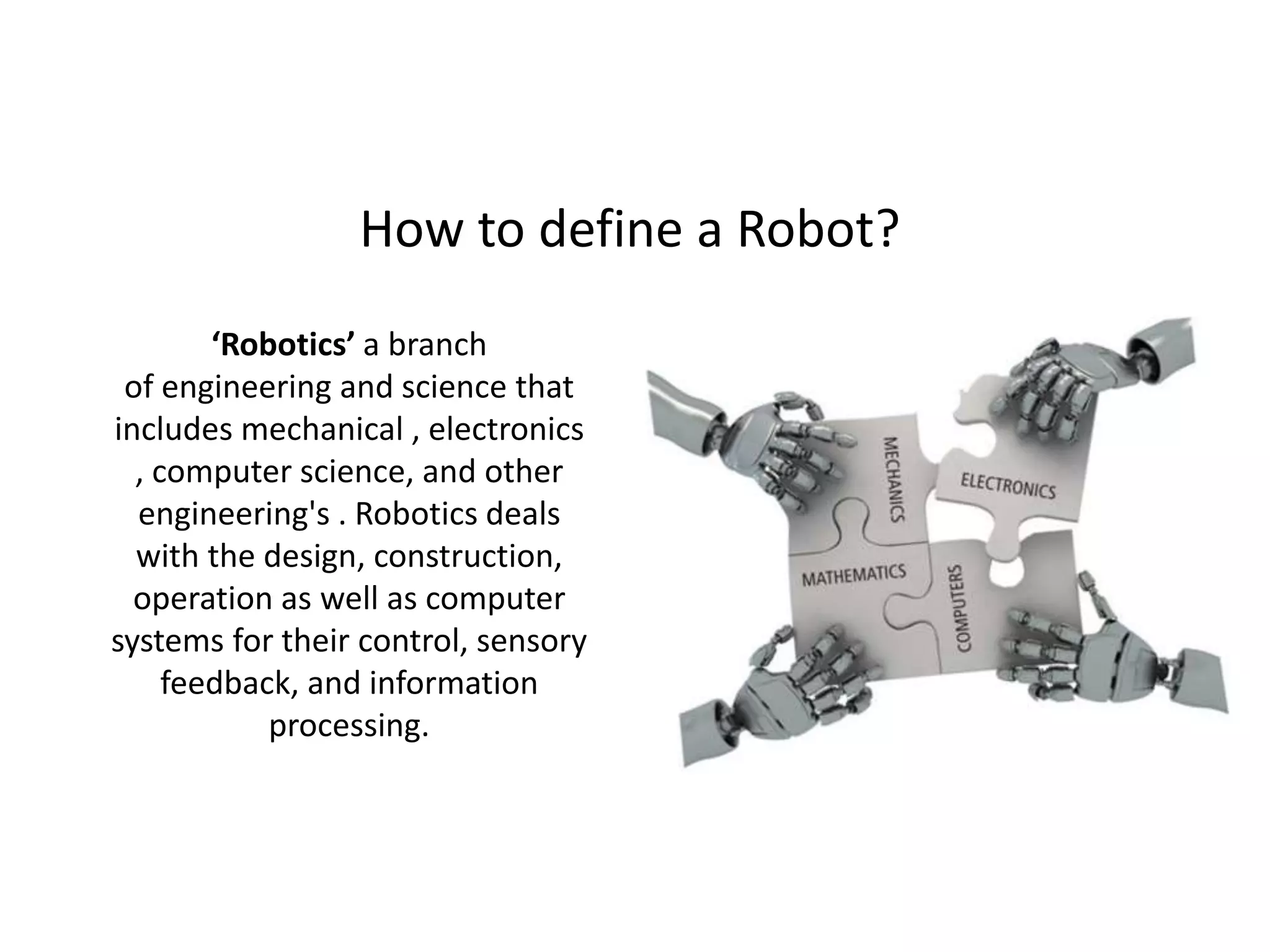
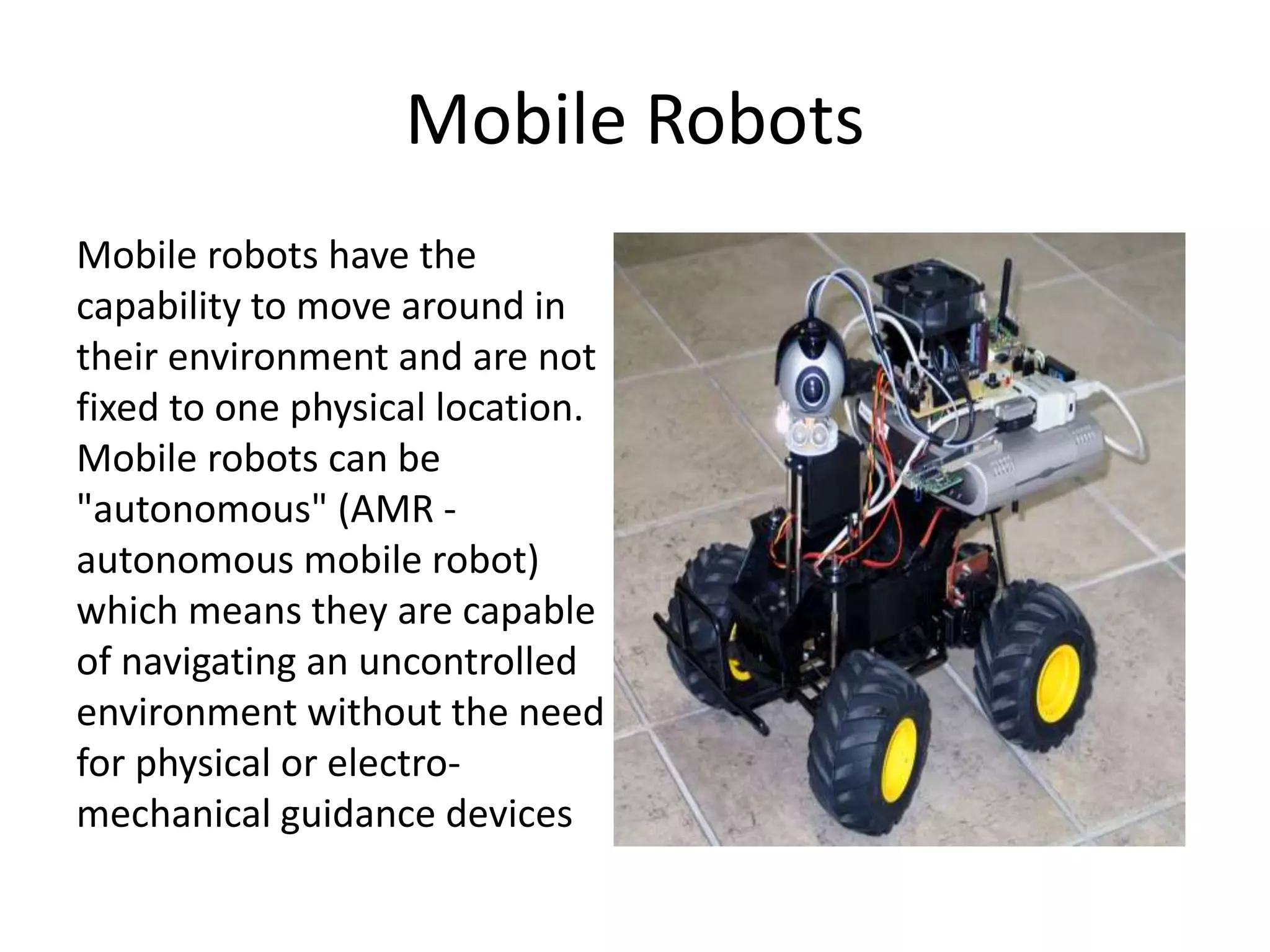
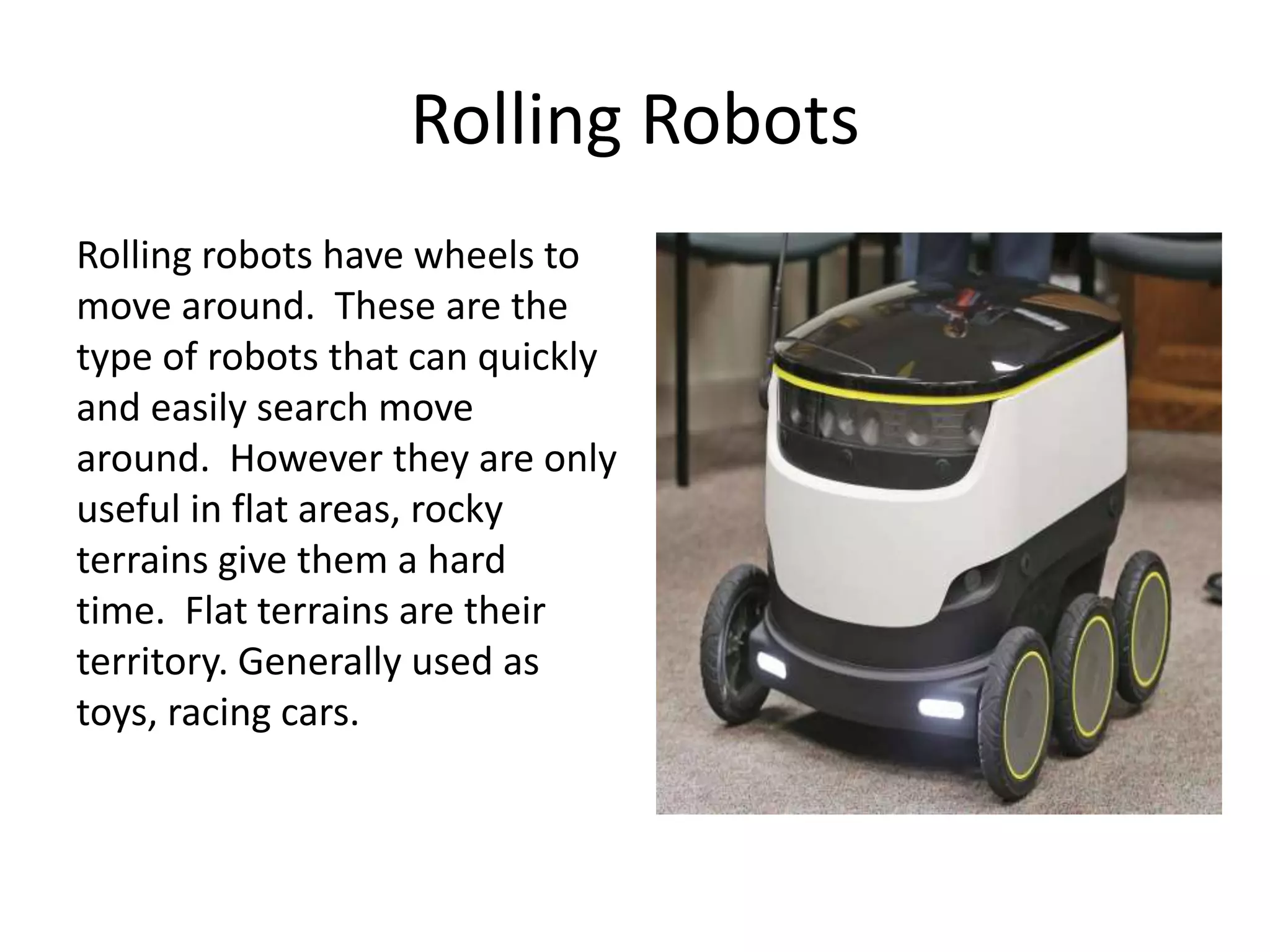
