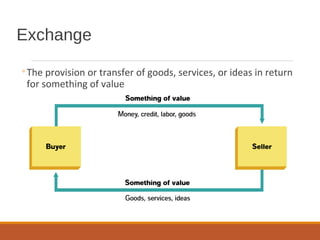
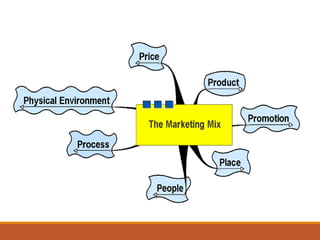
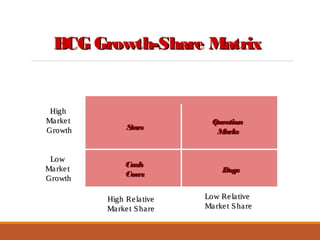
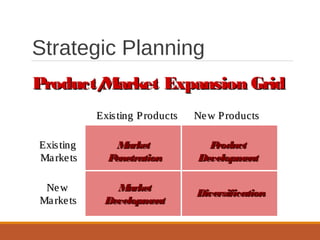
The document provides an overview of marketing management, defining marketing as a human activity aimed at satisfying needs and wants through exchanges. It discusses key concepts such as the marketing mix, strategic planning, and the dynamics of rural marketing in India, emphasizing the growth potential in rural areas and the importance of understanding consumer behavior. Additionally, it outlines challenges and strategies for effective marketing communication in rural markets.