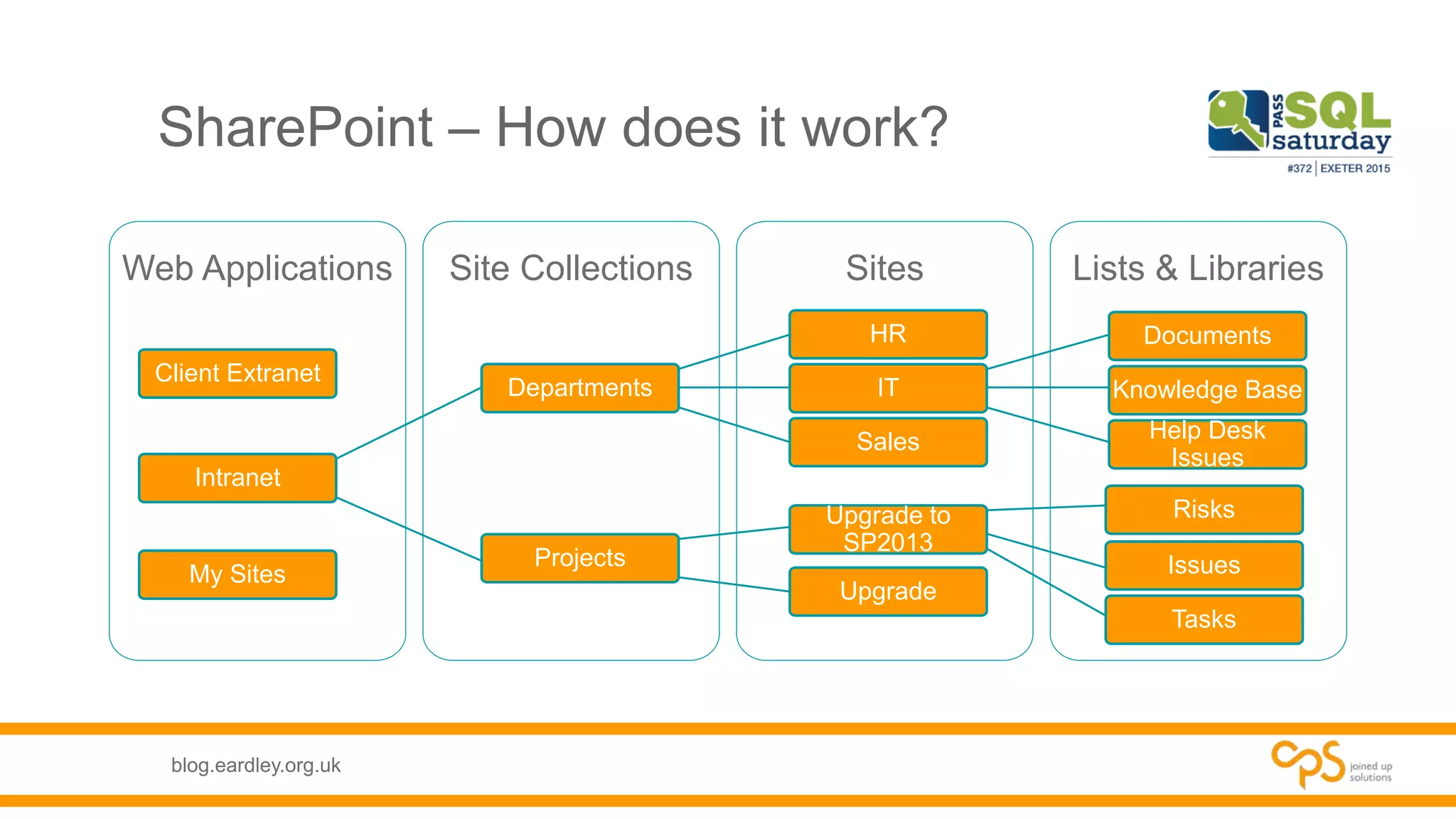
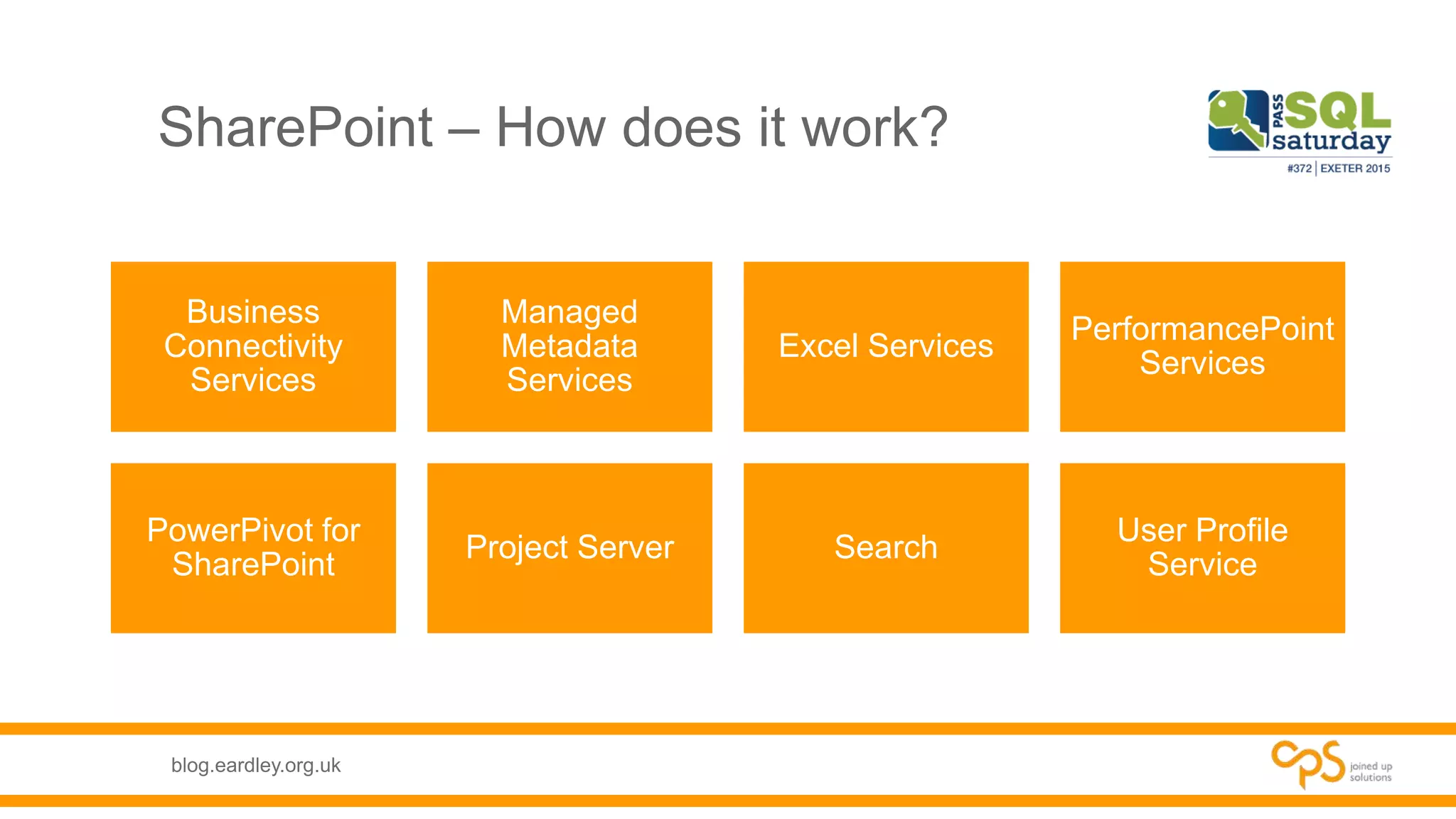
This document discusses SharePoint databases and provides information on:
- The speaker's background and areas of expertise in SharePoint and SQL Server.
