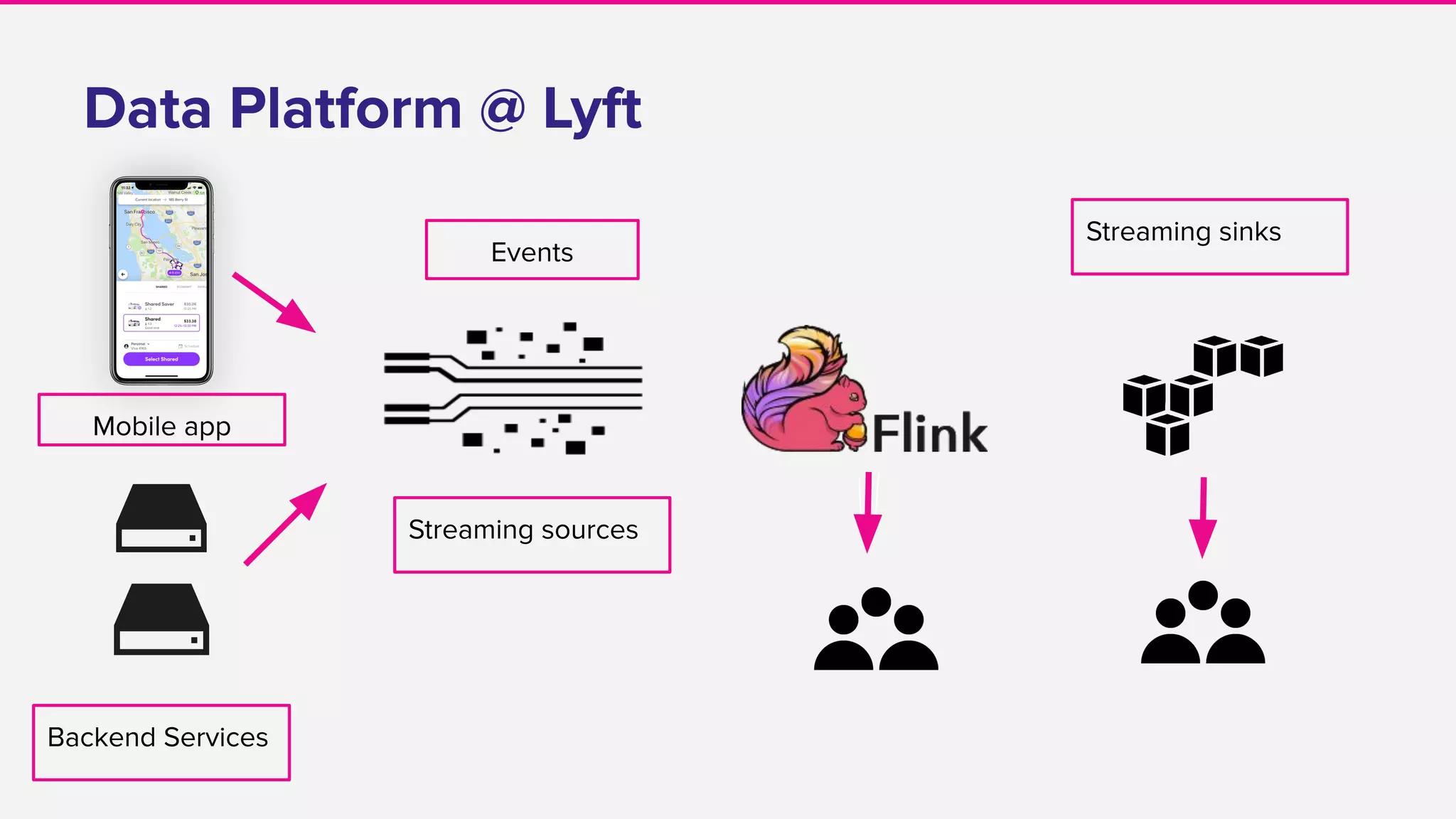
The document discusses the implementation and operation of Apache Flink at Lyft, highlighting various use cases such as dynamic pricing, fraud detection, and data pipeline management. It covers the lifecycle of a Flink job, challenges in production, integration with Kinesis streams, and improvements made for production stability and recoverability. Additionally, it mentions the release of the Flink operator for Kubernetes, which aims to streamline Flink job management and reduce downtime.



