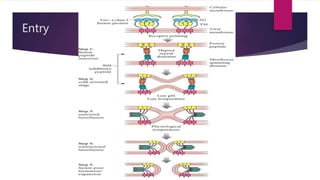
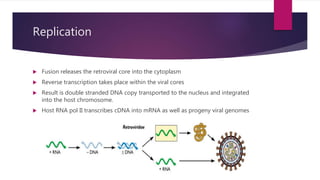
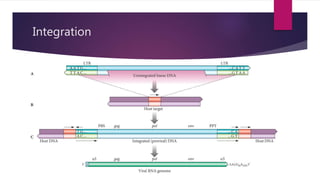
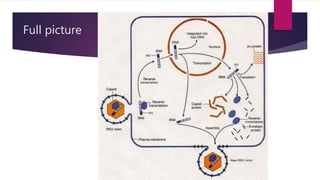
Bob Rooster noticed some of his chickens were sick and tumors were found upon autopsy of one chicken. Testing identified the infection as the Rous Sarcoma Virus (RSV), the first oncovirus discovered. RSV is an enveloped retrovirus that contains gag, pol, env, and src genes. The src gene encodes a tyrosine kinase that causes the virus to be oncogenic. Currently there is no effective treatment for RSV, but research into nucleotides may reduce virus yield and knock out the oncogenic gene.