- An overview of what will be covered, including how SharePoint uses SQL databases.
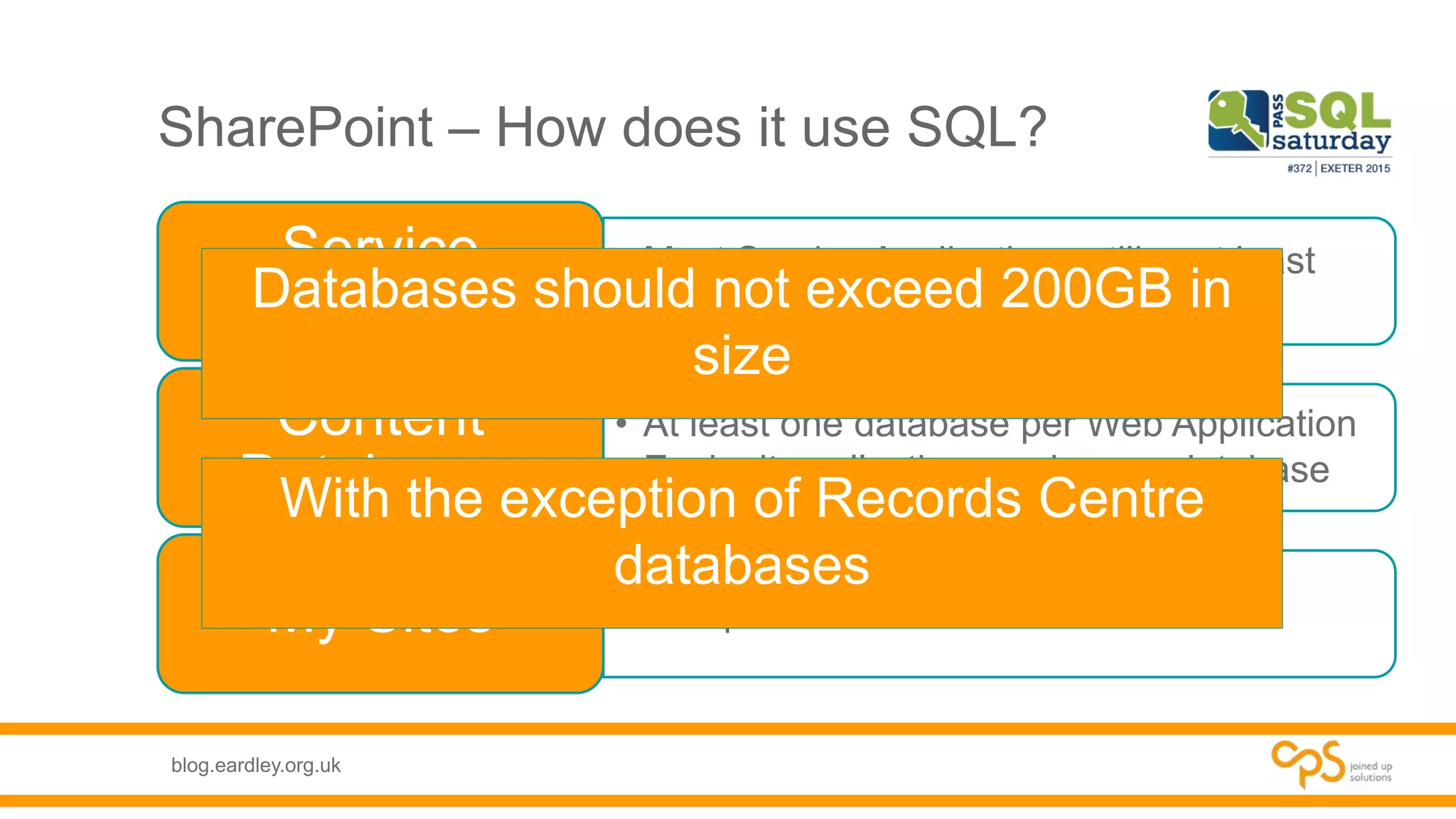