![8
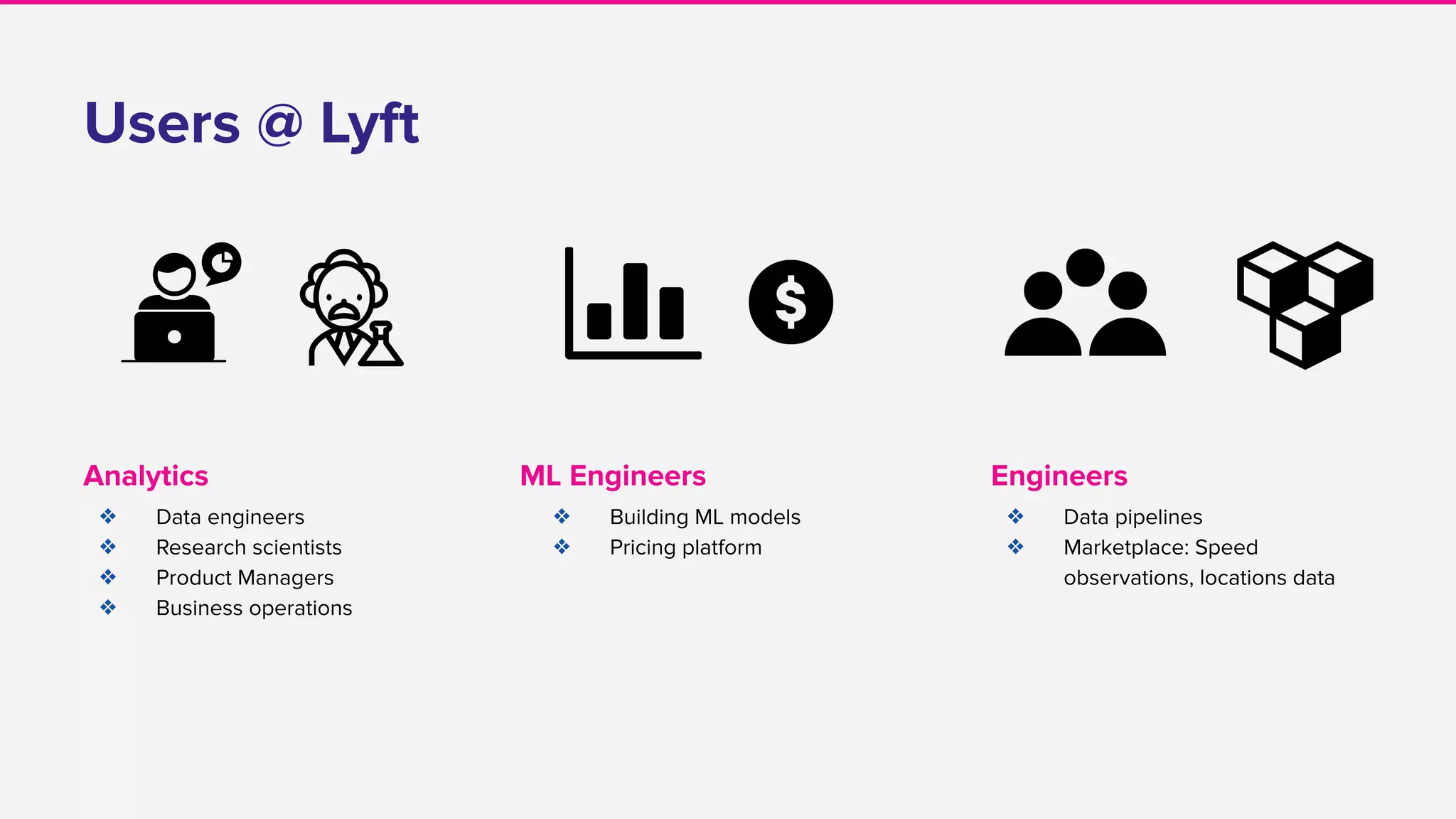
Abstraction levels
Flink jobs
API: Java
Users: Engineers
Use cases: Data pipelines,
ETA, Mapping
% Jobs: 45%
Dryft
API: Streaming SQL
Users: Research Scientists,
Data Engineers
Use cases: Fraud detection,
coupons
% Jobs: 53%
Flink + Python ⇒ Beam
API: Python
Users: ML Engineers
Use cases: Dynamic
Pricing[1]
% Jobs: 2%
2
1
3
Streaming Platform 0
[1] Streaming your Lyft ride prices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-8-2048.jpg)

