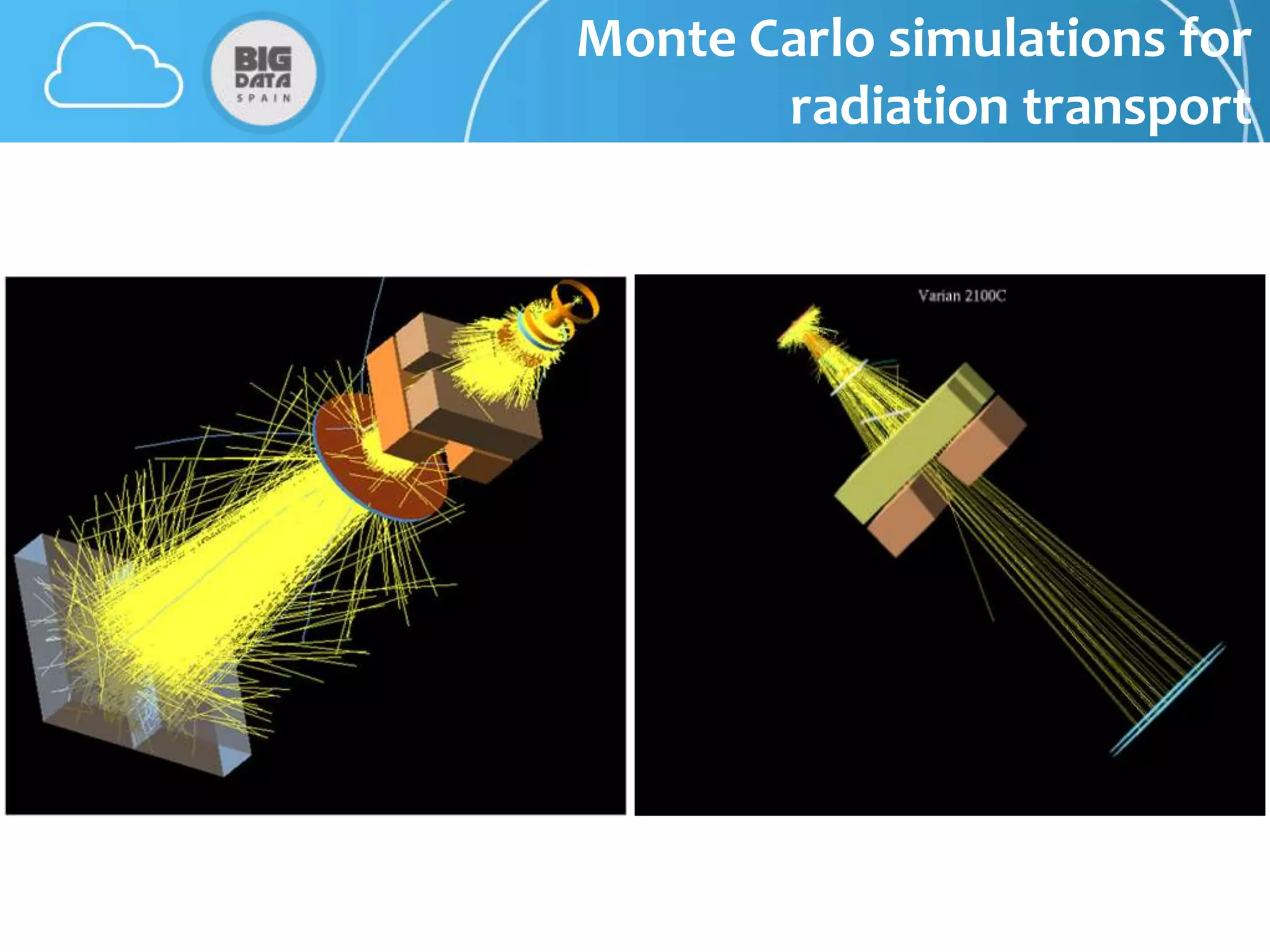
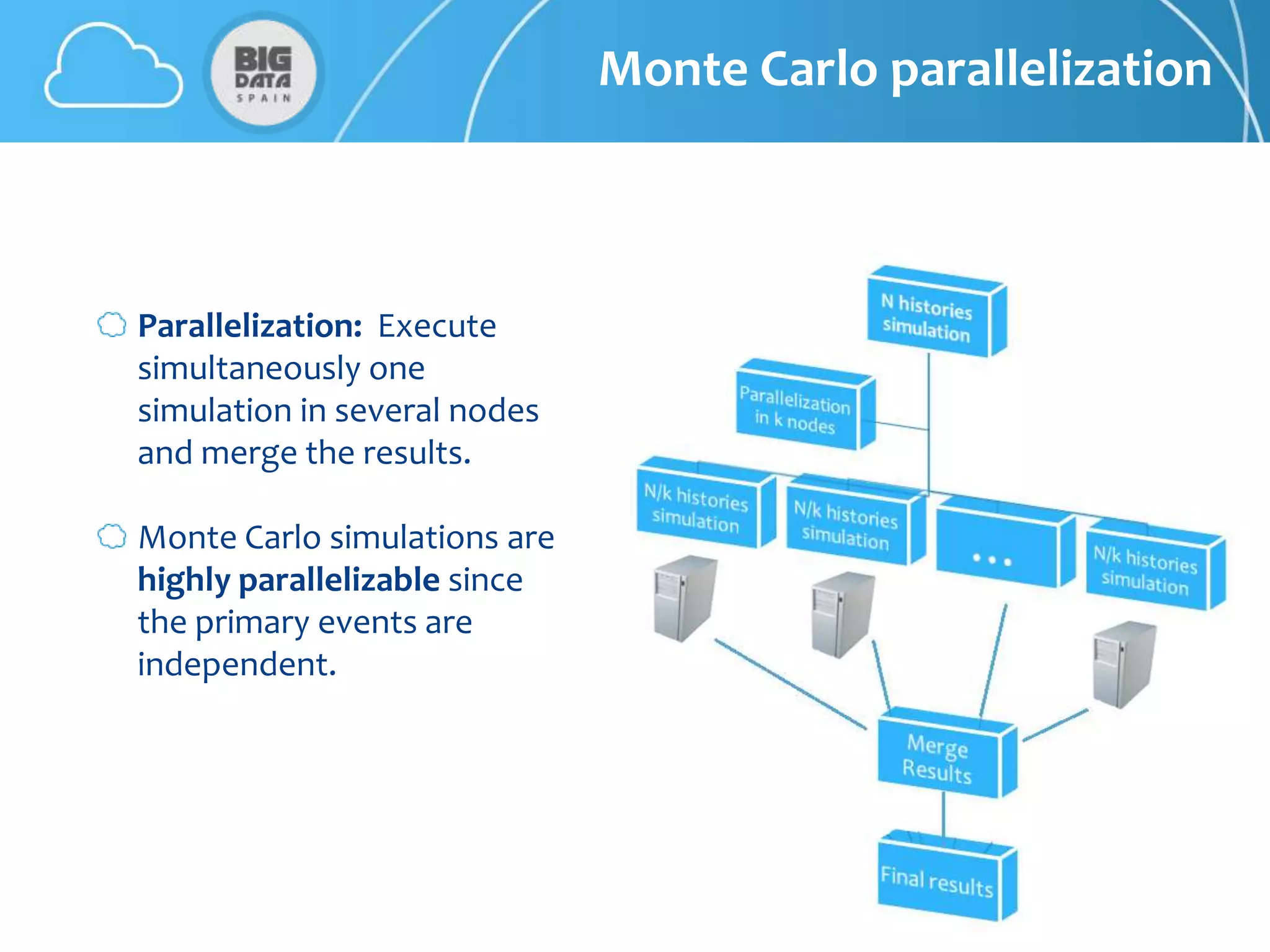
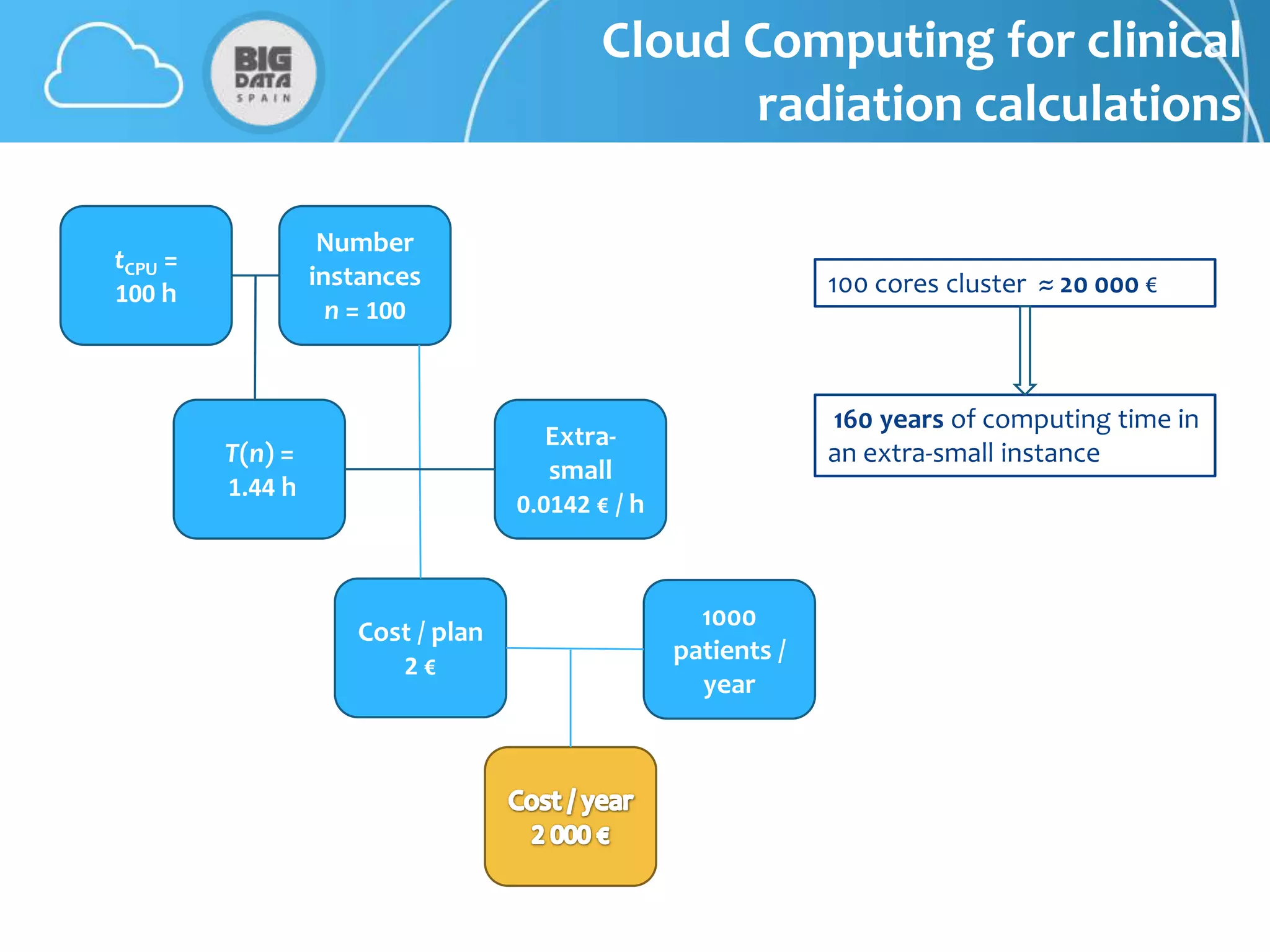
