roduction to Robotics – A Strategic Overview
Robotics has captured widespread global interest, driven by its immense potential to reshape industries, economies, and daily life. In popular imagination, robots are often anthropomorphic machines—machines that look and behave like humans. However, in technical reality, a robot is defined more precisely: it is a man-made mechanical device capable of autonomous movement, with motions that must be mathematically modeled, planned, sensed, actuated, and controlled. The robot’s behavior is programmable, allowing external influence over its operations and expanding its adaptability across numerous environments.
Historical Context and Technological Evolution
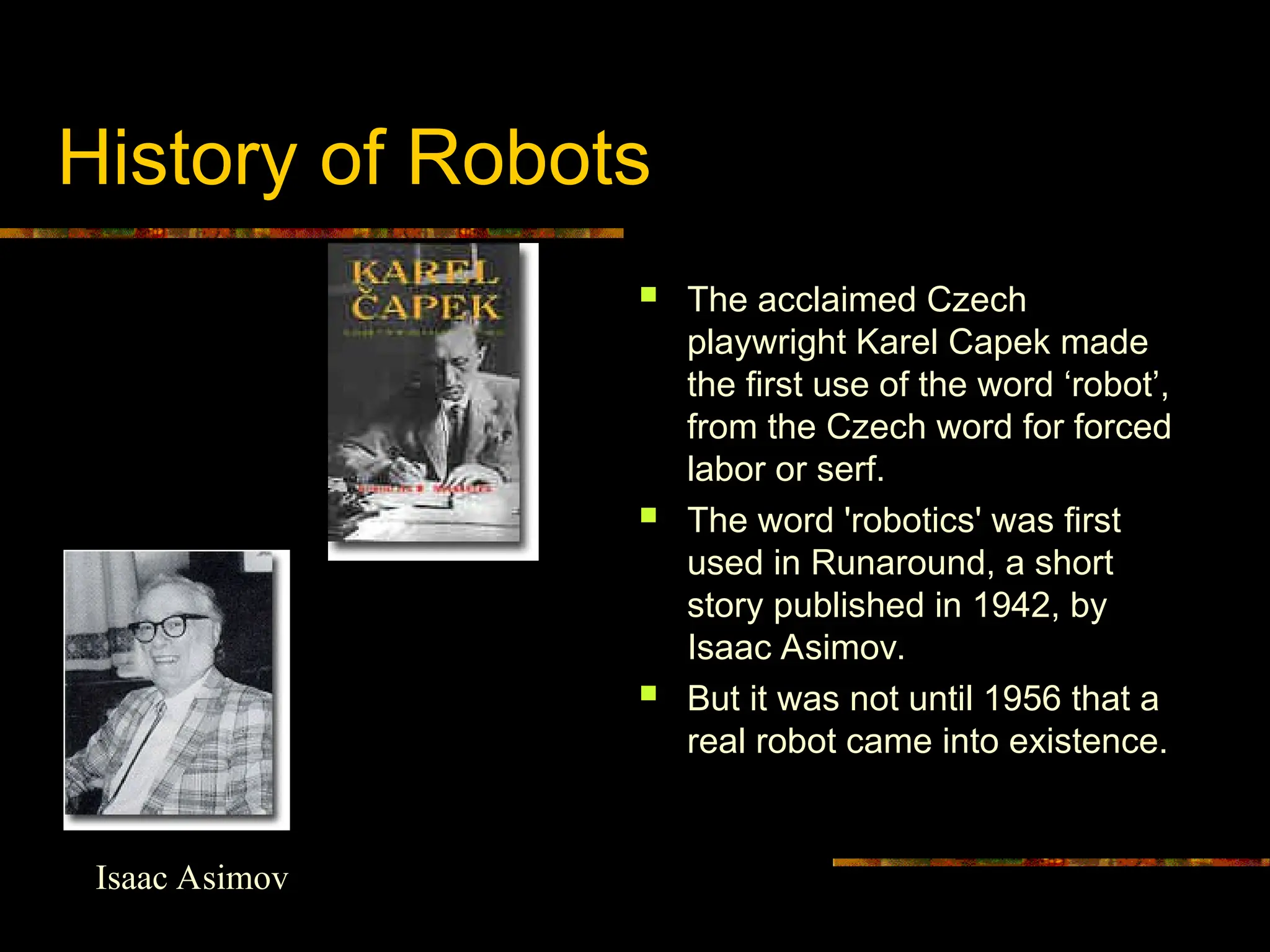
The term "robot" first emerged in 1920, introduced by Czech playwright Karel Čapek, derived from the word "robota," meaning forced labor or drudgery. Subsequently, the term "robotics" was coined by Isaac Asimov in his 1942 short story Runaround, where he also articulated his famous "Three Laws of Robotics." These early conceptualizations laid the philosophical groundwork for the field, but practical, physical robots only materialized much later.
