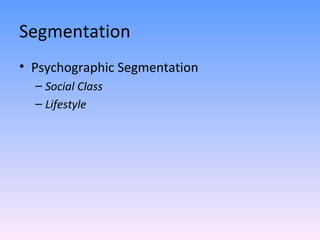
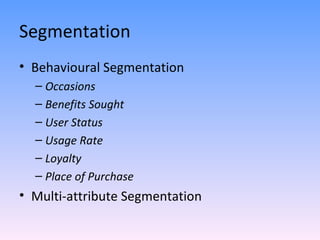
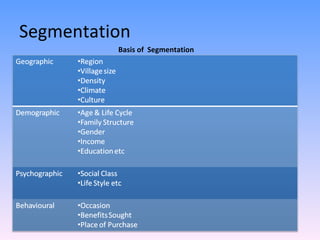
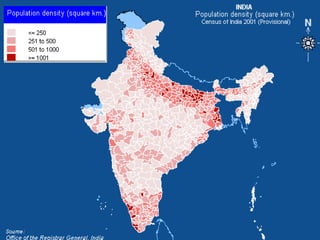
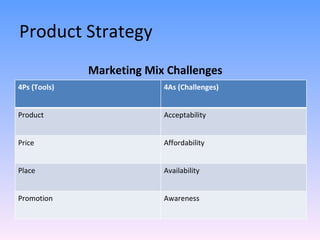
The document discusses strategies for segmenting, targeting, positioning, and developing product strategies for rural markets in India. It defines segmentation as dividing a heterogeneous market into homogeneous subgroups. Common bases for rural segmentation include geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors. Targeting involves evaluating segments based on attractiveness and resources, then selecting segments to target. Positioning determines how to design offerings to occupy a distinctive place in consumers' minds. An effective product strategy considers affordability, accessibility, and meeting basic consumer needs in rural contexts.