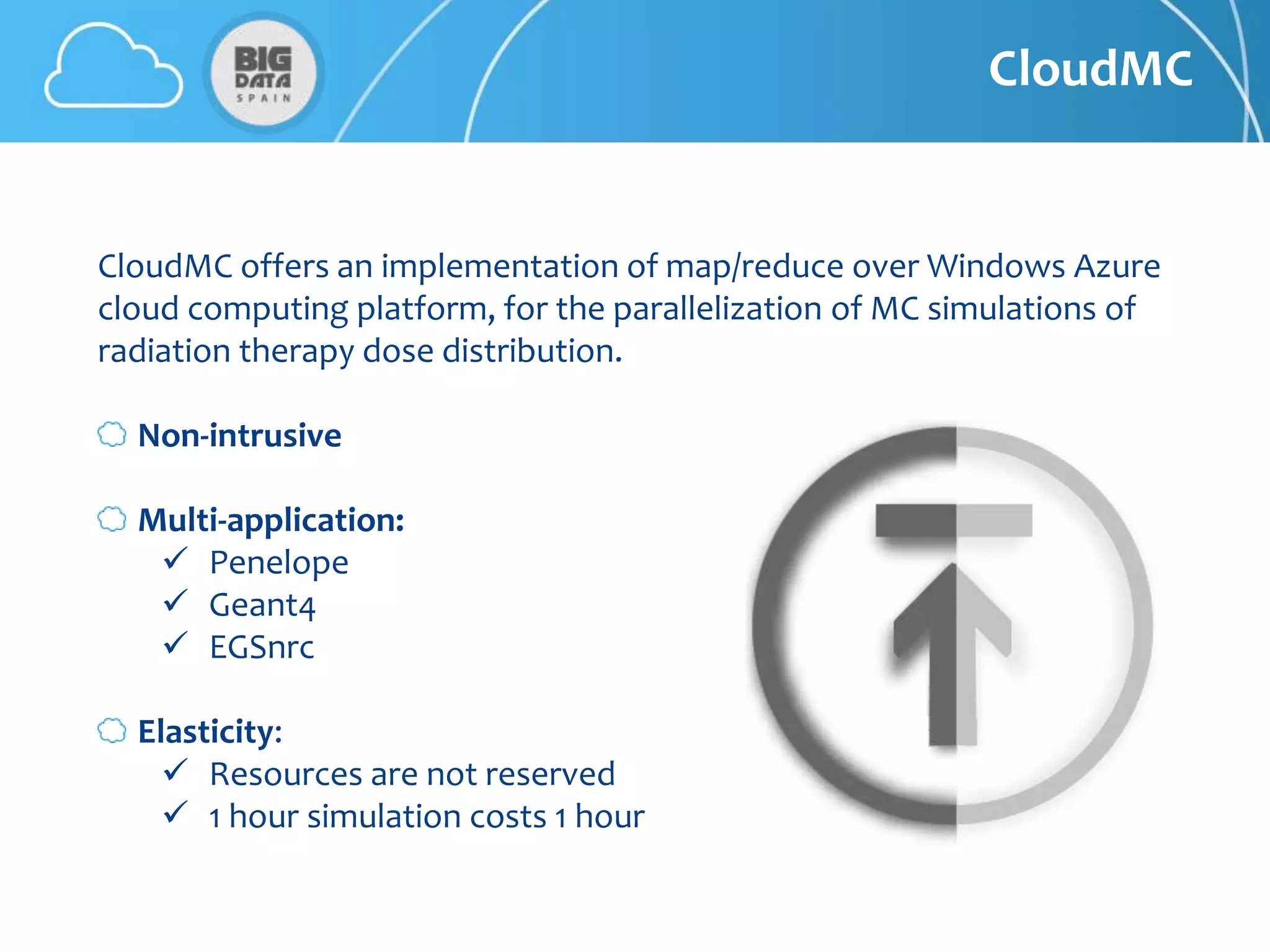
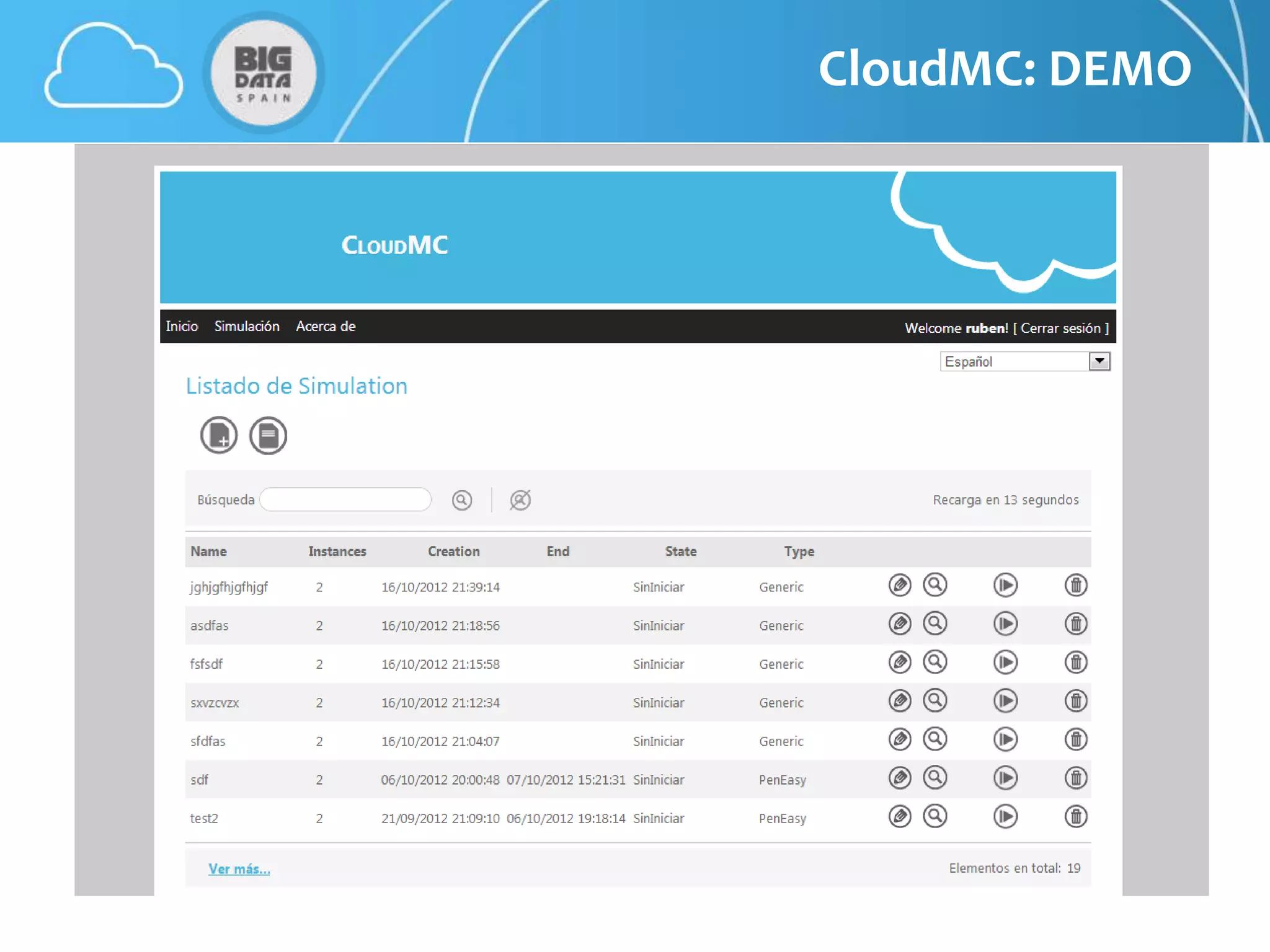
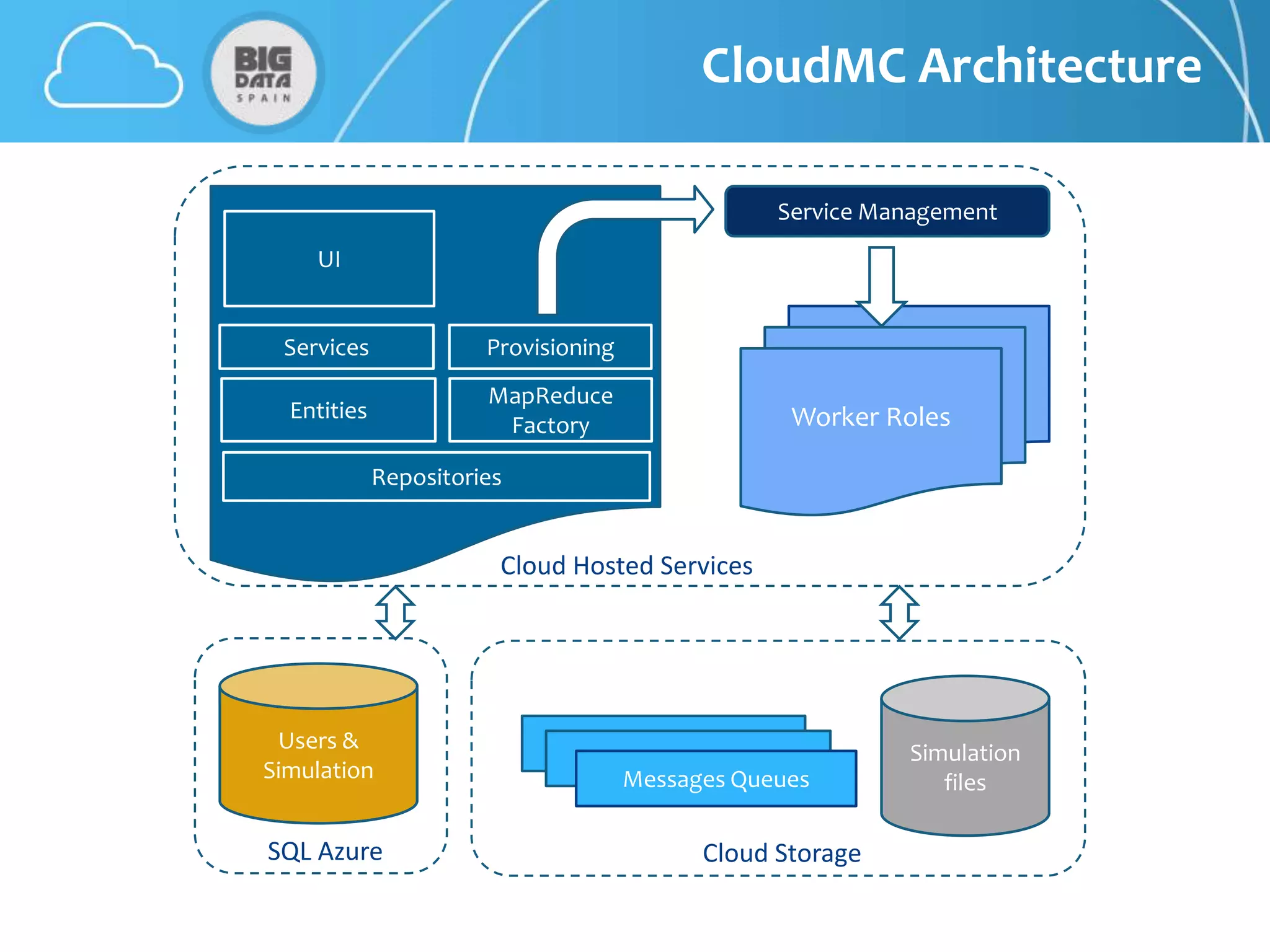