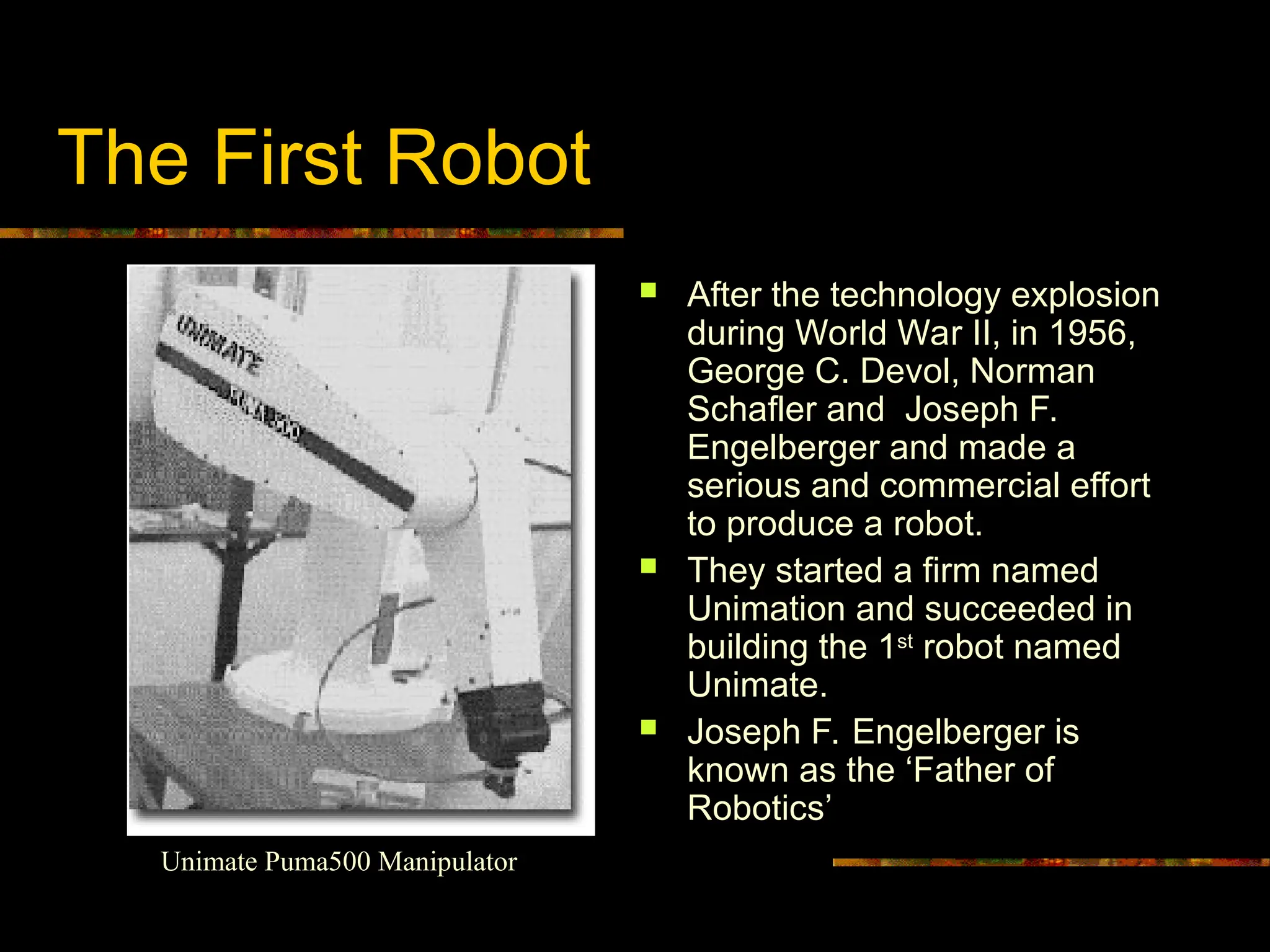
The first true robot was realized in 1956 when George C. Devol, Norman Schafler, and Joseph F. Engelberger launched Unimation, producing the groundbreaking Unimate robot. Engelberger, later dubbed the "Father of Robotics," was instrumental in translating theoretical robotics into a commercial reality. Unimate initially served General Motors, tasked with extracting die-castings and performing spot welding—physically demanding, repetitive, and hazardous jobs previously shouldered by human workers. The commercial success of Unimate catalyzed a revolution, ushering in the era of industrial automation and fundamentally altering labor practices in manufacturing.