![10
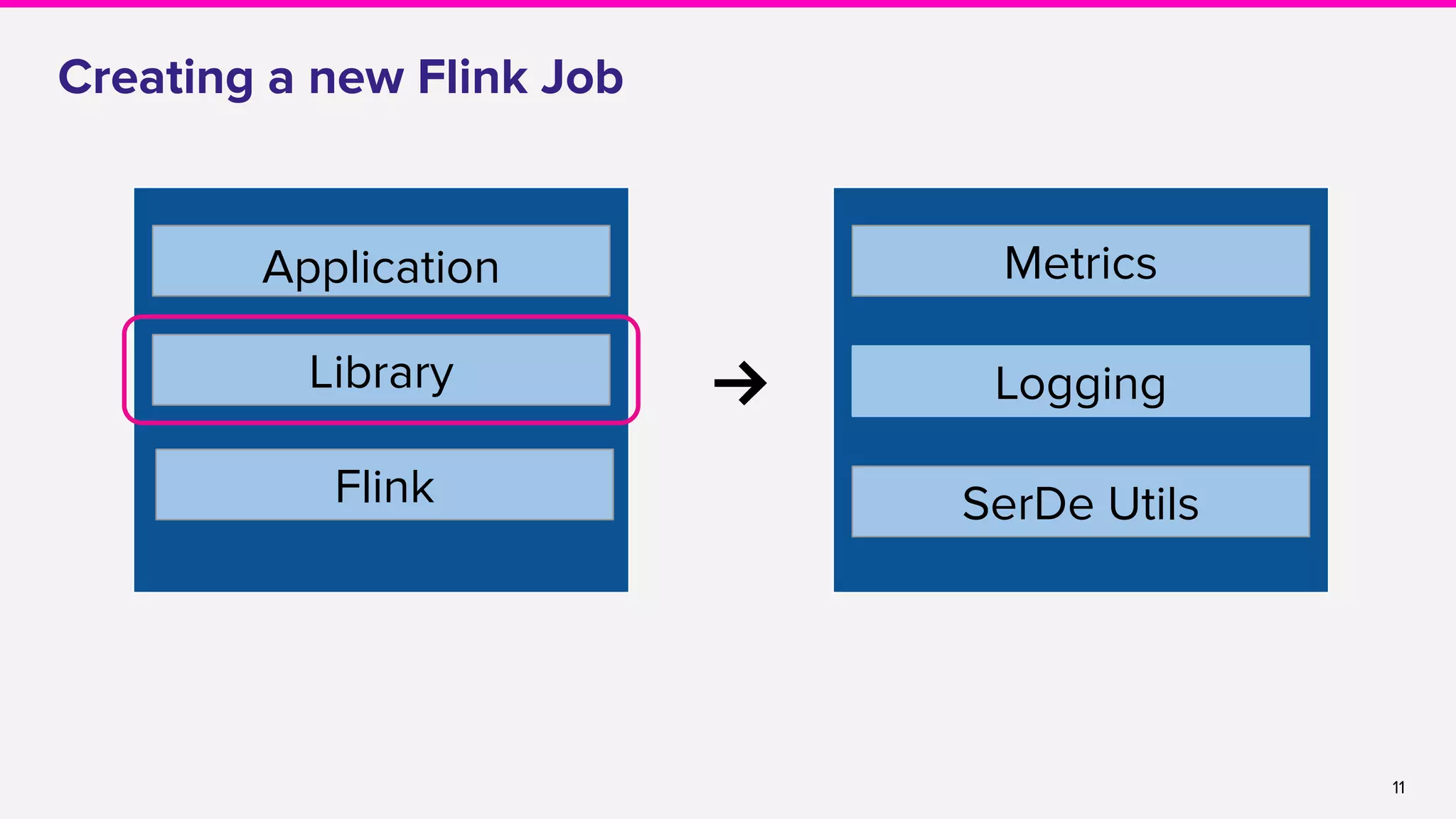
Creating a new Flink Job
● Boilerplate generator to kickstart a new Flink job
● https://yeoman.io/ → [yo streamingservice helloworld]
● A representative example to make development easy
DataStream<KinesisRecord> recordStream = env.addSource(sourceFunc).name("source").uid("source");
DataStream<UserAndCount> locationStream =
recordStream
.flatMap(new LocationEventExtractor())
.filter(new LocationFilter())