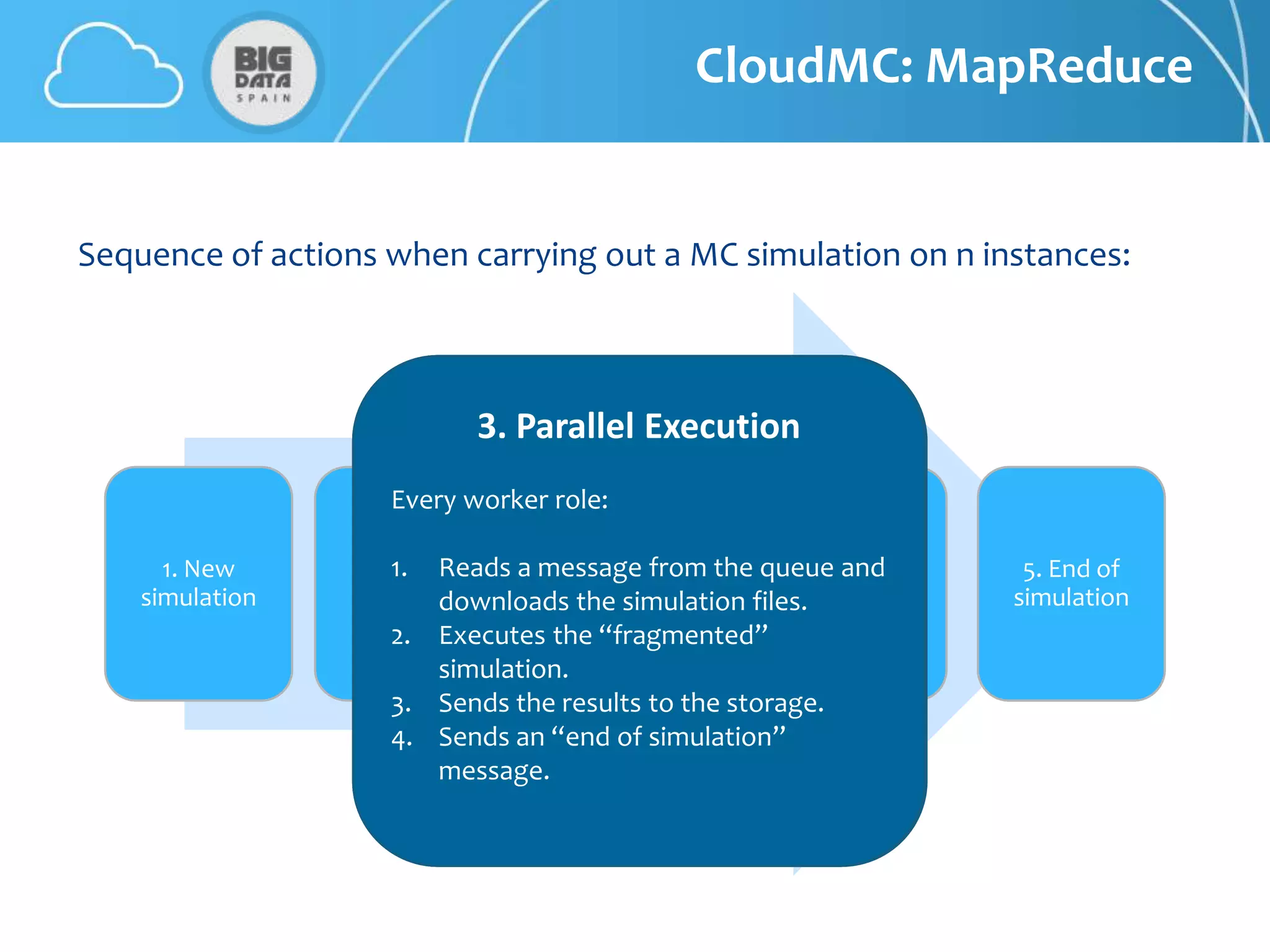
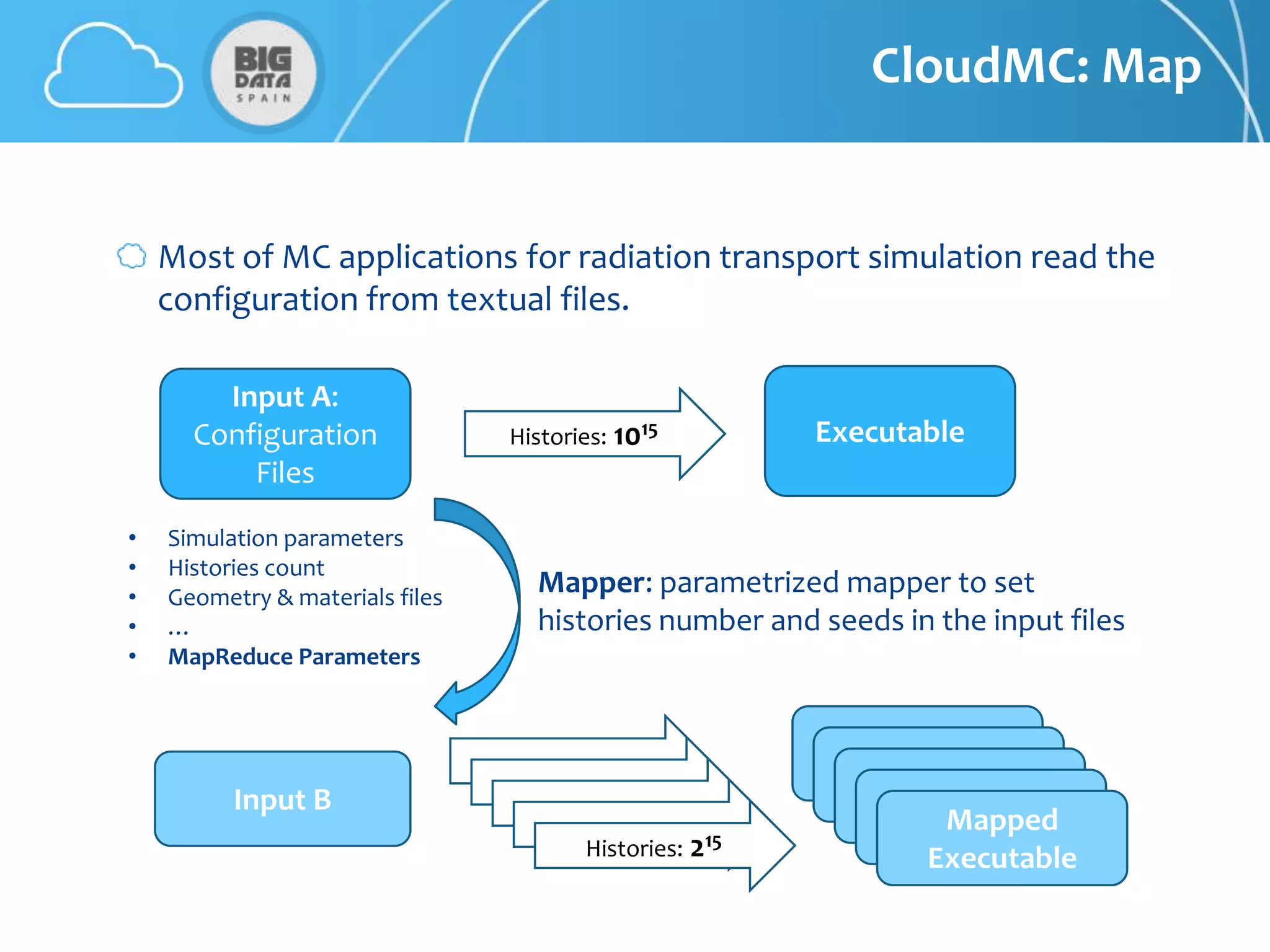
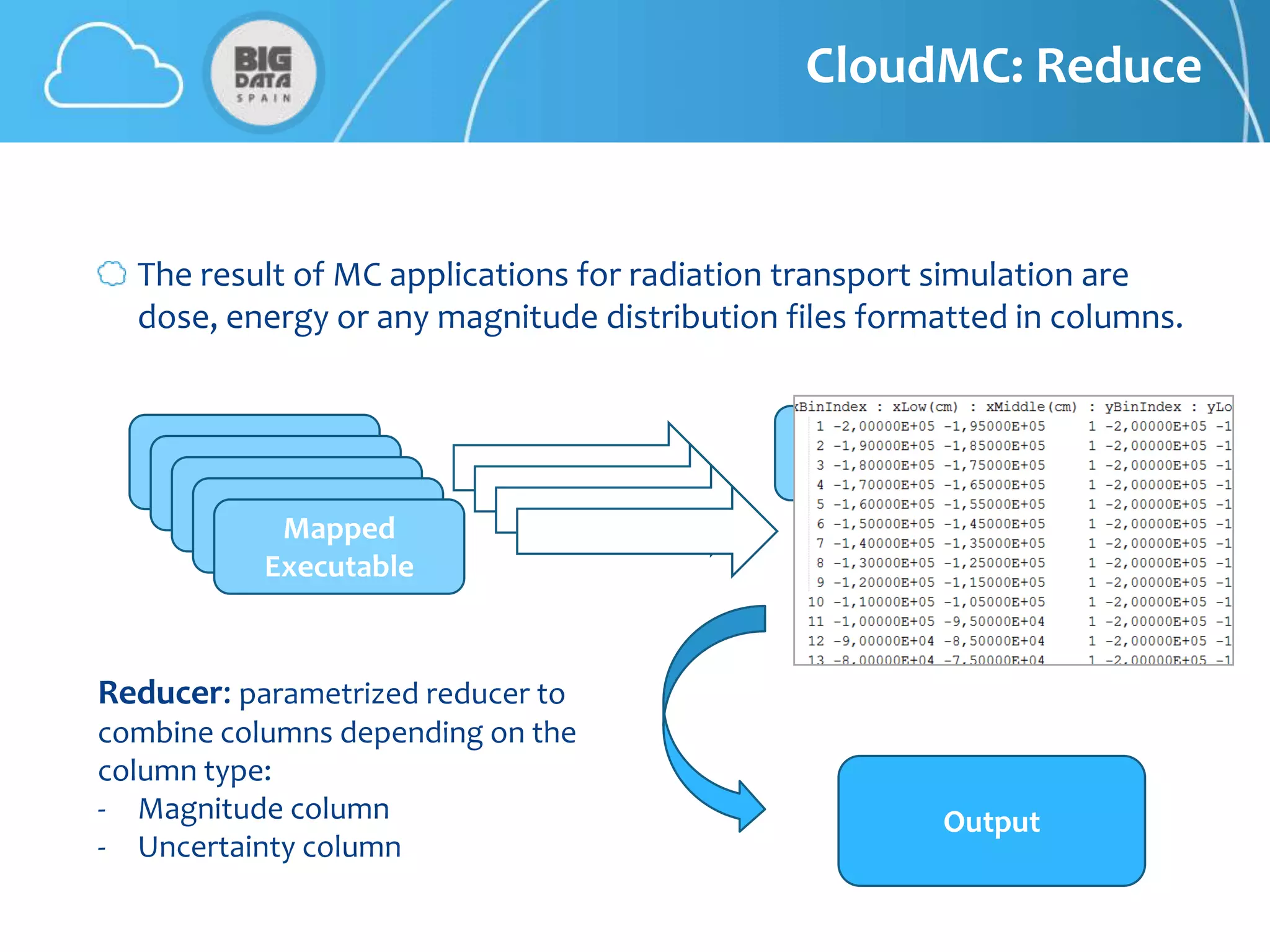
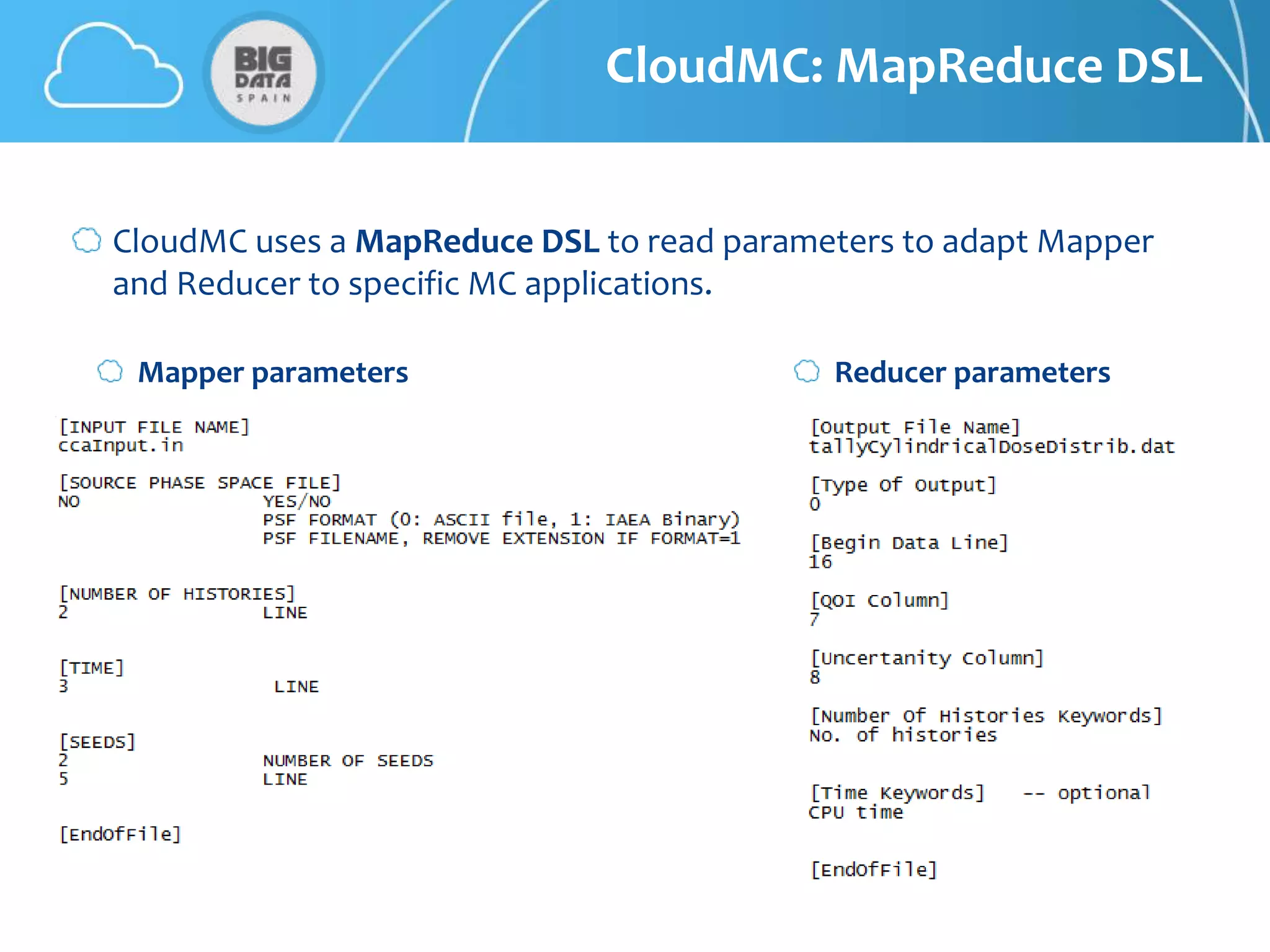
