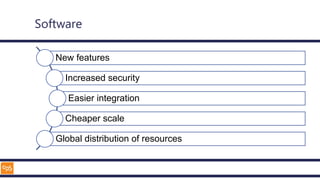
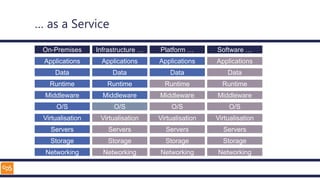
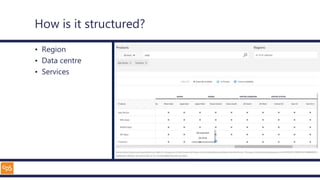
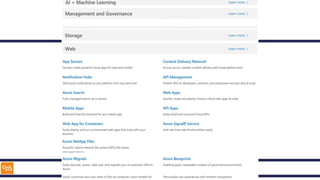
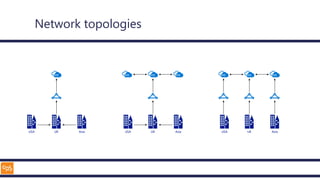
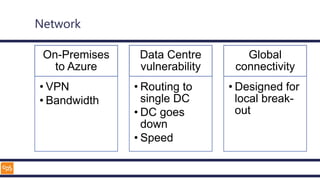
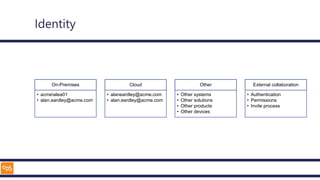
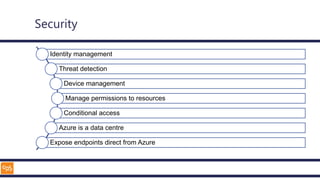
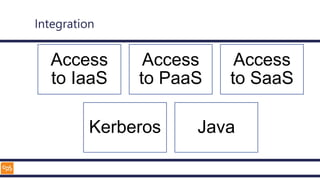
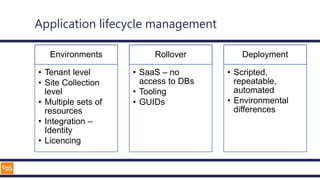
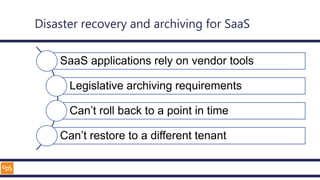
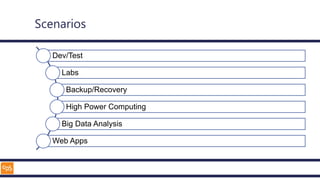
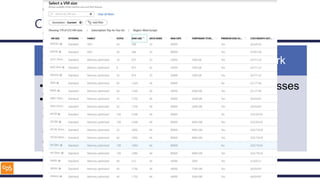
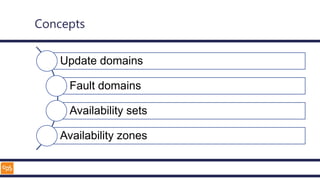
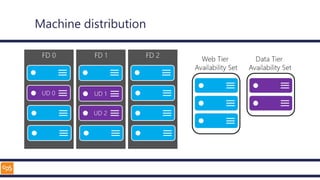
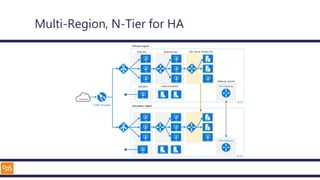
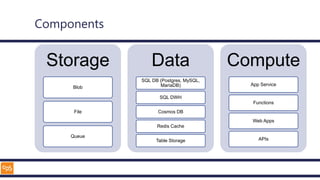
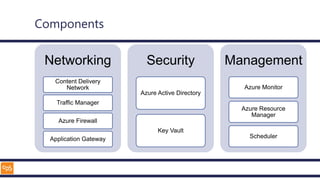
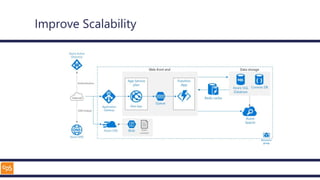
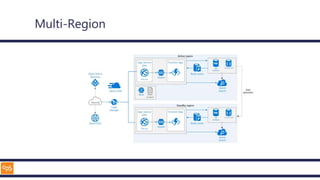
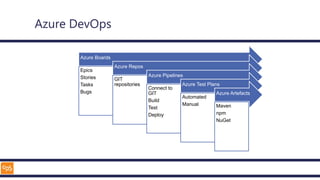
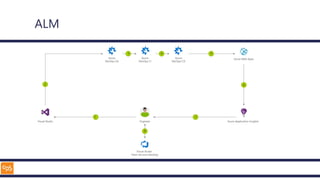
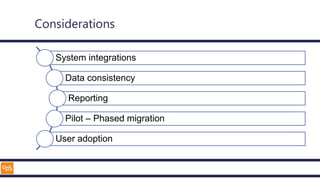
The document outlines an introduction to Microsoft Cloud, covering its definition, objectives for transitioning to the cloud, and specifics about Azure services, including SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. It details various architectural components, considerations for migration, and best practices for security and management. The content emphasizes the strategic advantages of adopting cloud technology in business operations.