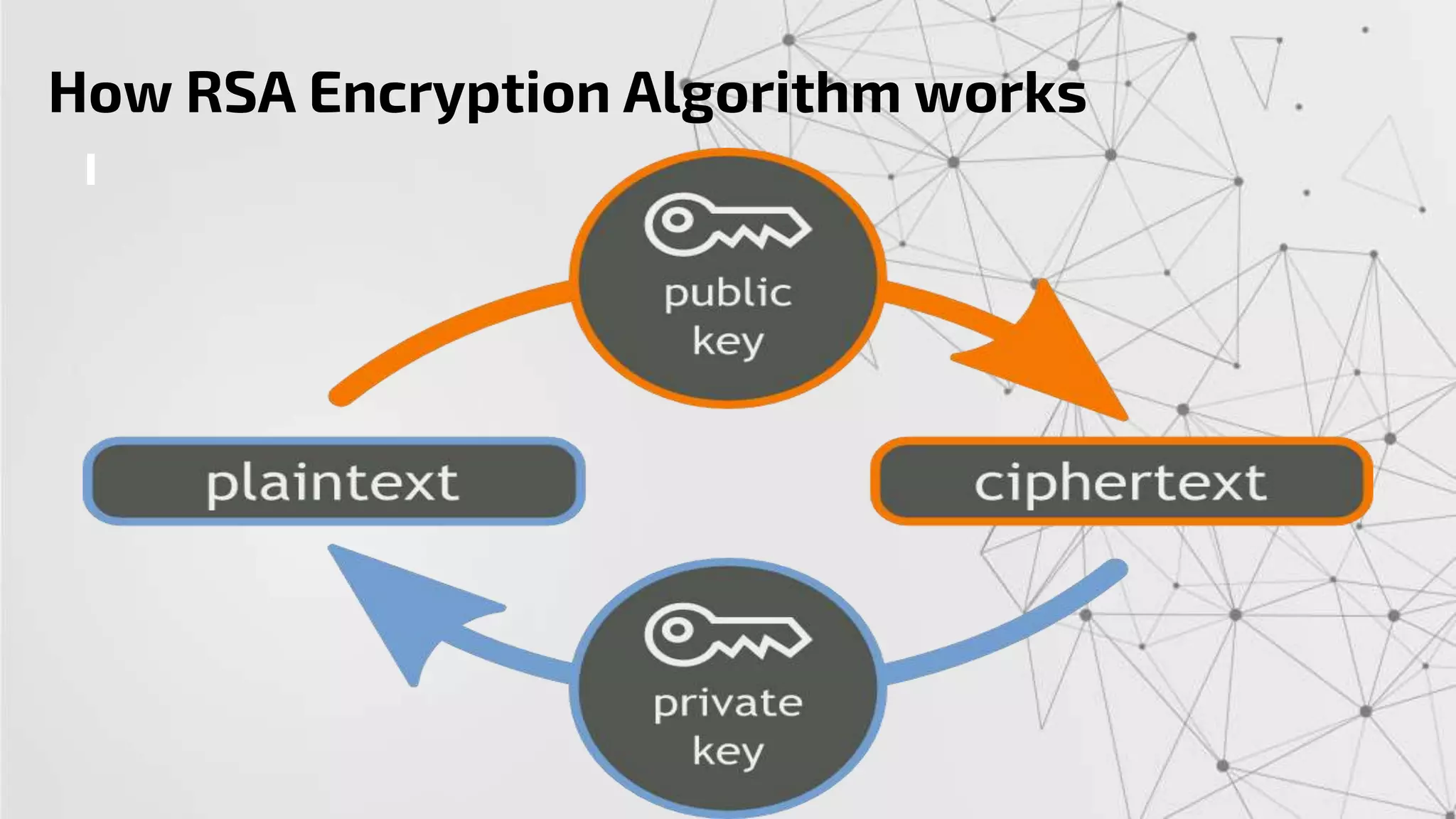
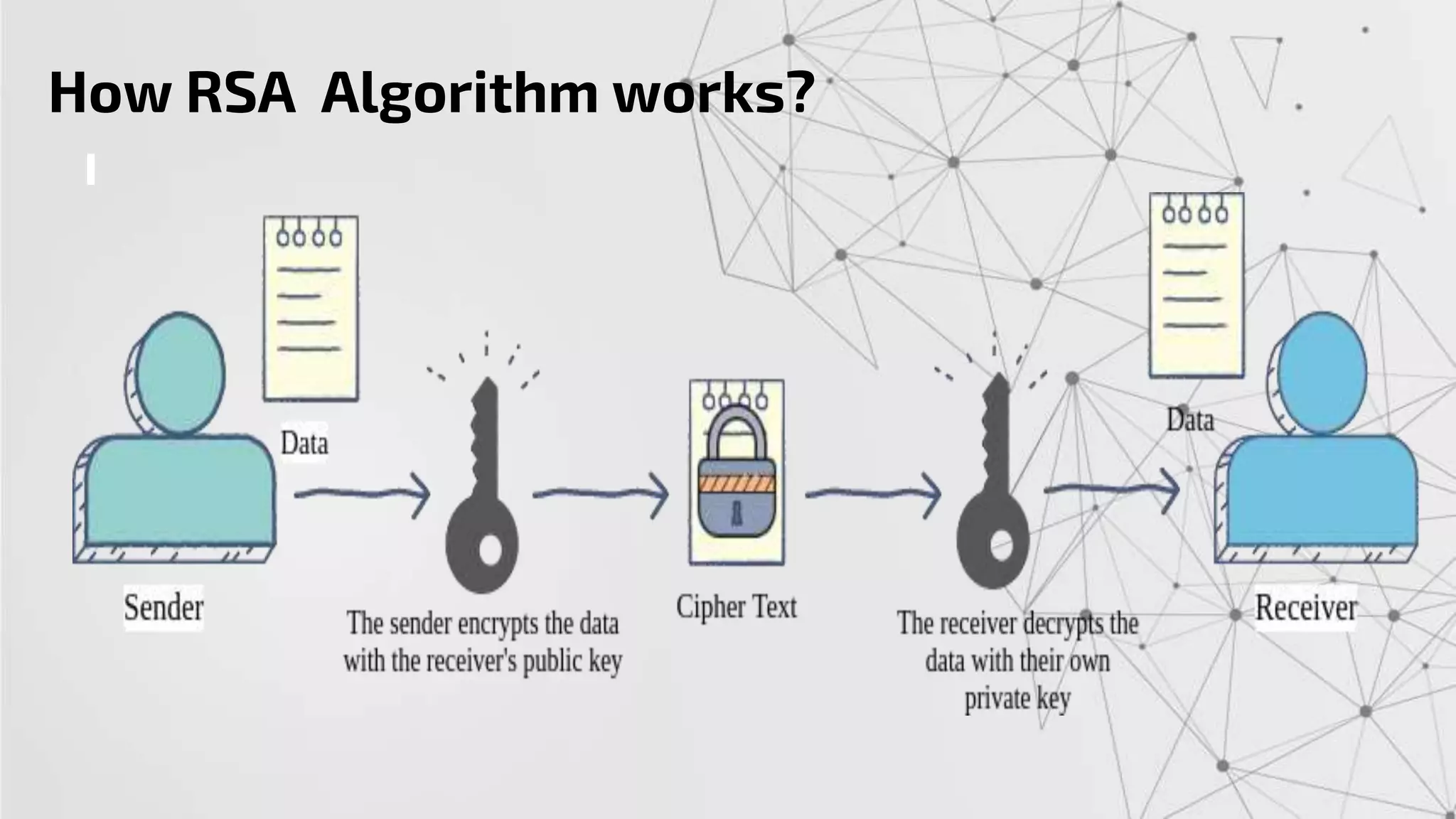
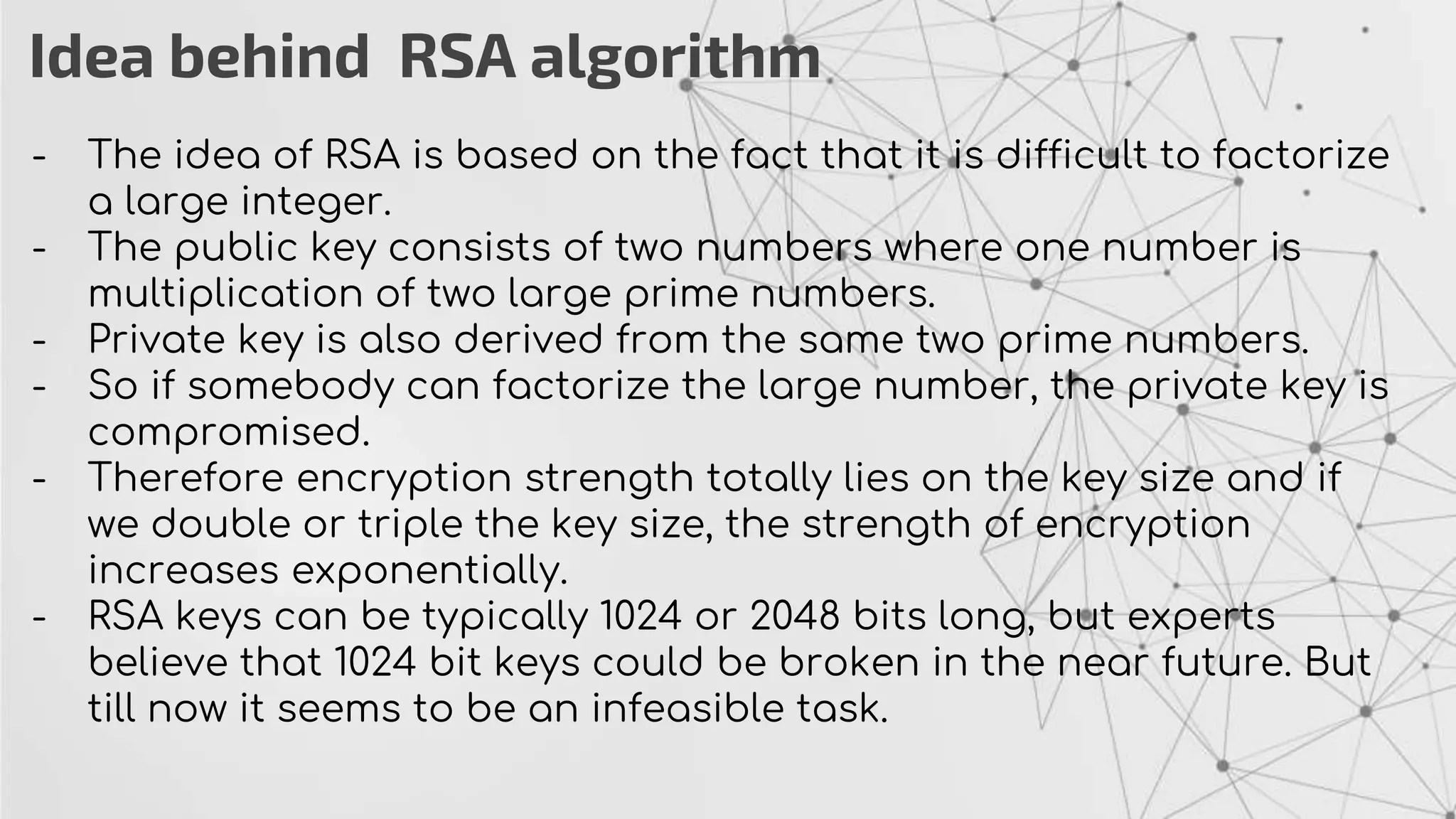