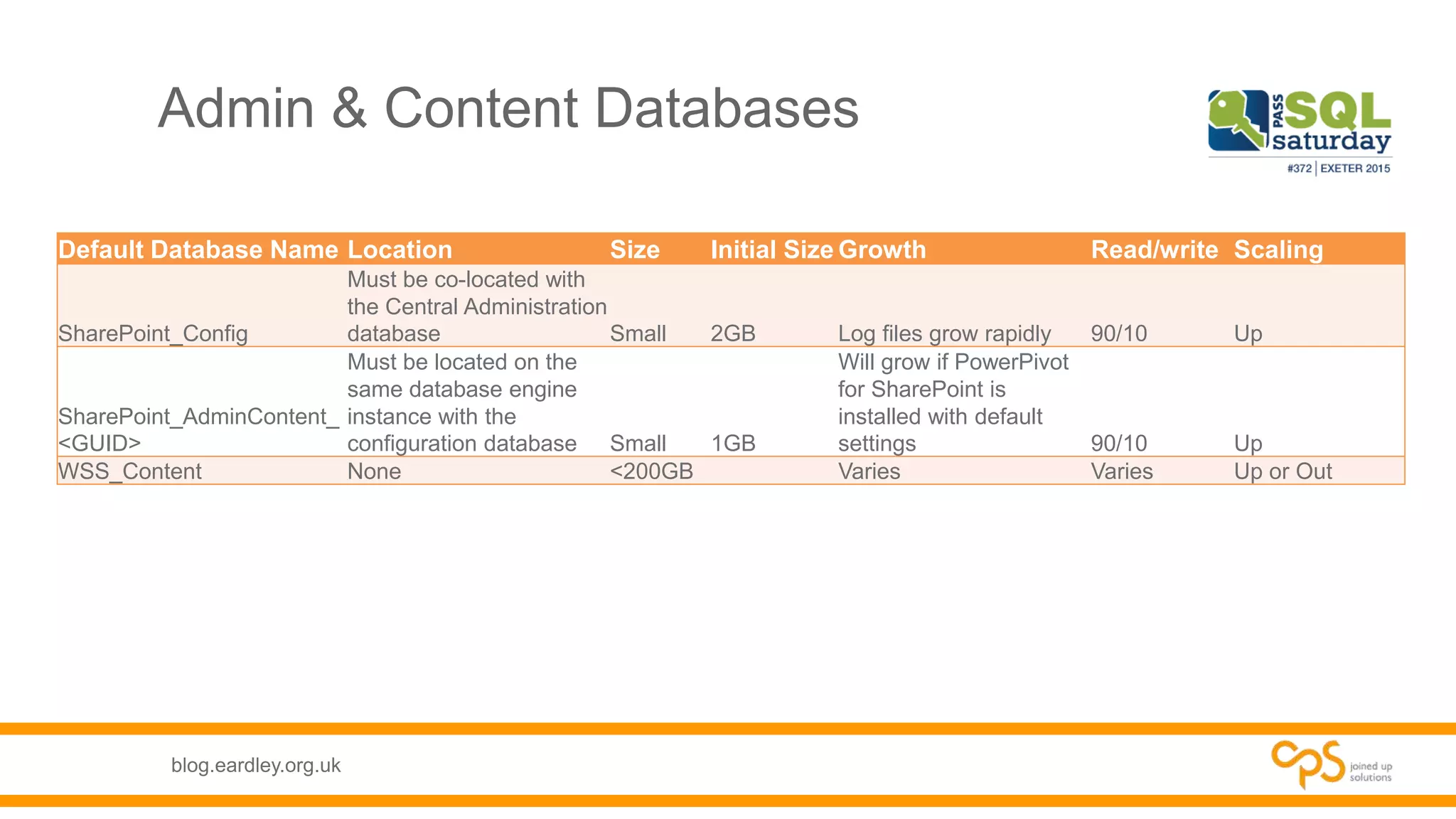
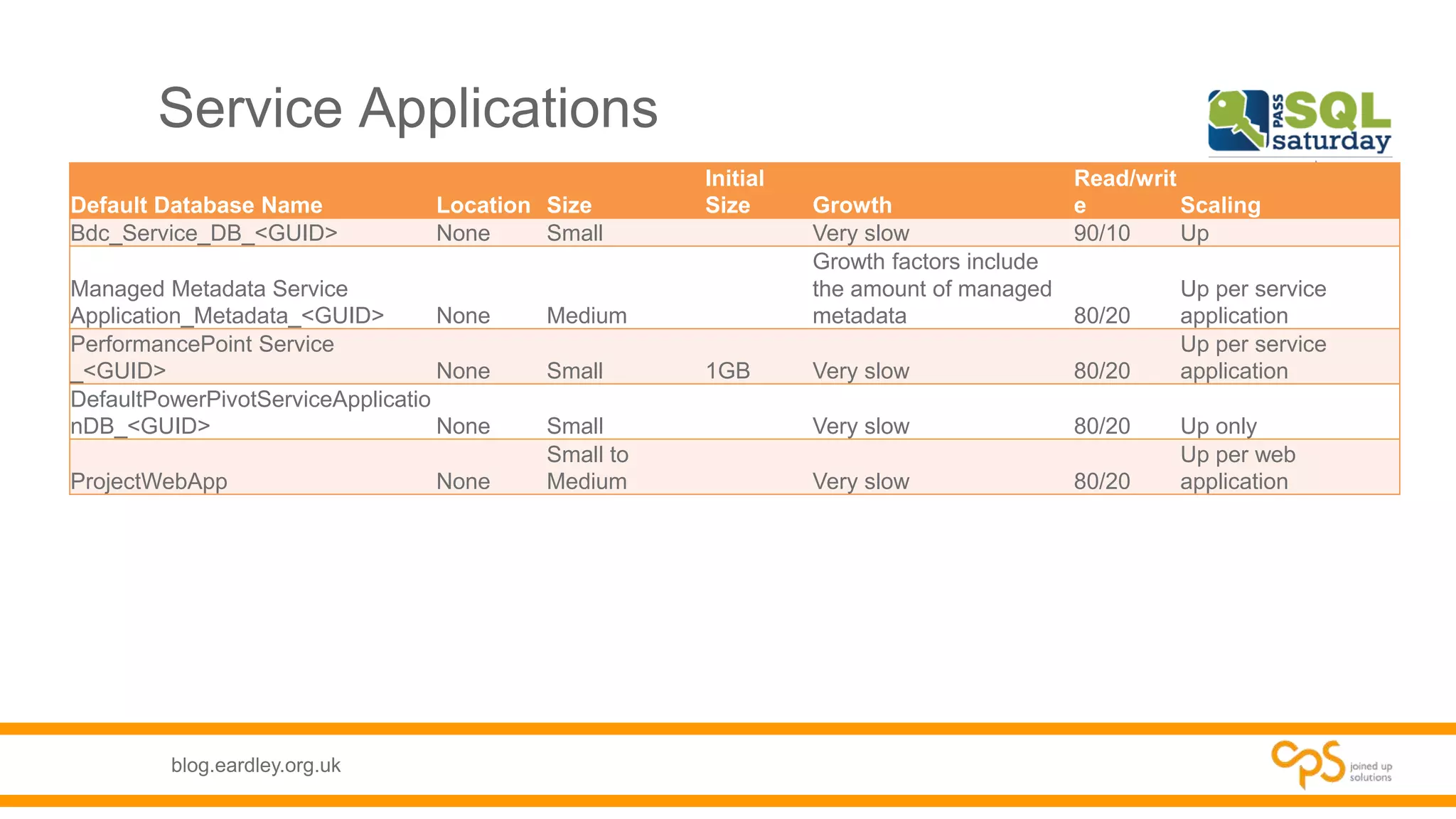
