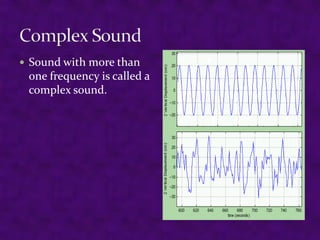
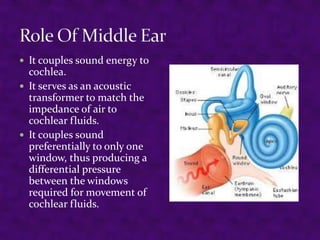
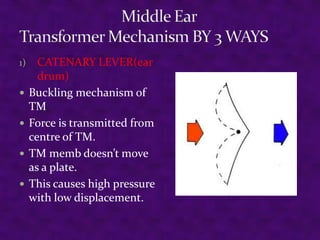
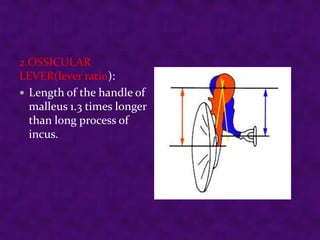
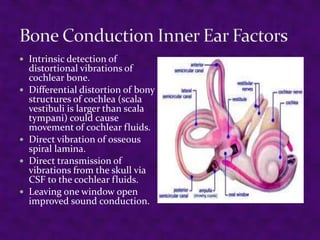
Sound is a form of energy produced by vibrating objects that travel in waves. A sound wave consists of alternating compressions and rarefactions of the medium molecules. The document discusses the properties of sound waves including frequency, wavelength, intensity, and pitch. It describes how the outer, middle, and inner ear work together to detect sound and transmit it to the cochlea. The cochlea contains three fluid-filled canals and uses the traveling wave principle to analyze complex sounds into their frequency components.