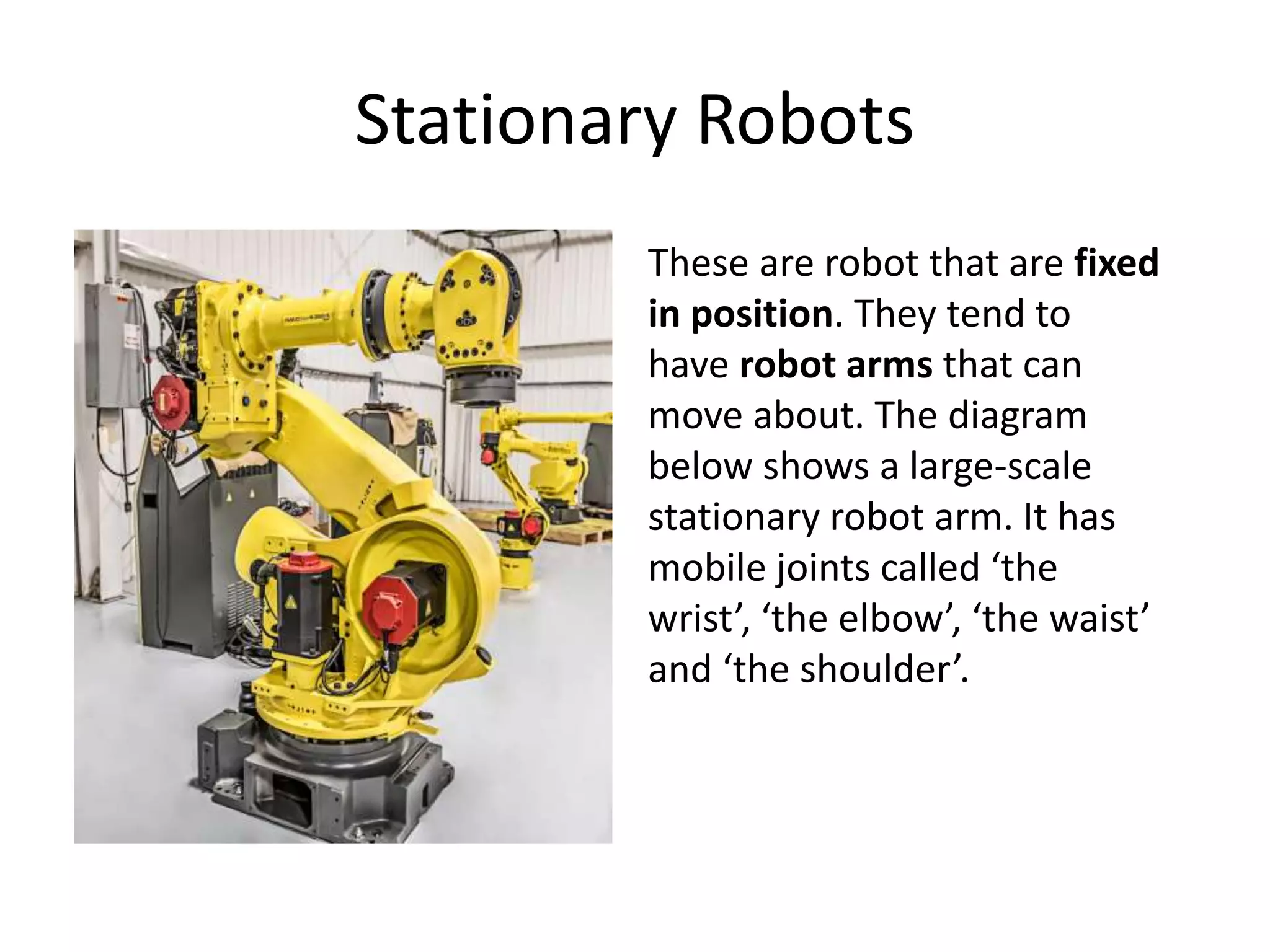
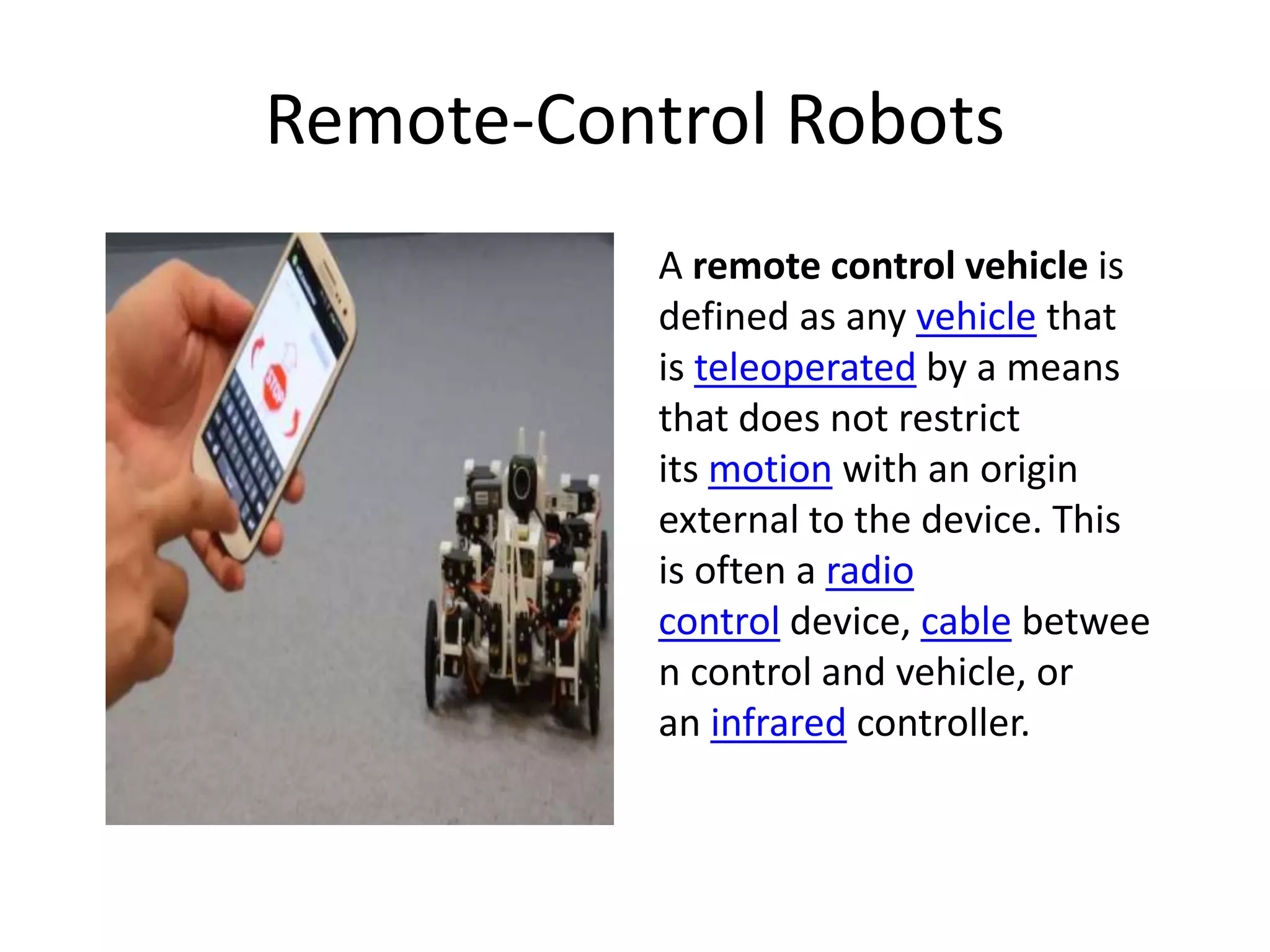
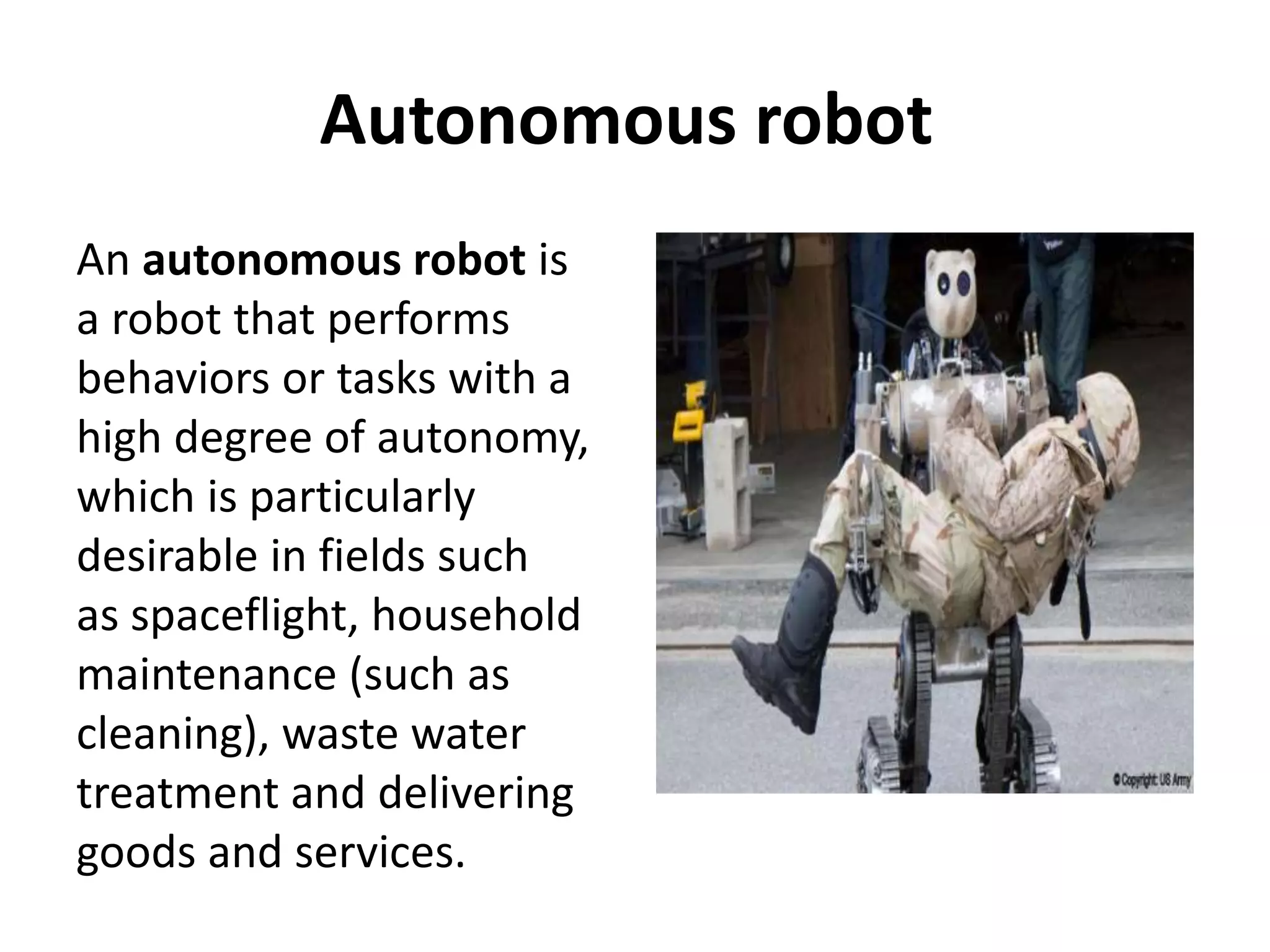
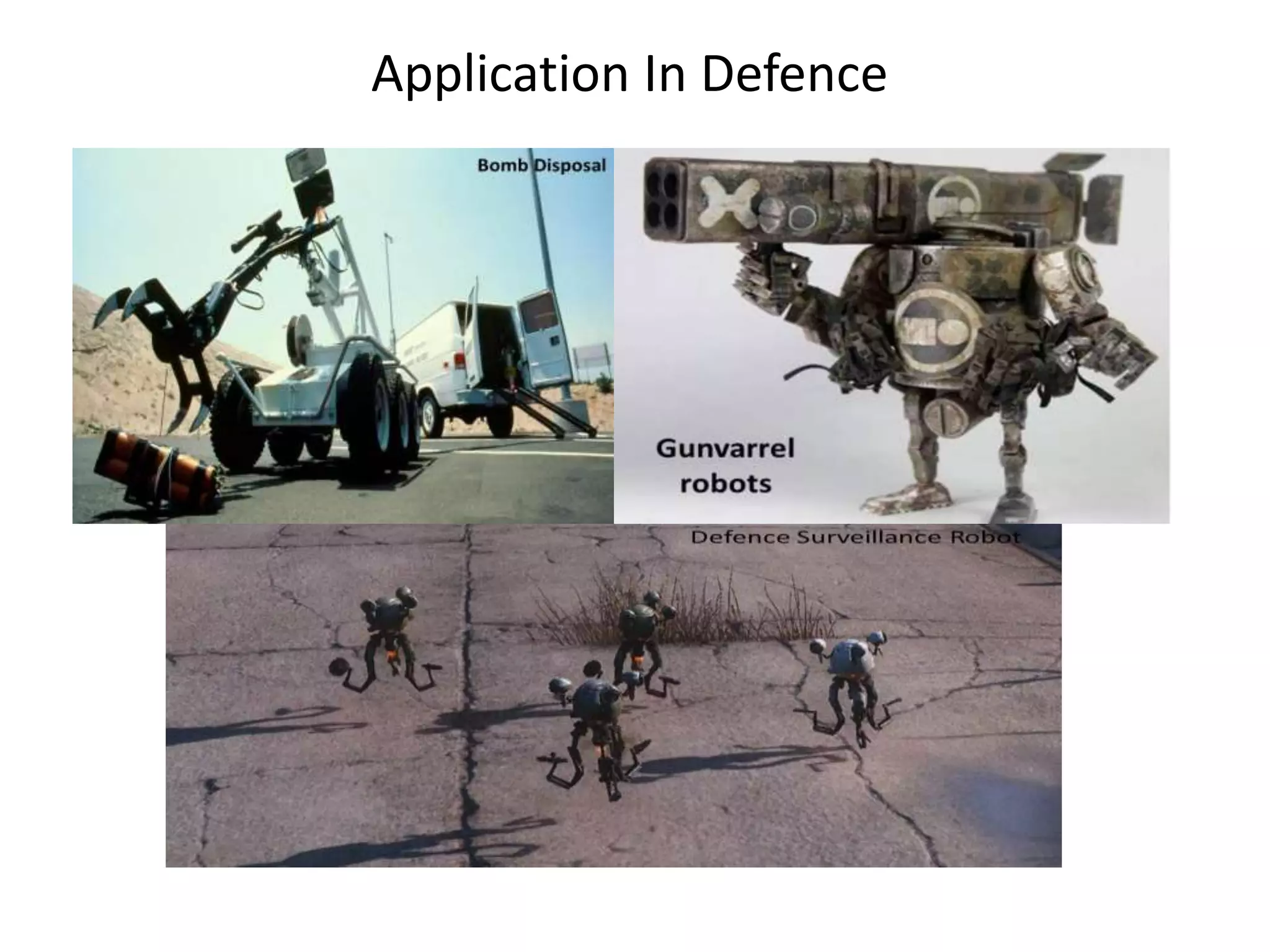