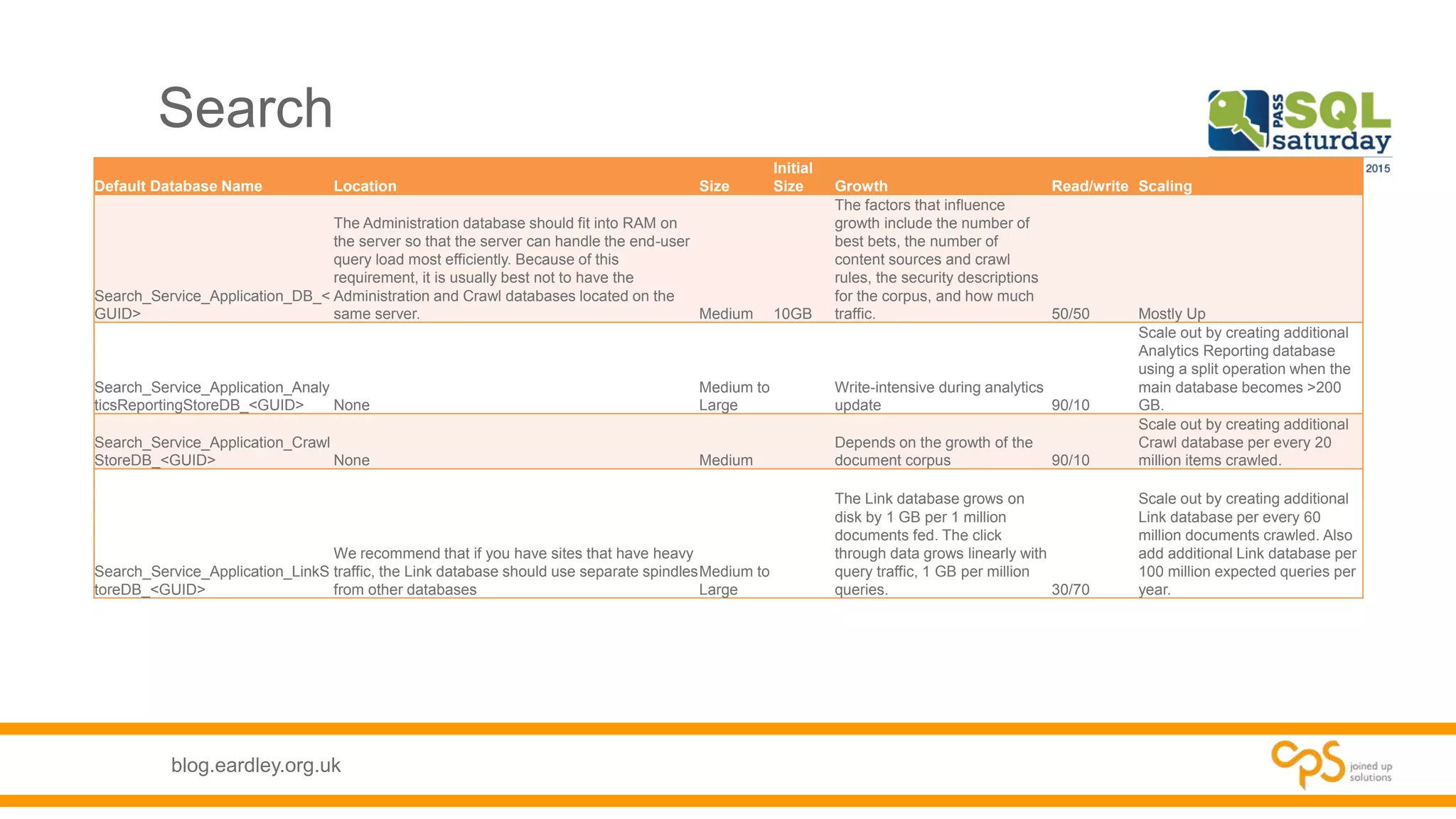
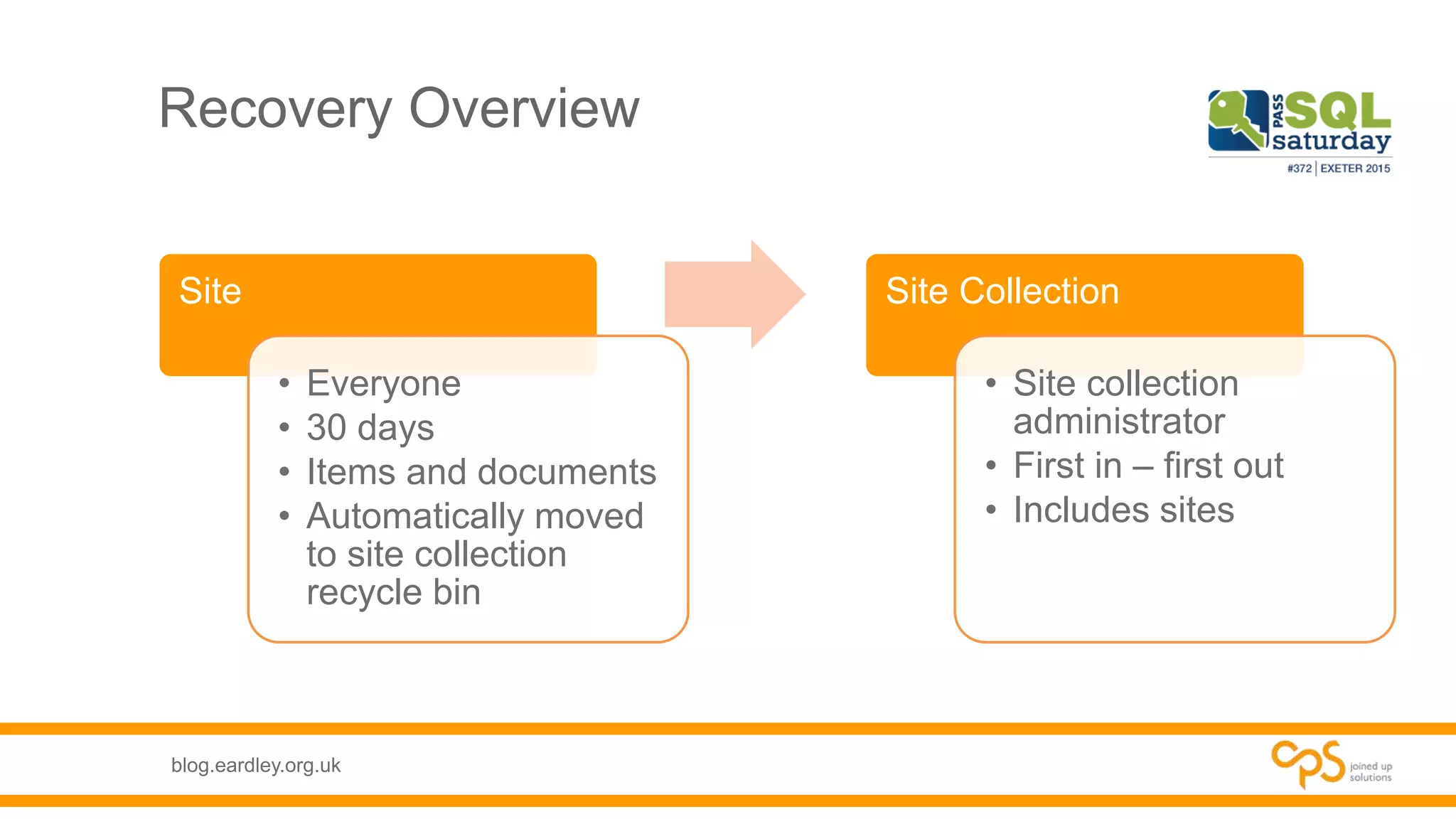
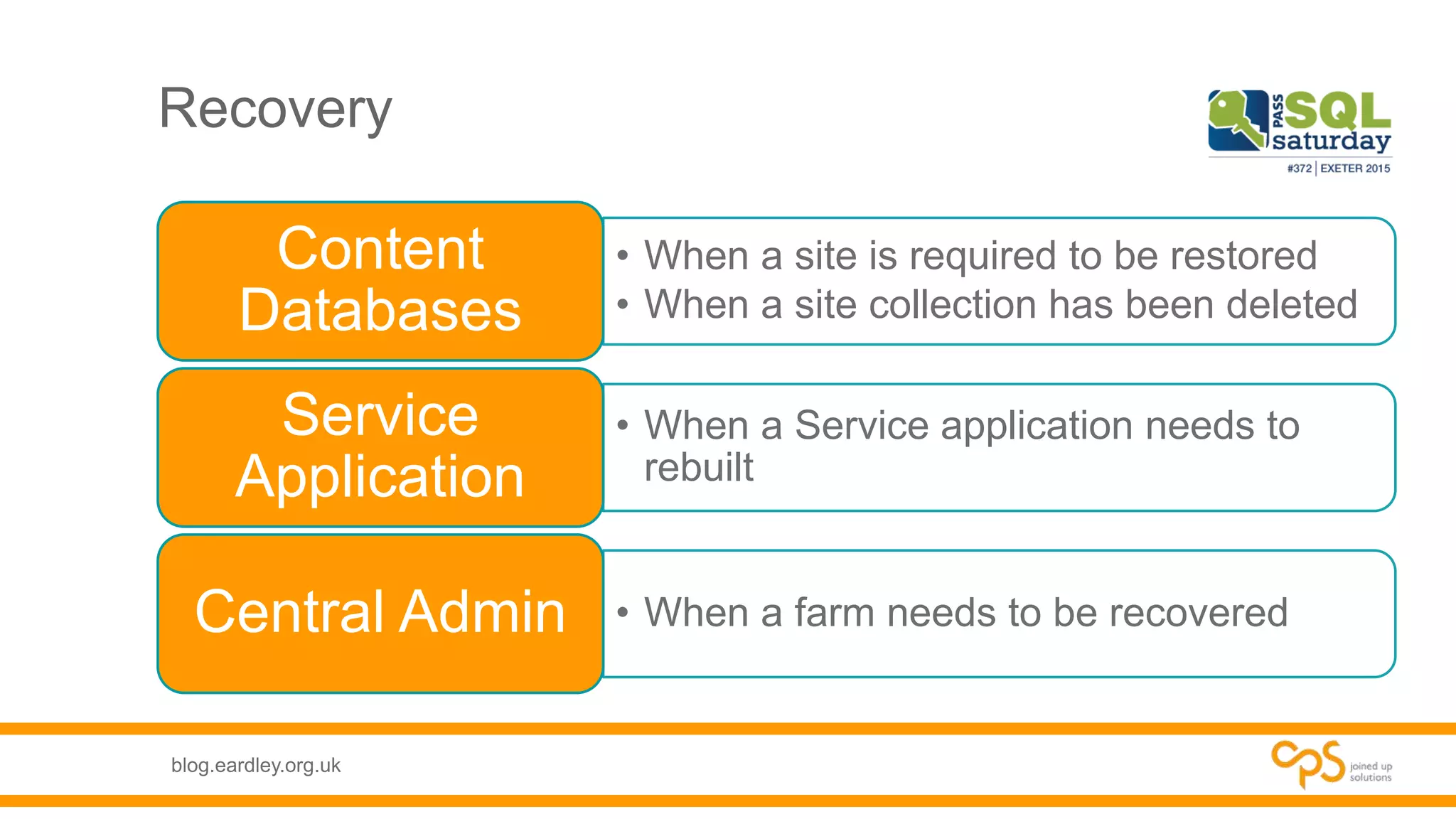