Types of Robots – Strategic Classifications
Robotic systems have diversified into several distinct categories, each addressing specific operational challenges:
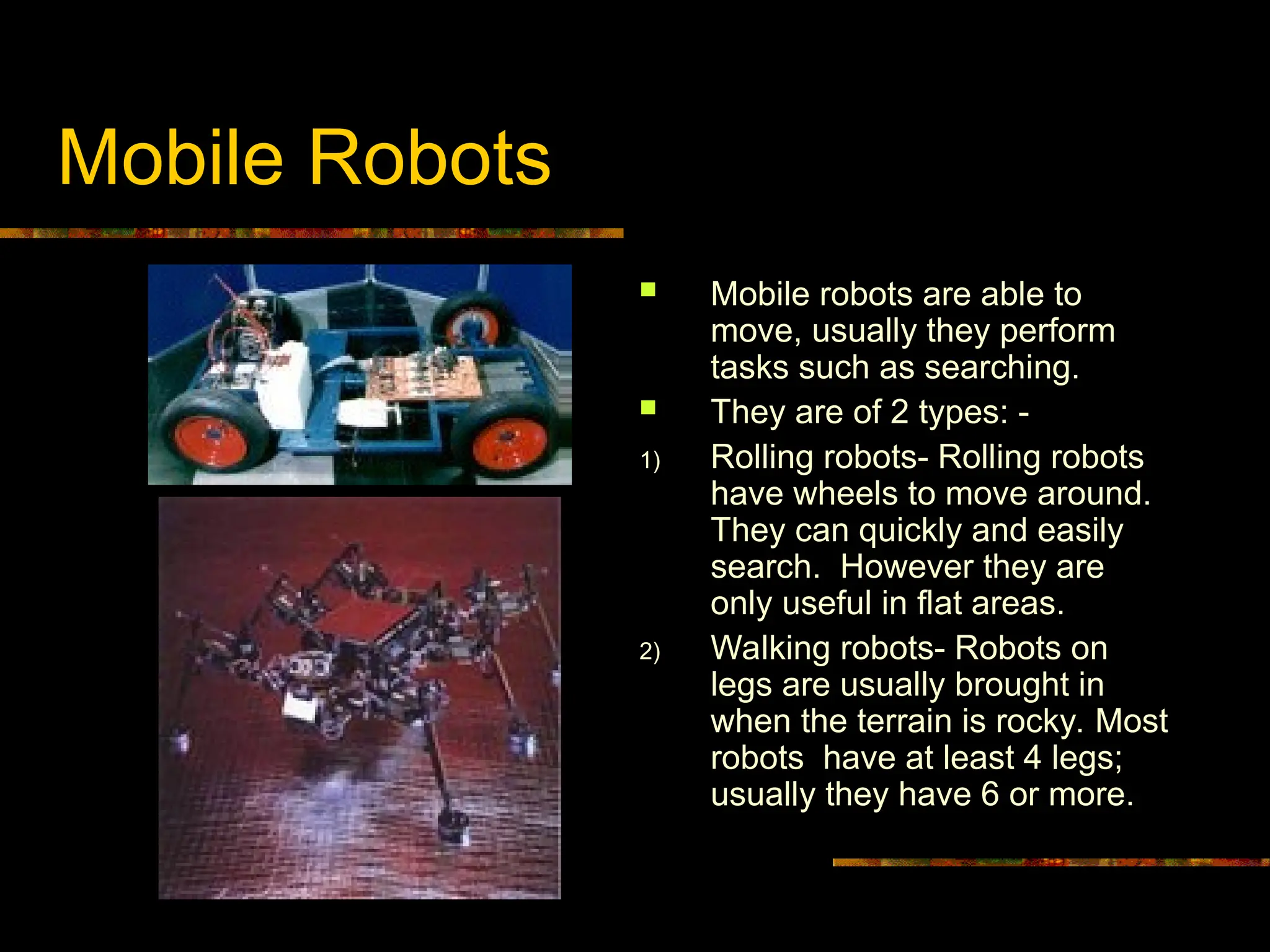
Mobile Robots: Designed for movement, these systems are critical for search and exploration tasks. Subcategories include:
Rolling Robots: Equipped with wheels, optimized for flat surfaces.