.keyBy("userId")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(1))
.aggregate(new LocationsCounter())
.uid("locations-counter");
locationStream.addSink(sinkFunc).name("sink").uid("sink");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-10-2048.jpg)


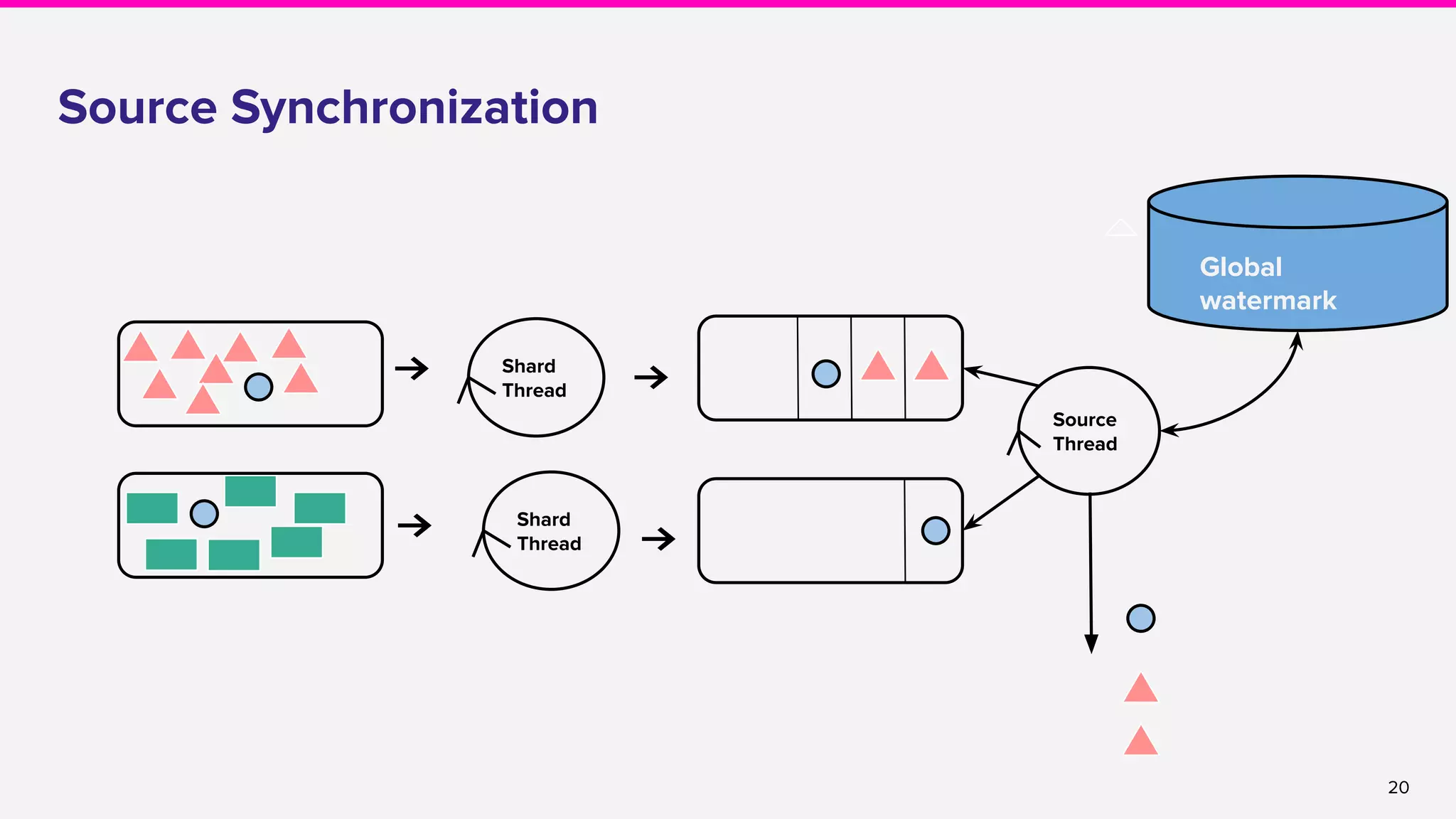
![22
Flink contributions
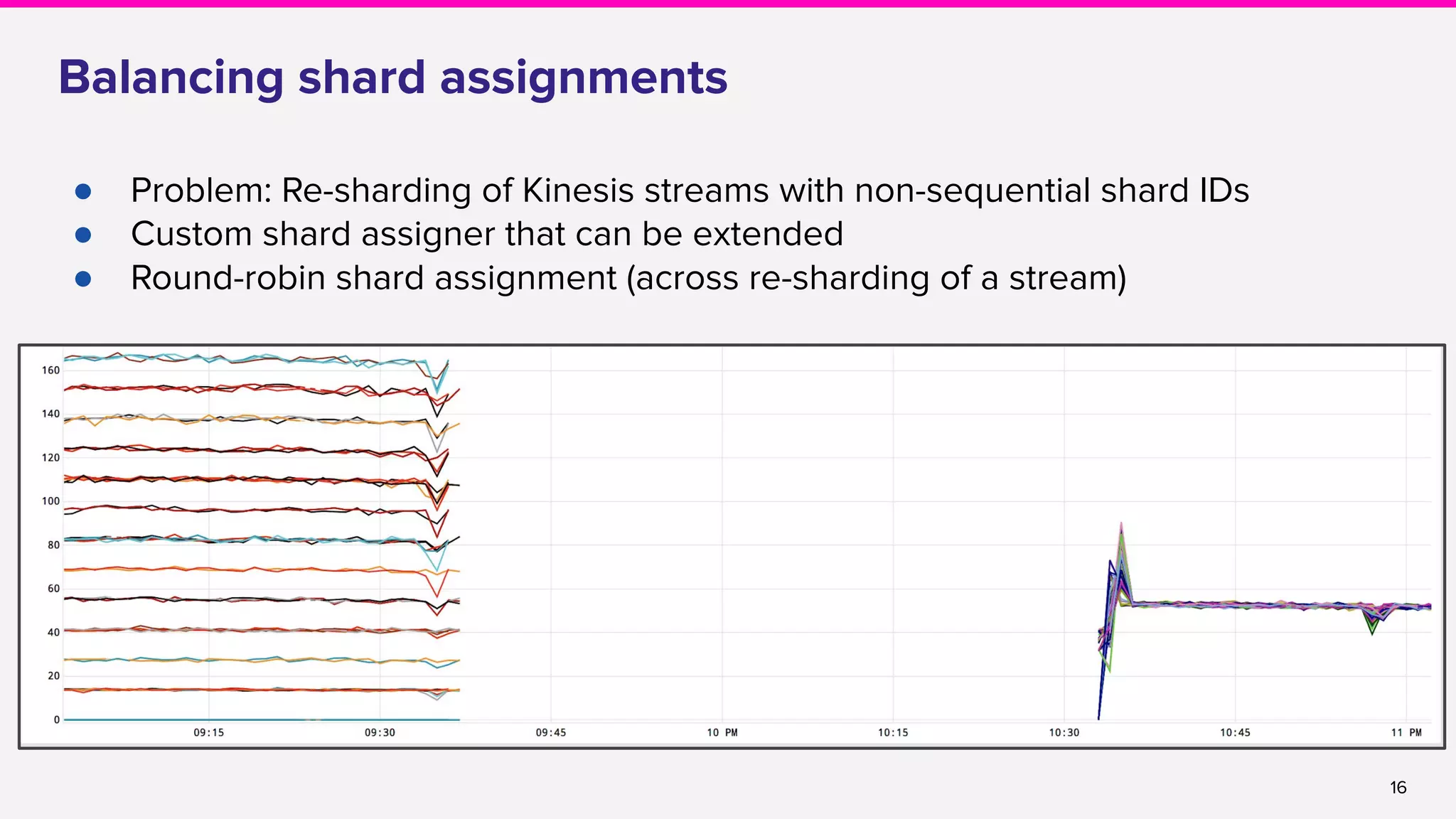
● Shard balancing
○ Per-shard watermarking [FLINK-5697]
○ Custom Shard assignment [FLINK-8516]
○ ListShards API [FLINK-8944]