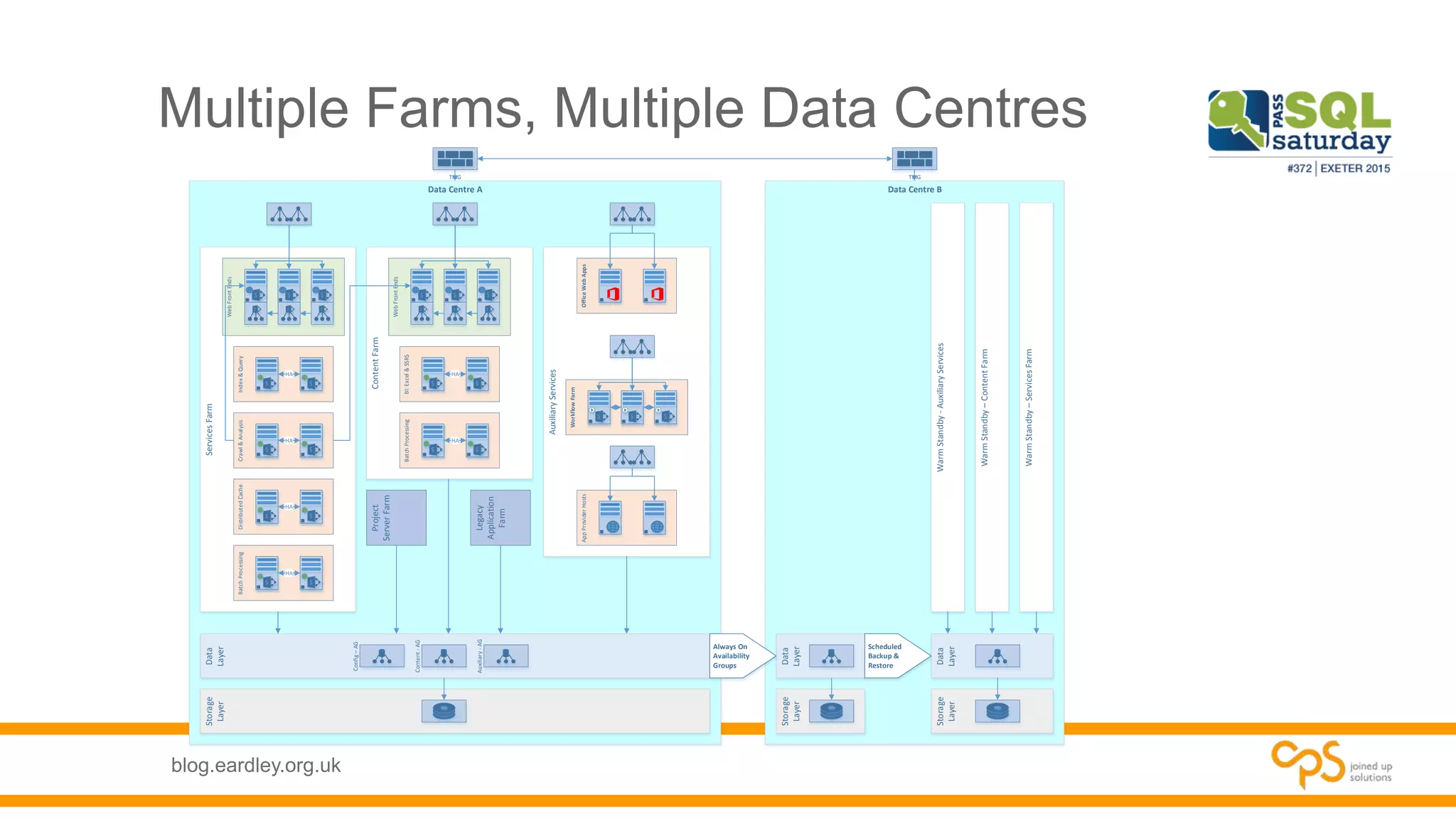
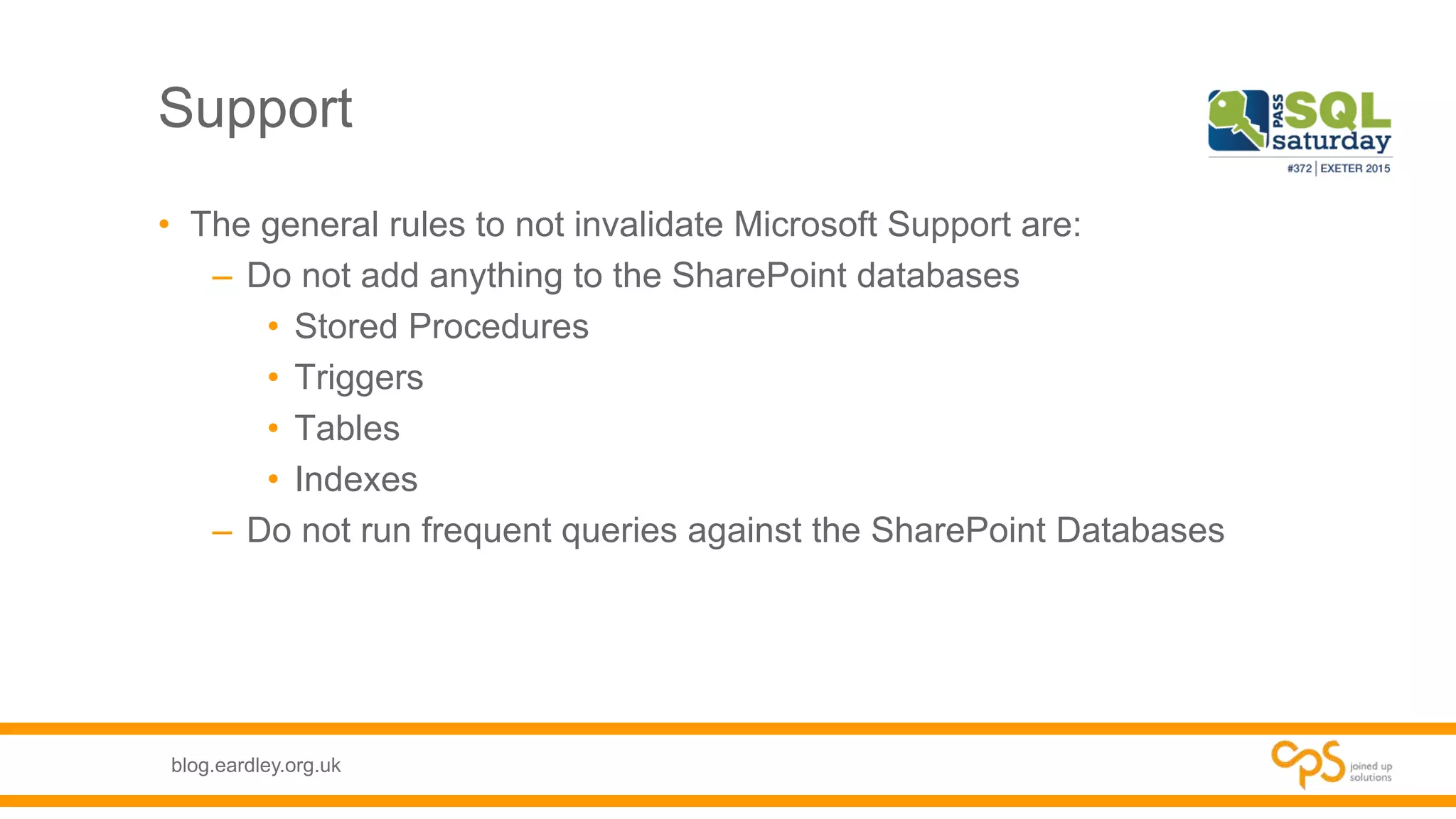
- Details on the different types of databases needed for SharePoint including content, service application, and administrative databases.