Walking Robots: Employ multiple legs (four, six, or more) to navigate rugged terrains, often where wheeled mobility is impractical.
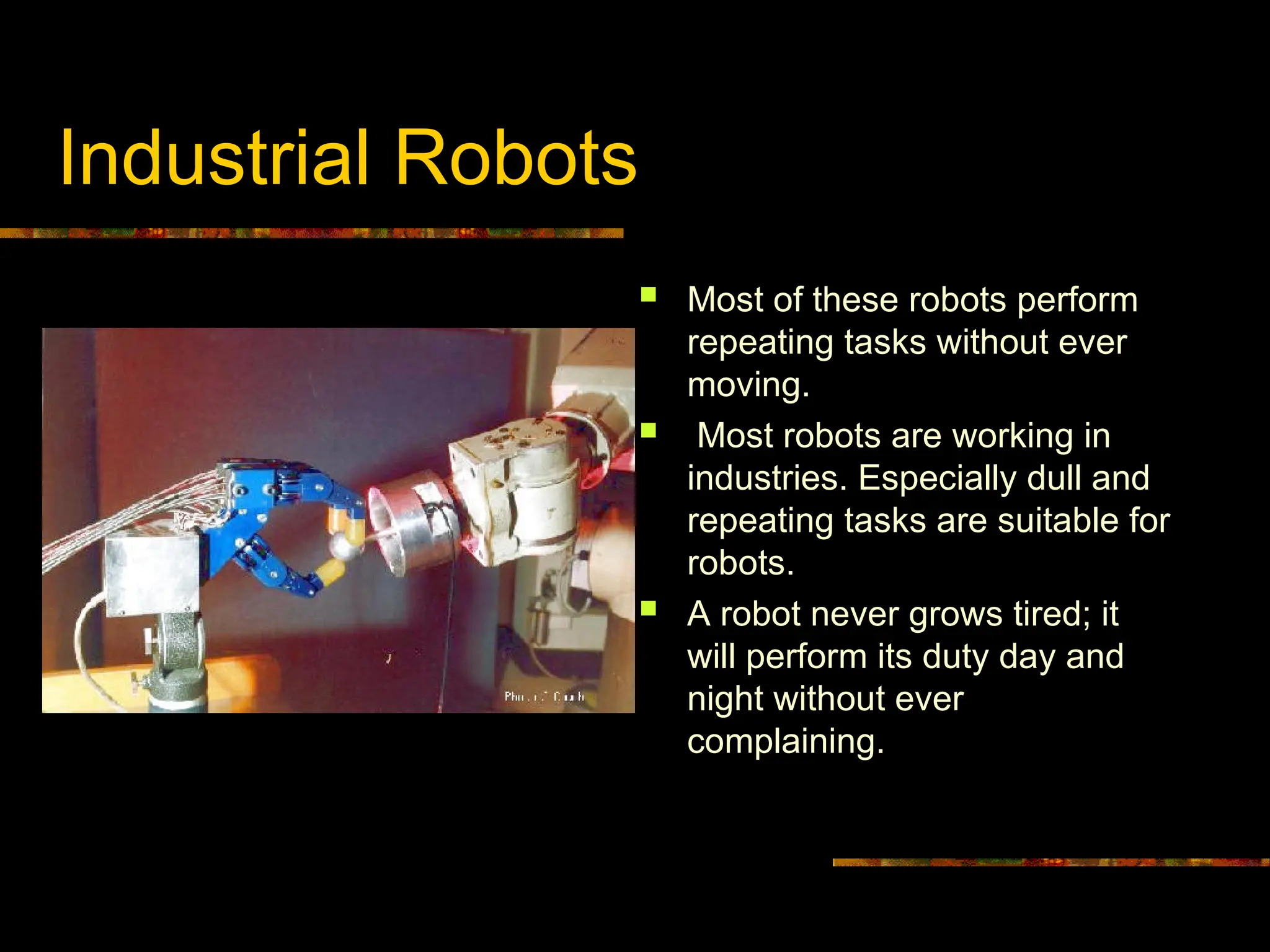
Industrial Robots: Deployed extensively across manufacturing sectors, these stationary robots excel at repetitive, monotonous tasks. Their tireless, error-resistant performance has redefined production paradigms.