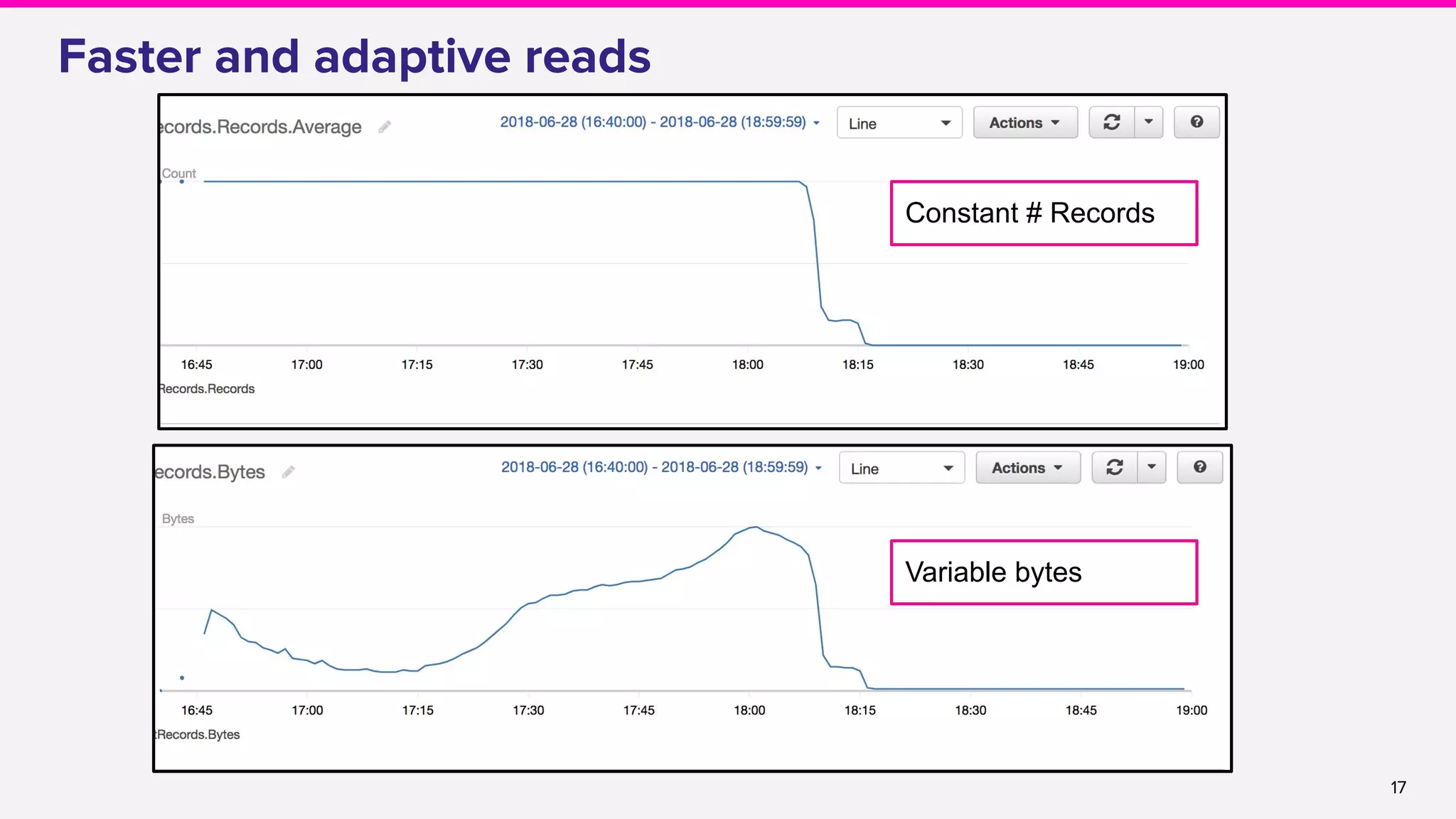
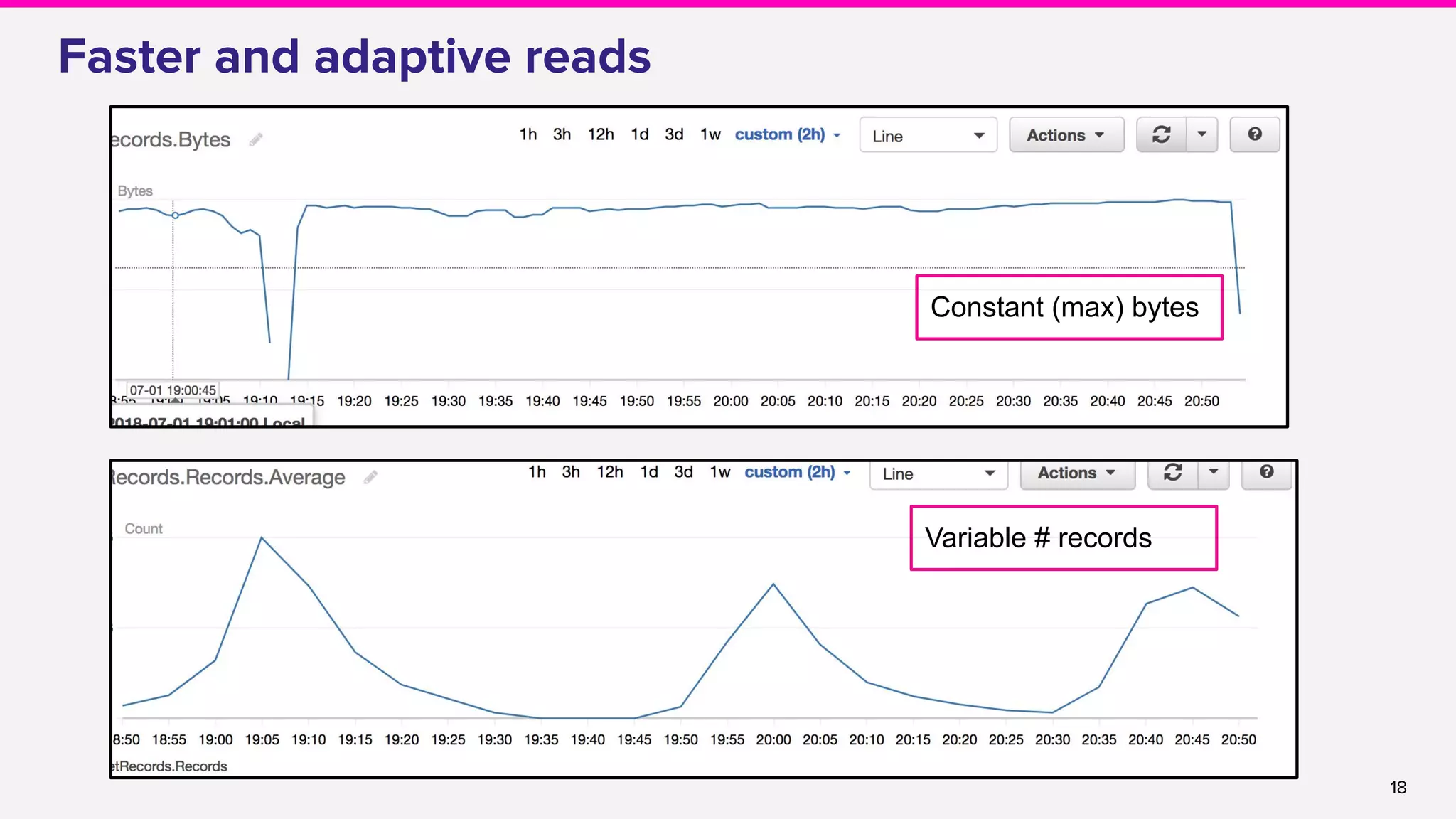
● Adaptive reads
○ Adding adaptive reads [FLINK-9692]
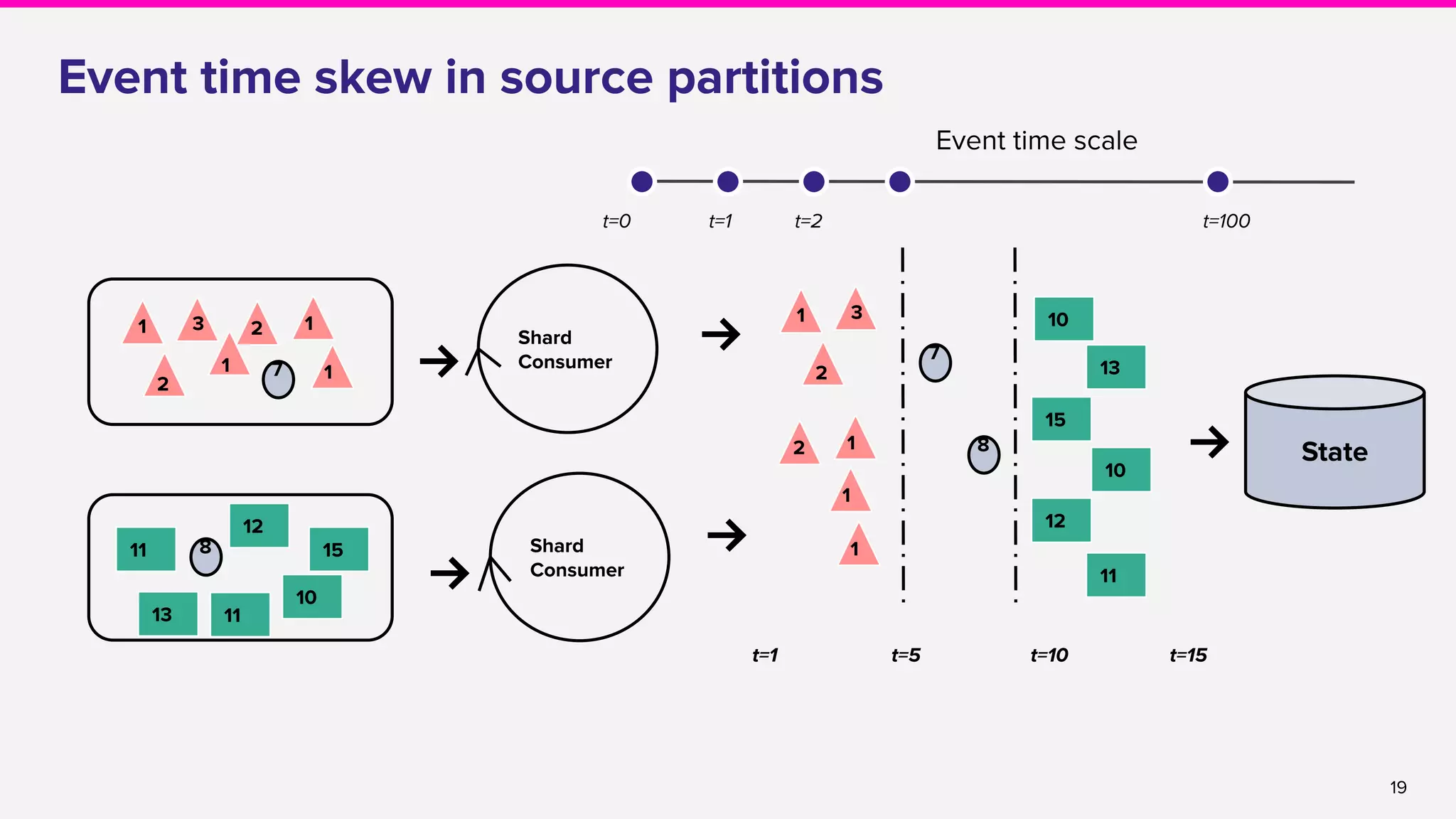
● Source synchronization
○ Global Aggregate Manager in JobMaster [FLINK-10887]
○ Source synchronization in the Kinesis connector [FLINK-10921]
○ (Long term) Event time alignment as a part of FLIP-27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-22-2048.jpg)
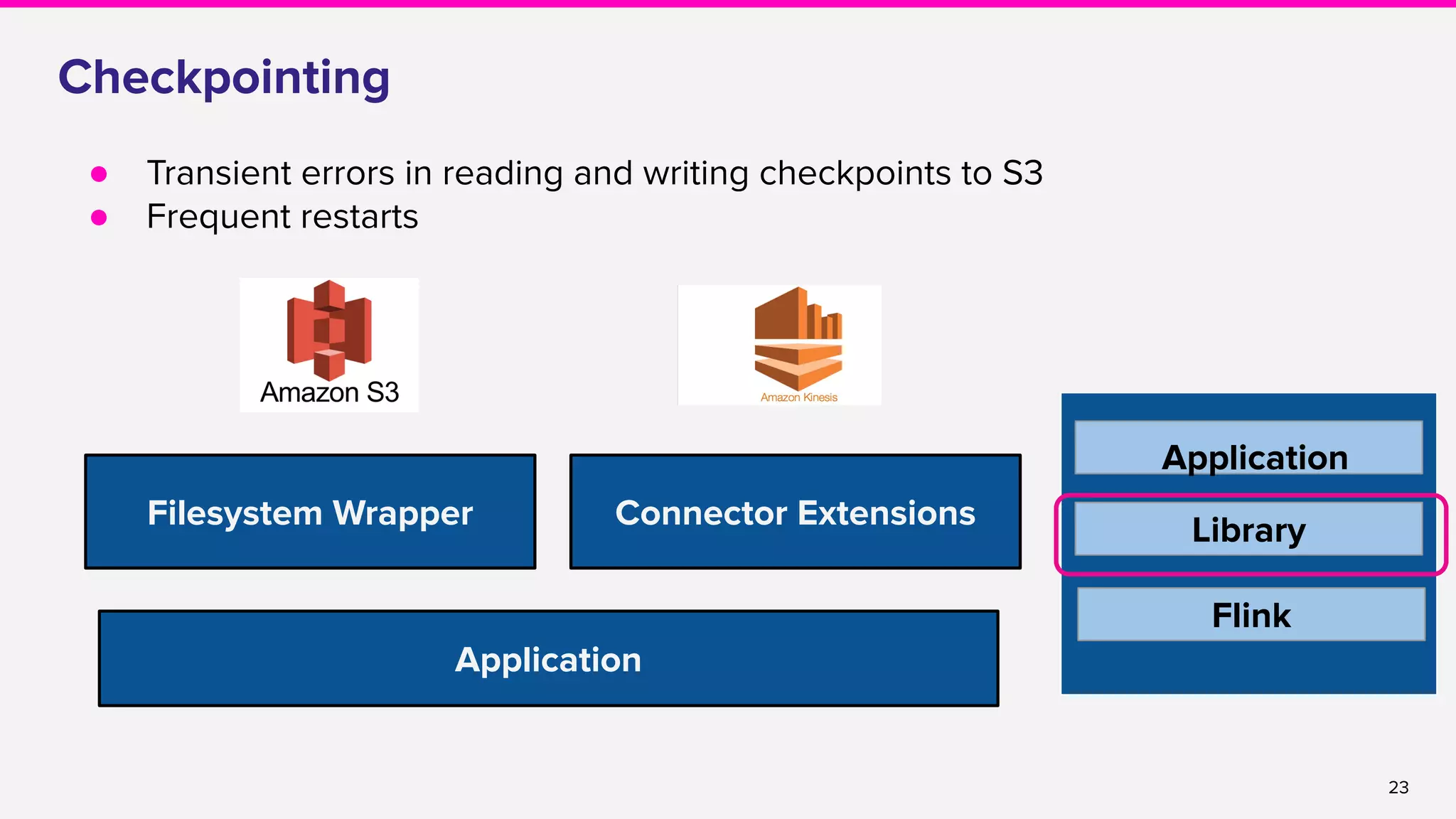
