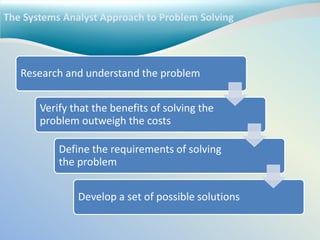
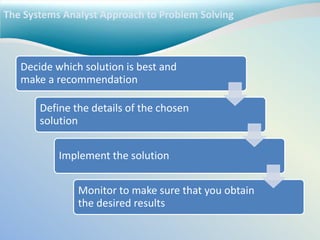
The systems analyst uses analysis and design techniques to solve business problems using information technology. They understand the business needs and technical requirements, evaluate solutions, and implement the chosen solution. A systems analyst requires knowledge of computers, networks, databases, programming languages, and operating systems as well as business processes, organizational structure, and how people work and communicate. They use tools like databases, IDEs, and CASE tools to develop system specifications and employ techniques such as project planning, requirements modeling, and database design.