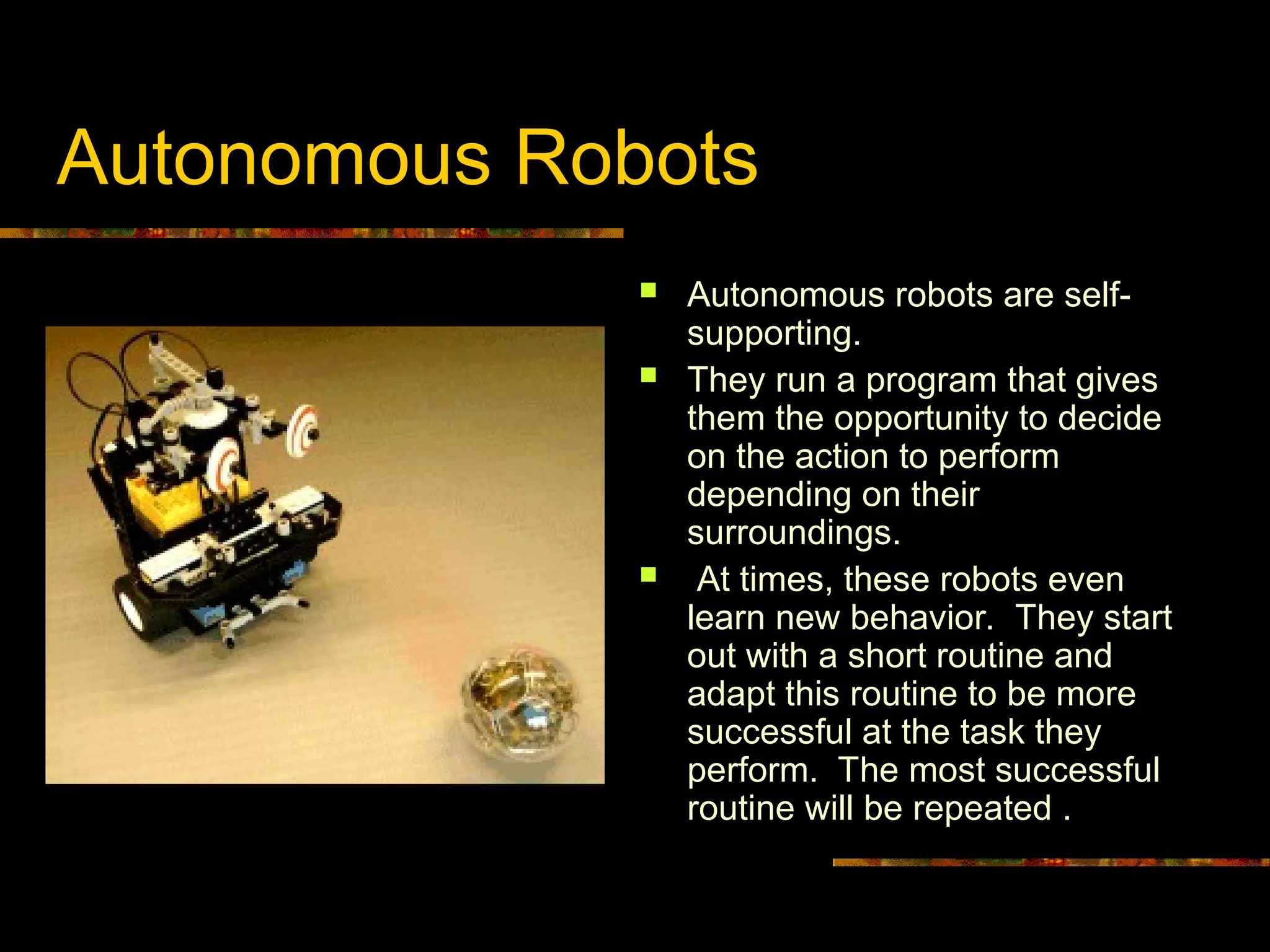
Autonomous Robots: Operating independently, these robots use onboard programming and environmental sensors to adapt and learn. Over time, autonomous systems evolve by refining their operational routines based on experiential success.
Remote-Controlled Robots: Where environmental uncertainty or task complexity exceeds current AI capabilities, human operators guide robots via remote control. This paradigm enables safe intervention in hazardous settings, as demonstrated b