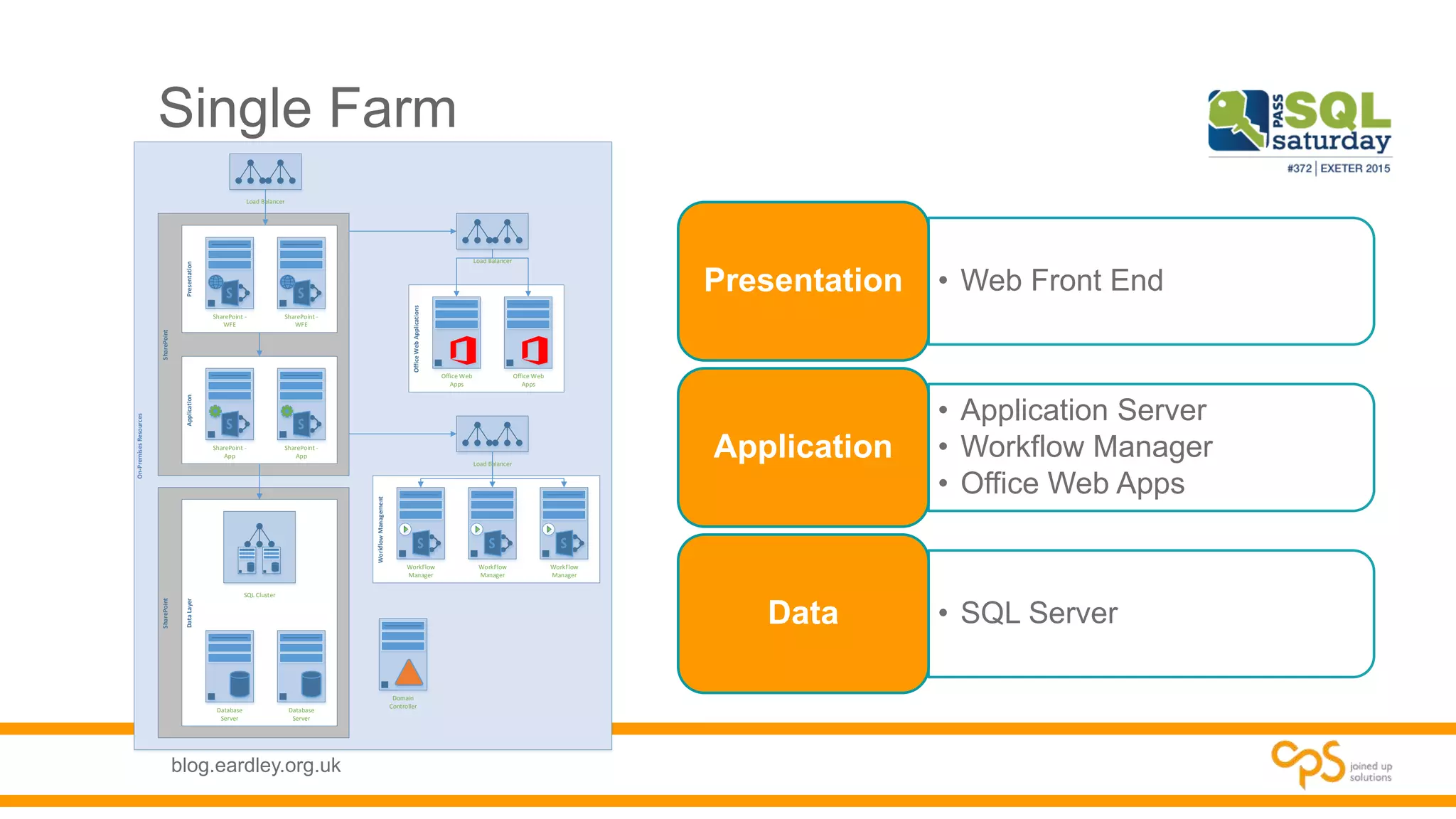
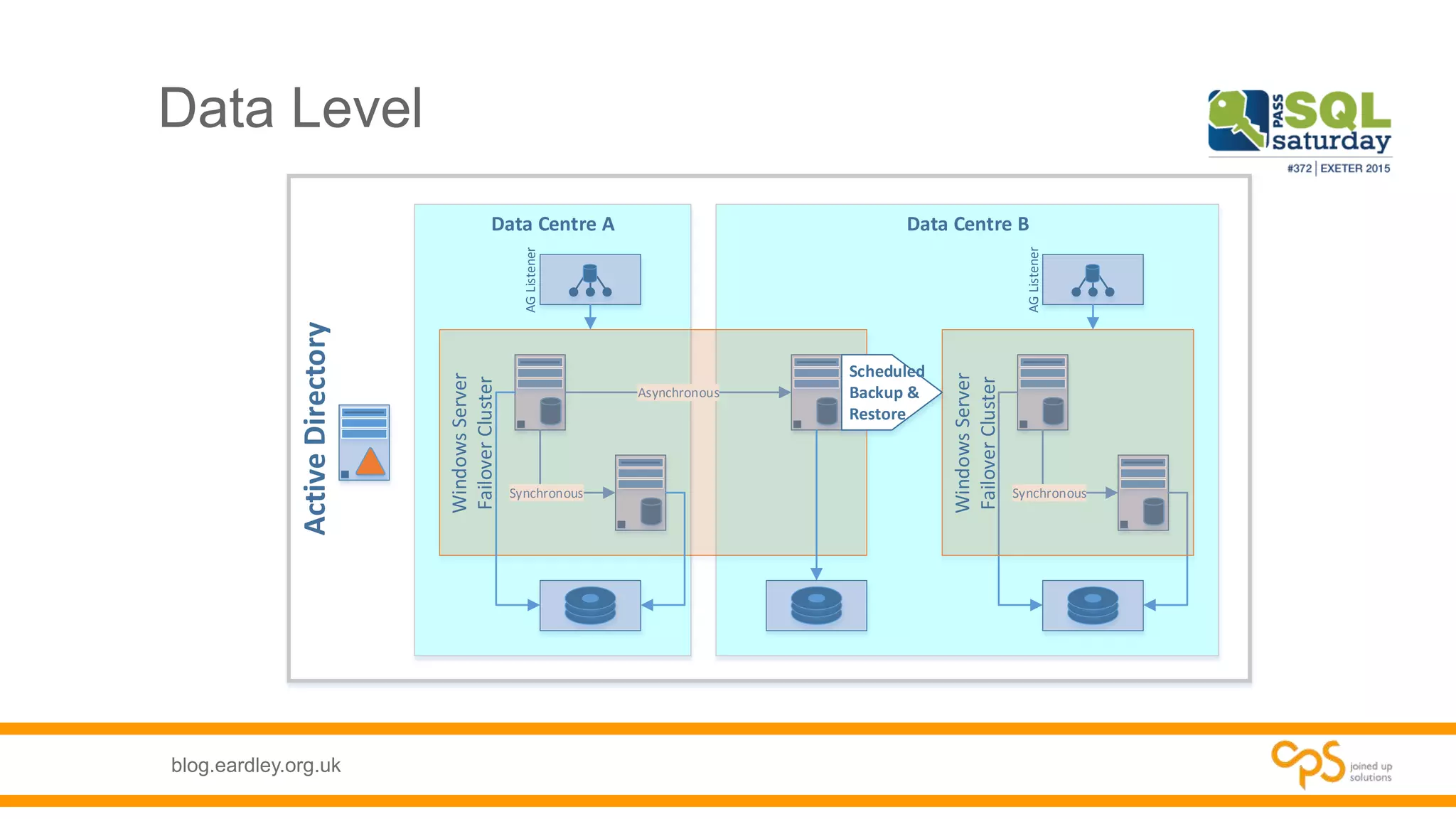
- Best practices for planning database needs including sizing, growth, and high availability options.
