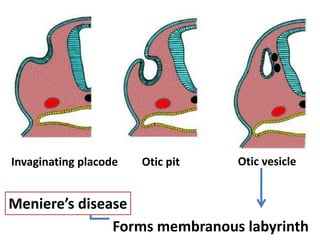
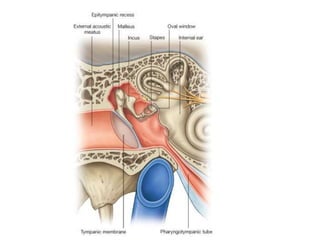
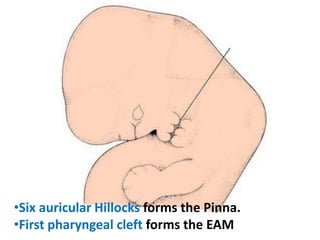
The document discusses the development of the ear, including the external, middle, and internal ear structures. It describes how the otic placode invaginates to form the otic vesicle, which then develops into the membranous labyrinth. The ventral part forms the saccule and cochlear duct, while the dorsal part forms the semicircular ducts and utricle. The first pharyngeal pouch develops into the middle ear cavity and auditory tube, while the first pharyngeal cleft forms the external acoustic meatus. Various congenital deformities of the external ear are also mentioned.