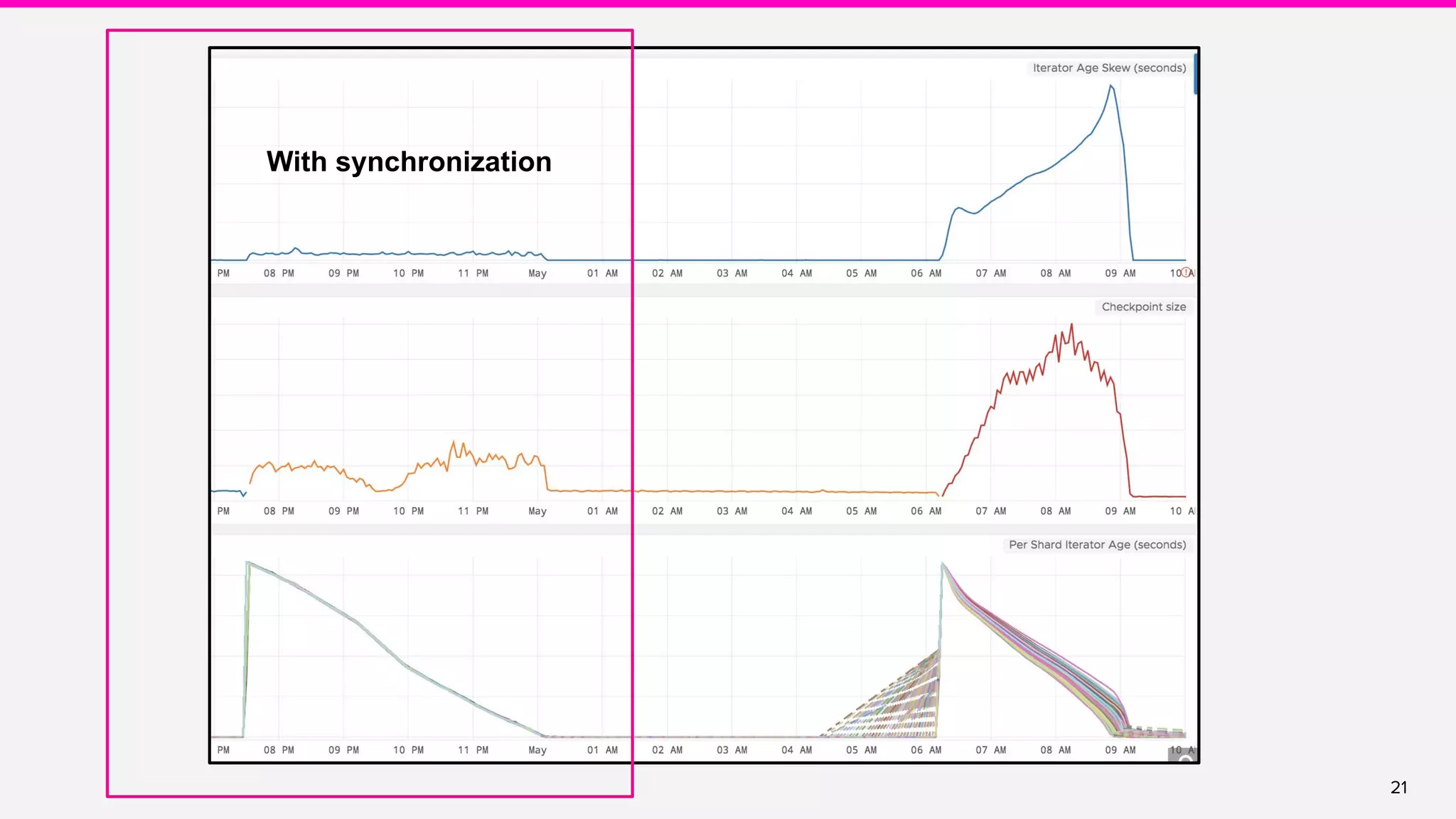
![24
Checkpointing
● Hot partitions
s3://<bucket>/application/checkpoints/
● [FLINK-9061] Entropy injection
● Entropy injected path
s3://<bucket>/<HASH>/application/checkpoints/
● Externalized checkpoints ✅](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-24-2048.jpg)
![25
Challenges
● A lot of data pipeline use cases
○ Log ingestion to Kibana
○ Change data capture logs
○ Analytics event pipeline
● Common requirement
○ Data freshness