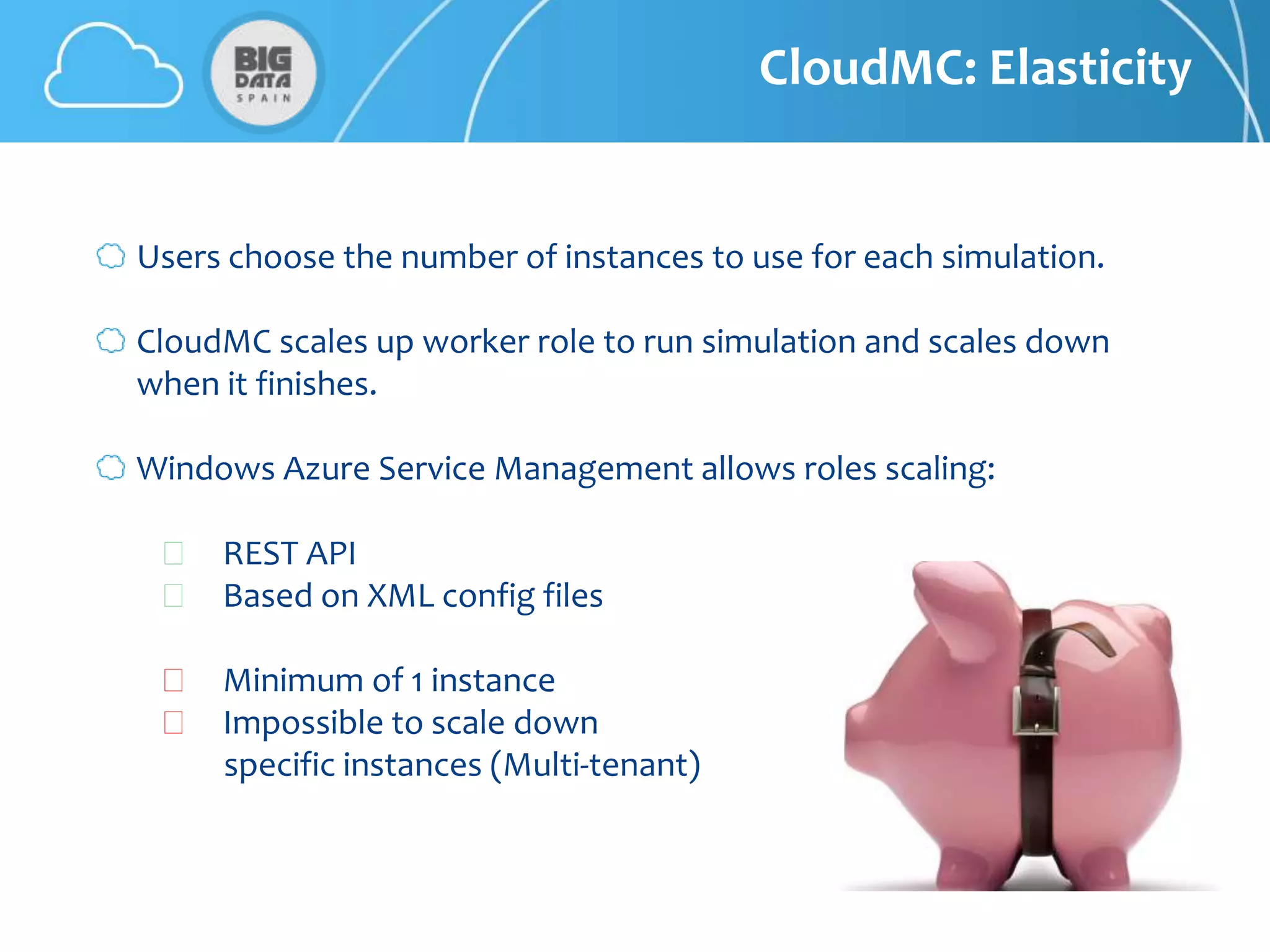
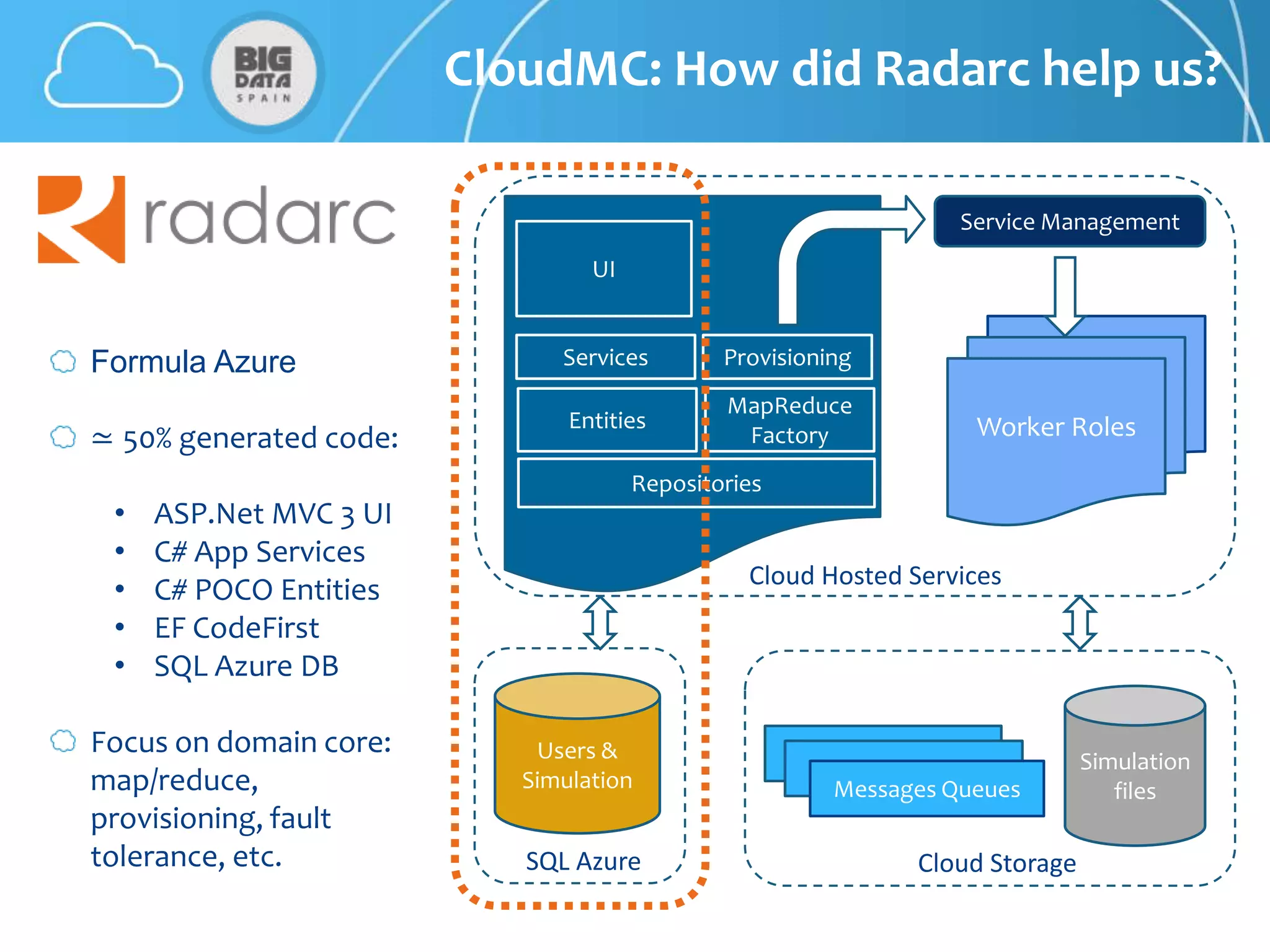
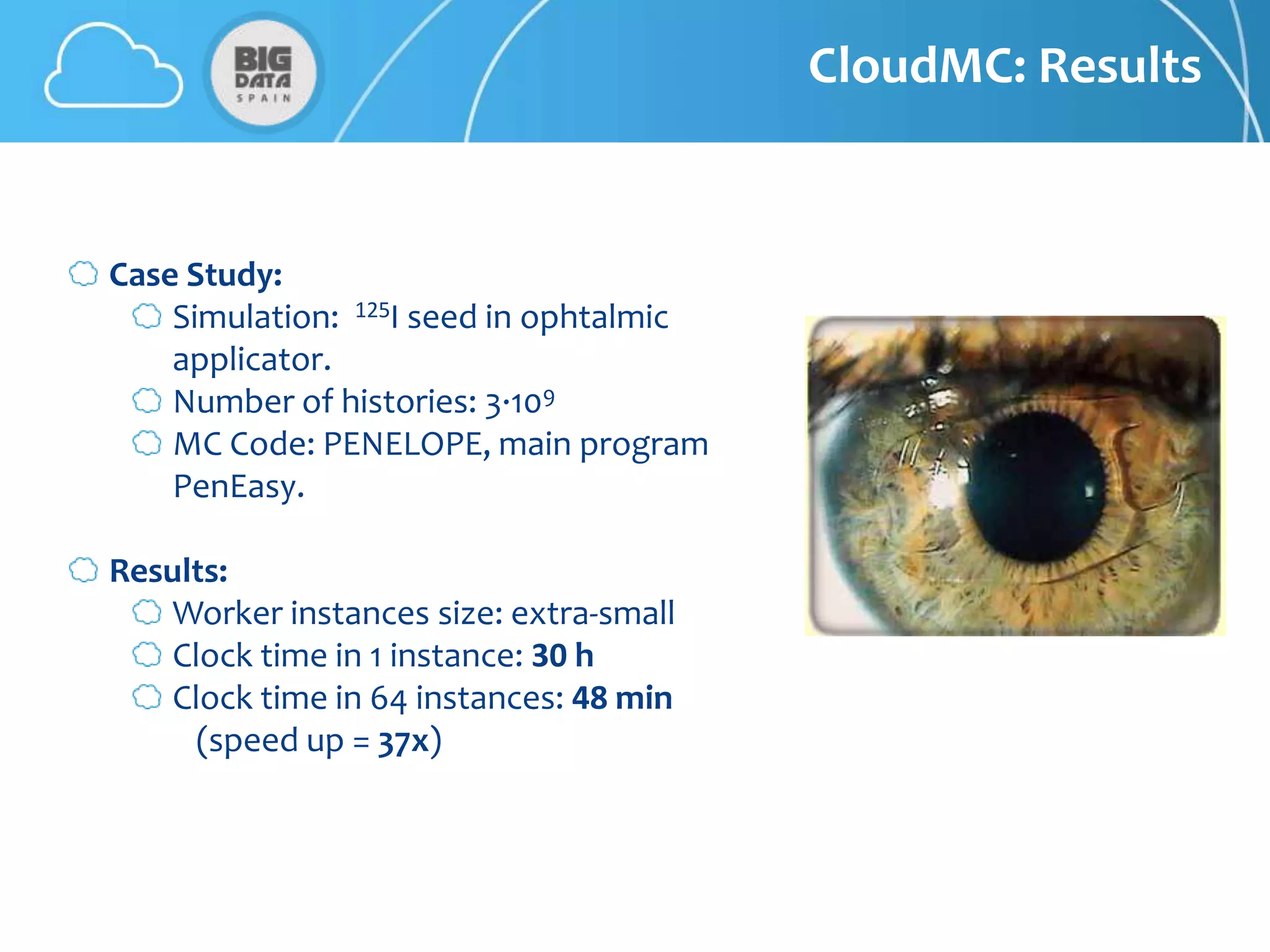