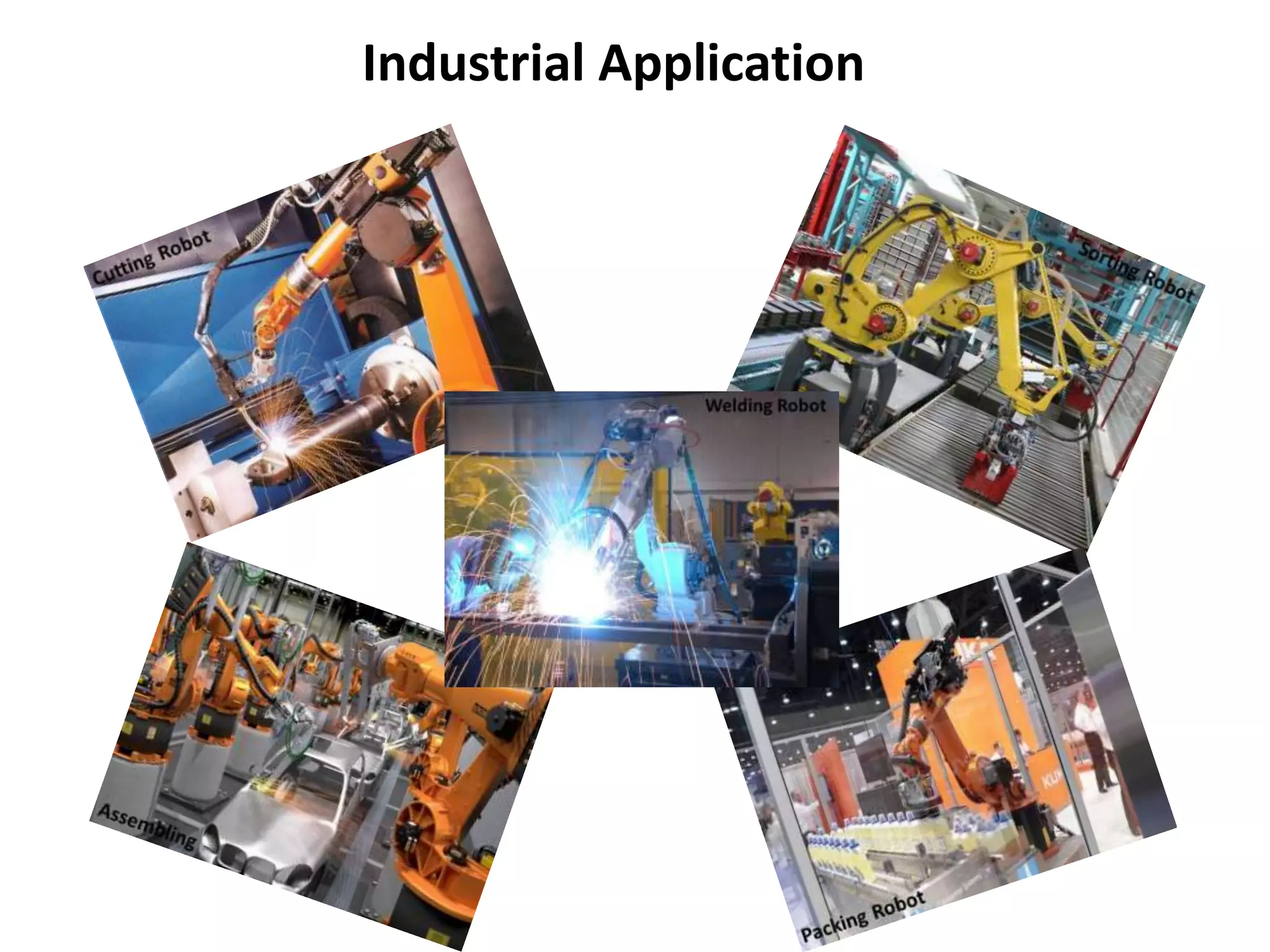
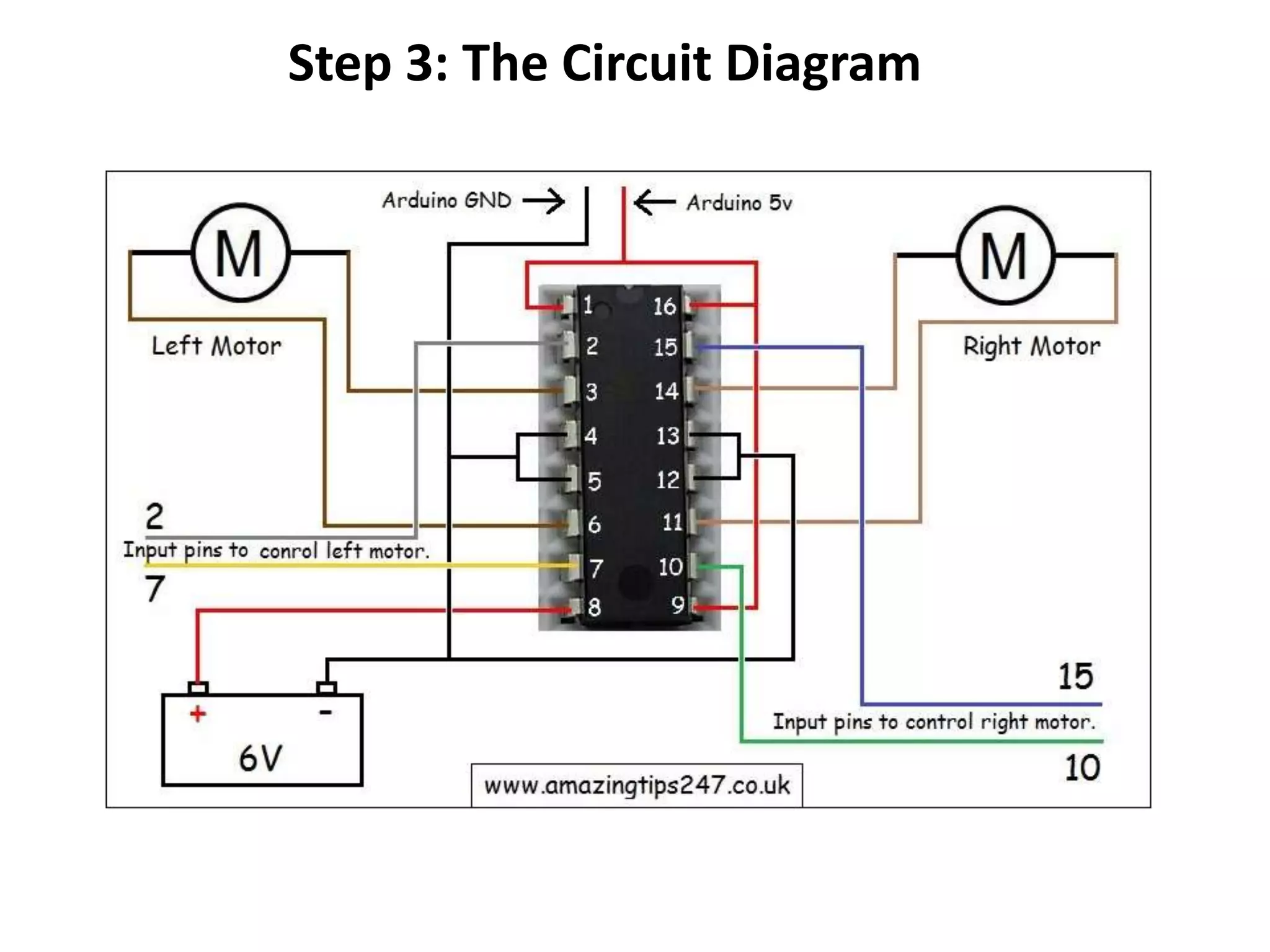
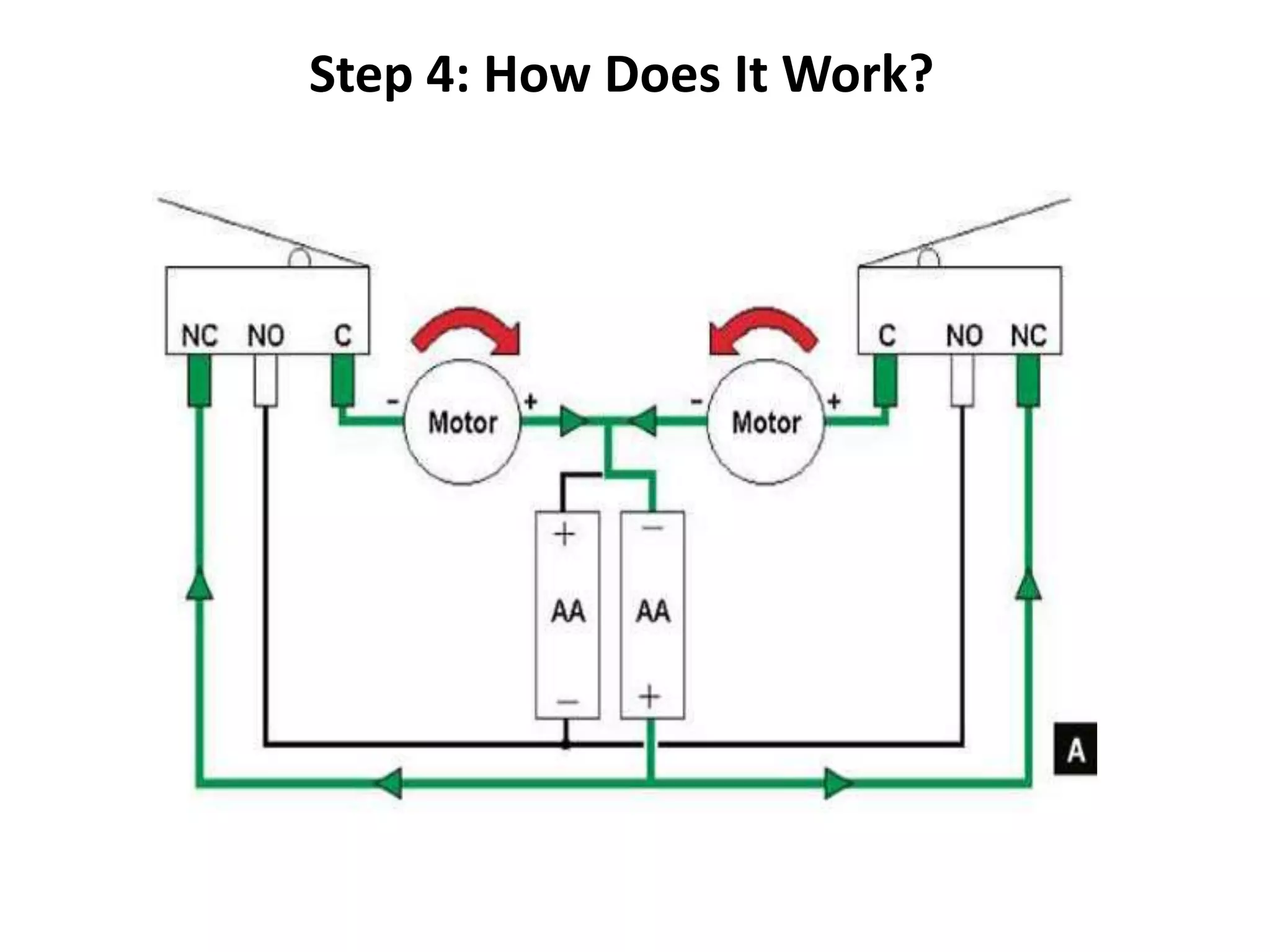