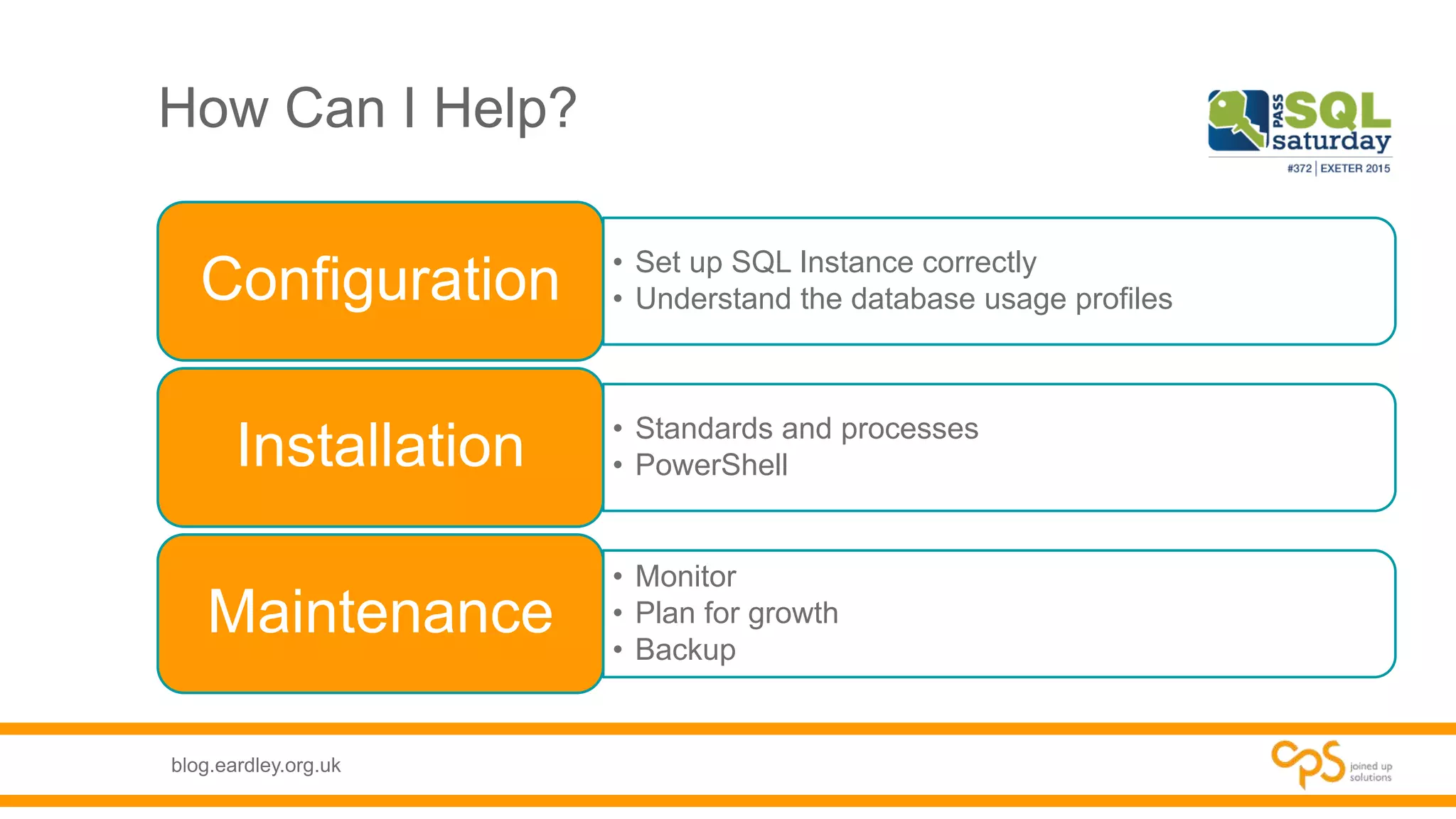
- How a DBA can help with configuration, monitoring, backup, and other database maintenance tasks for SharePoint.