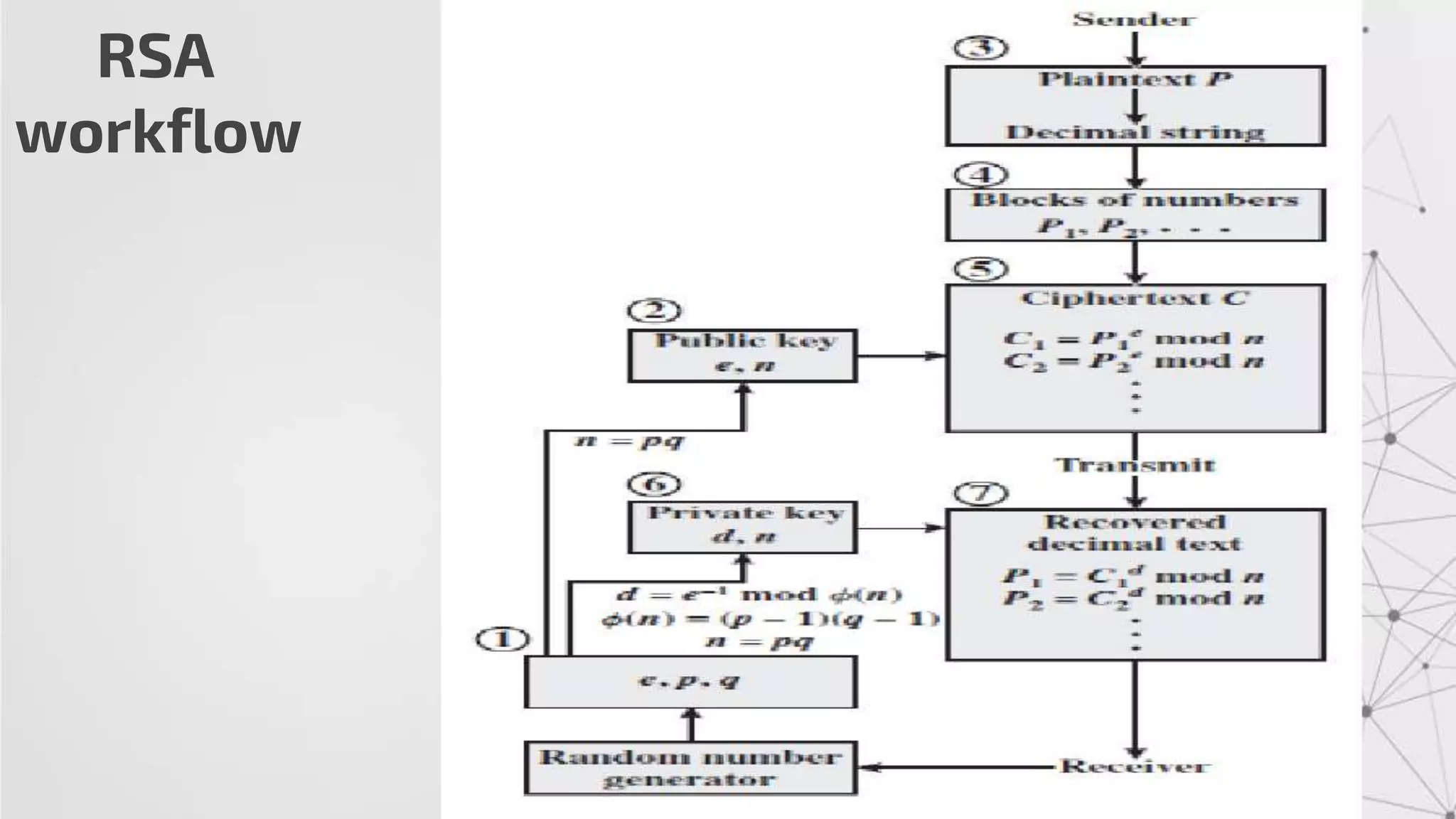
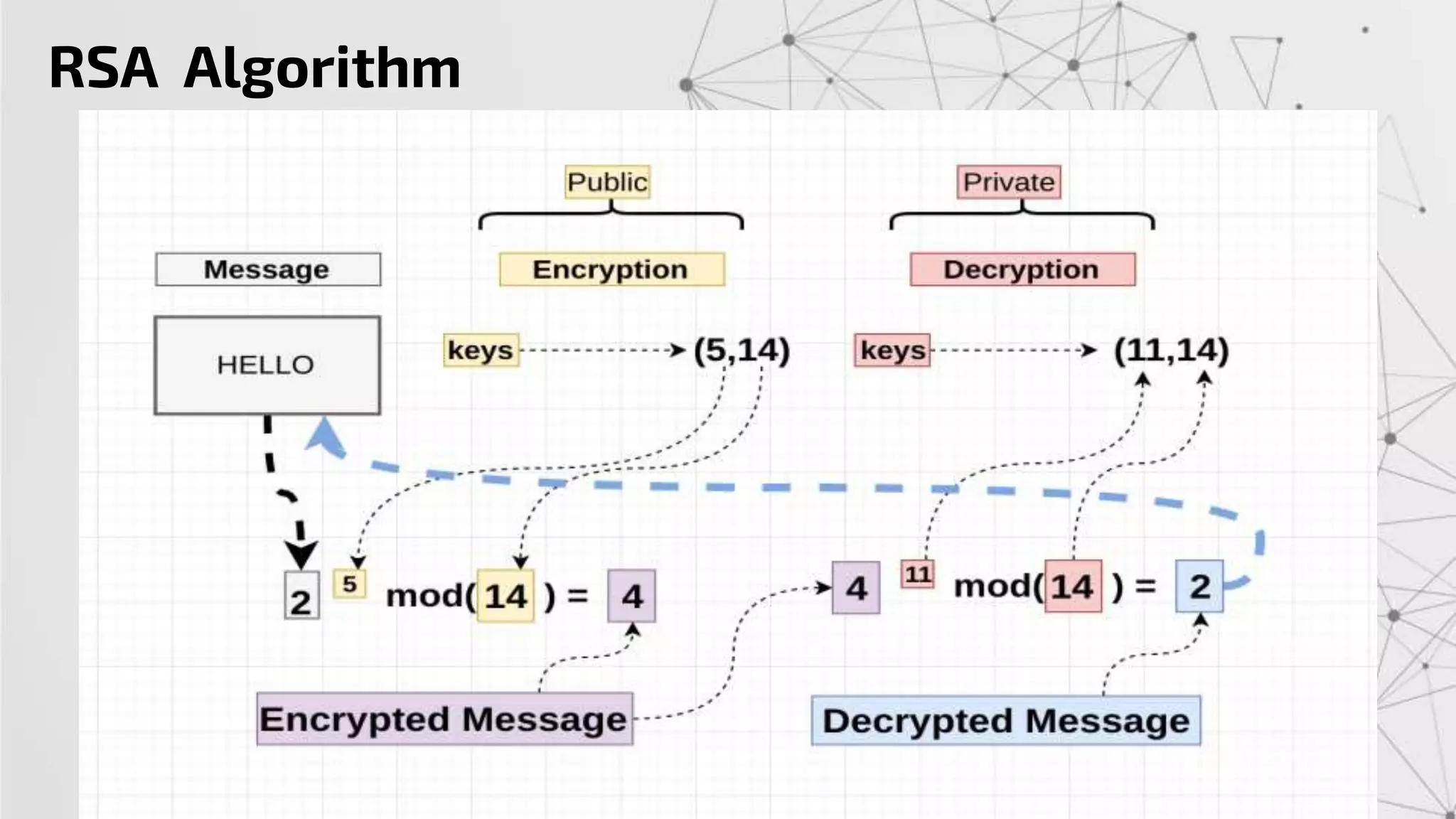