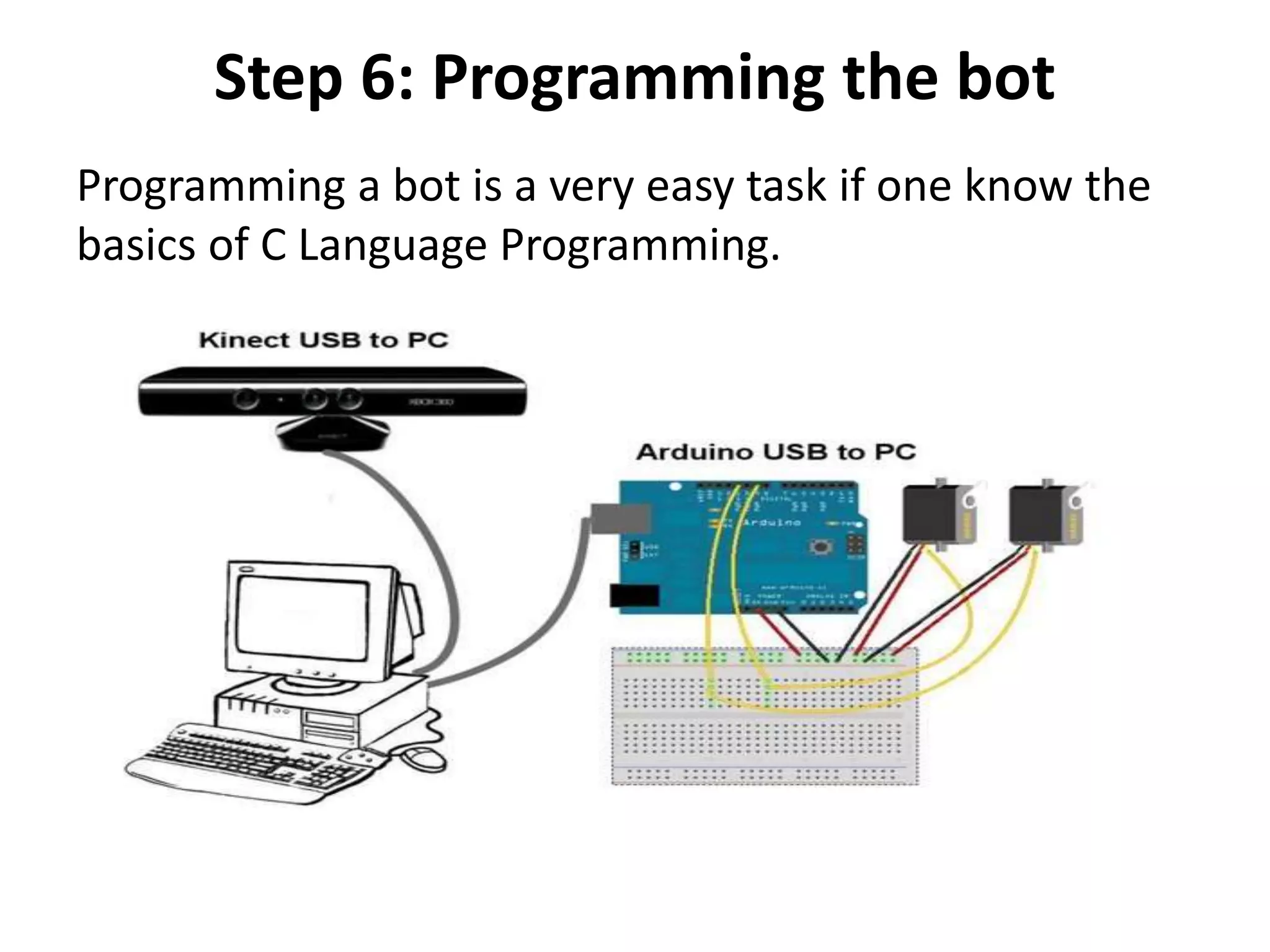
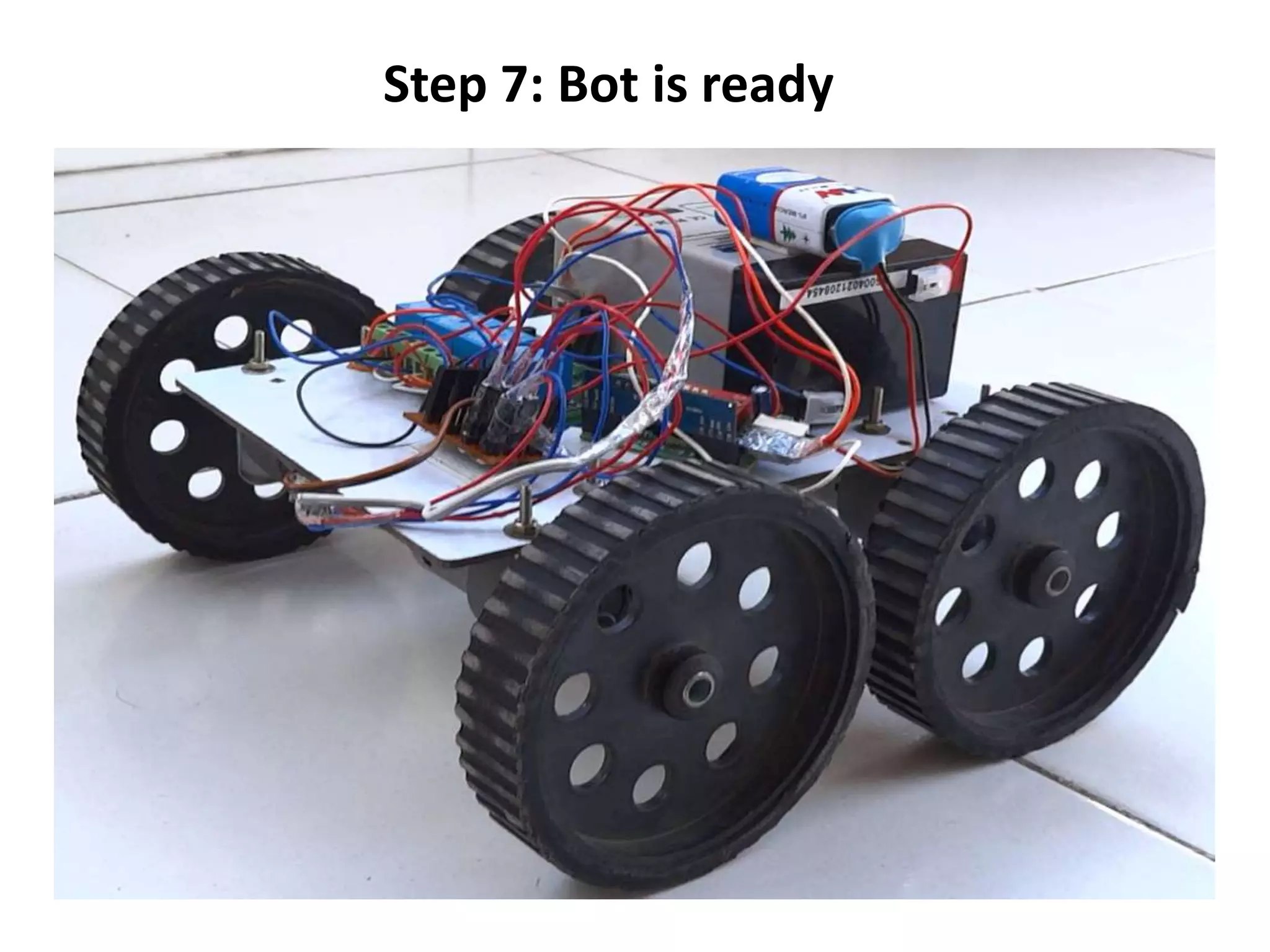
Robotics is a field that involves the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. It draws from many disciplines including engineering, computer science, and other fields. There are several types of robots including mobile, stationary, walking, rolling, autonomous, remote-controlled, and line-following robots. Robots have various applications in fields like defense, medical, and industry. Building a robot involves obtaining materials and tools, designing circuits and programming, and assembling and wiring the components. The future of robotics includes making robots that more closely resemble humans in appearance and movement.