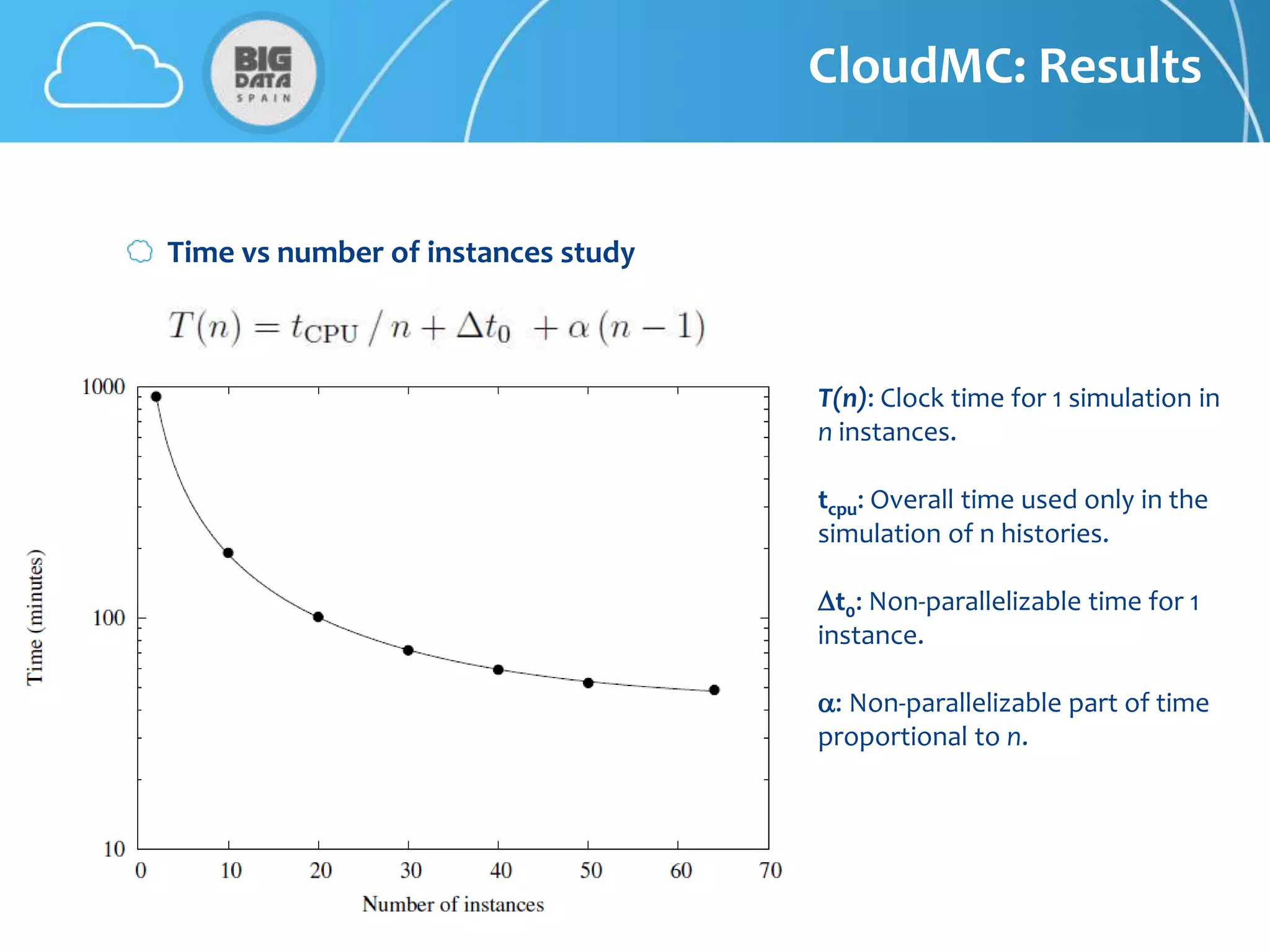
The document discusses CloudMC, a cloud computing implementation for parallelized Monte Carlo simulations used in radiotherapy for cancer treatment. It outlines the architecture and functionality of CloudMC, including its MapReduce capabilities and elasticity for resource allocation. The results demonstrate significant speed improvements in simulations when utilizing multiple instances, highlighting the benefits of cloud computing for clinical applications in radiation transport.