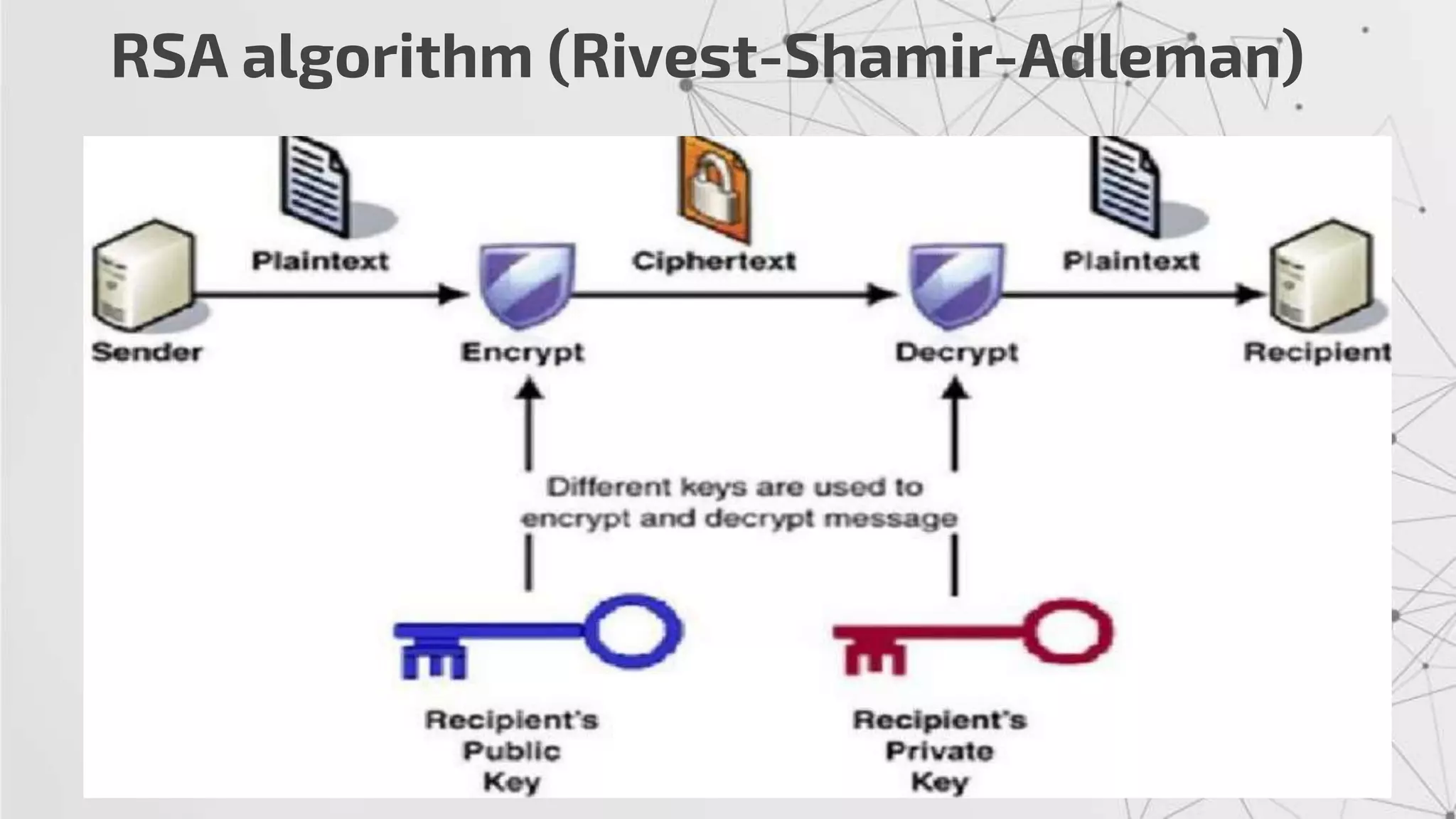
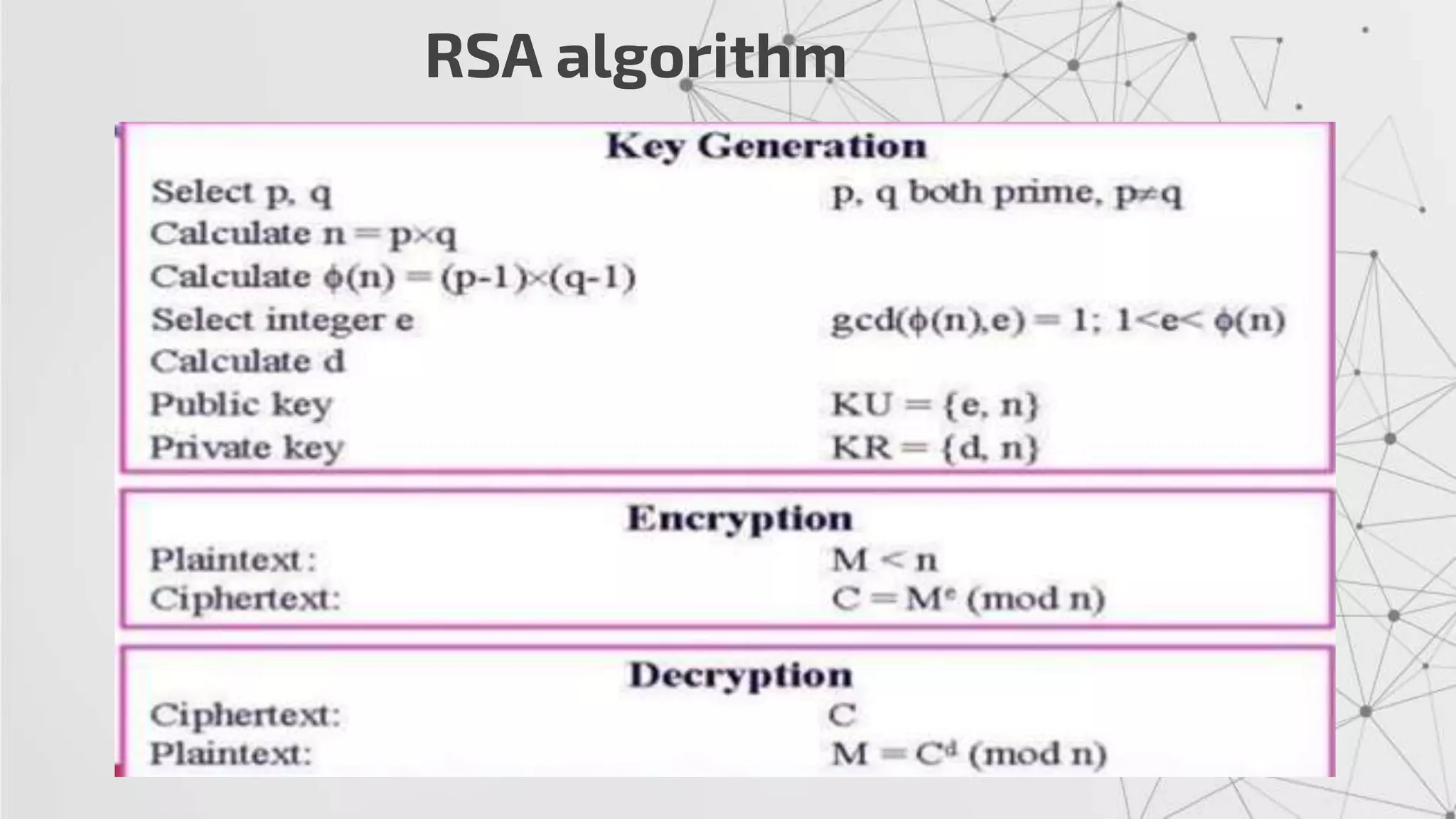
The RSA algorithm is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm used for public-key encryption and digital signatures. It uses two different keys - a public key can be shared publicly, and a private key must be kept secret. The security of RSA is based on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. RSA allows a client to securely send encrypted data to a server, which can only be decrypted by someone with the corresponding private key.