○ Data completeness (eventual)
● During an outage
○ Recover job and resume real-time data
processing
○ Backfill mechanism
● Checkpointing under backpressure
○ Failing checkpoints
○ Limited forward progress
○ [FLIP-76]
○ Debugging bottleneck is hard
● Kafka consumer improvements
○ Idle partition detection
○ Source synchronization
● Recovery and HA
○ Partial recovery from task failures [FLIP-1]
○ Zookeeper and HA [FLINK-10030]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-25-2048.jpg)



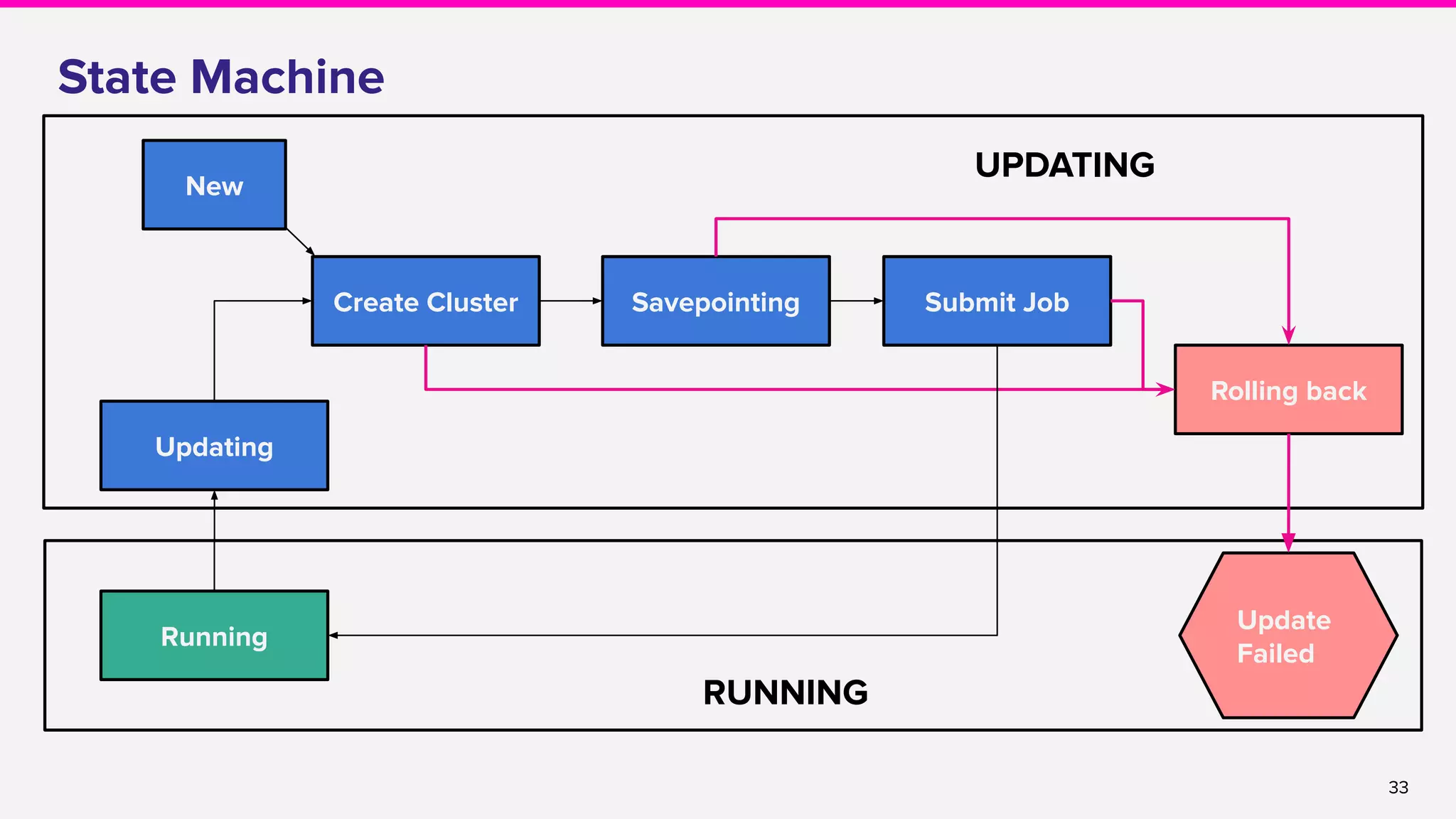
![30
Flink on k8s: Overview
● Core component: Flinkk8soperator[1]
● Operator manages Flink applications
Job
Definition
JM
TM
Flink
operator
TM
TM TM
[1] Managing Flink on Kubernetes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runningflinkinproductionthegoodthebadandthein-between-lakshmiraolyft1-191014111241/75/Running-Flink-in-Production-The-good-The-bad-and-The-in-Between-Lakshmi-Rao-Lyft-1-30-2048.jpg)