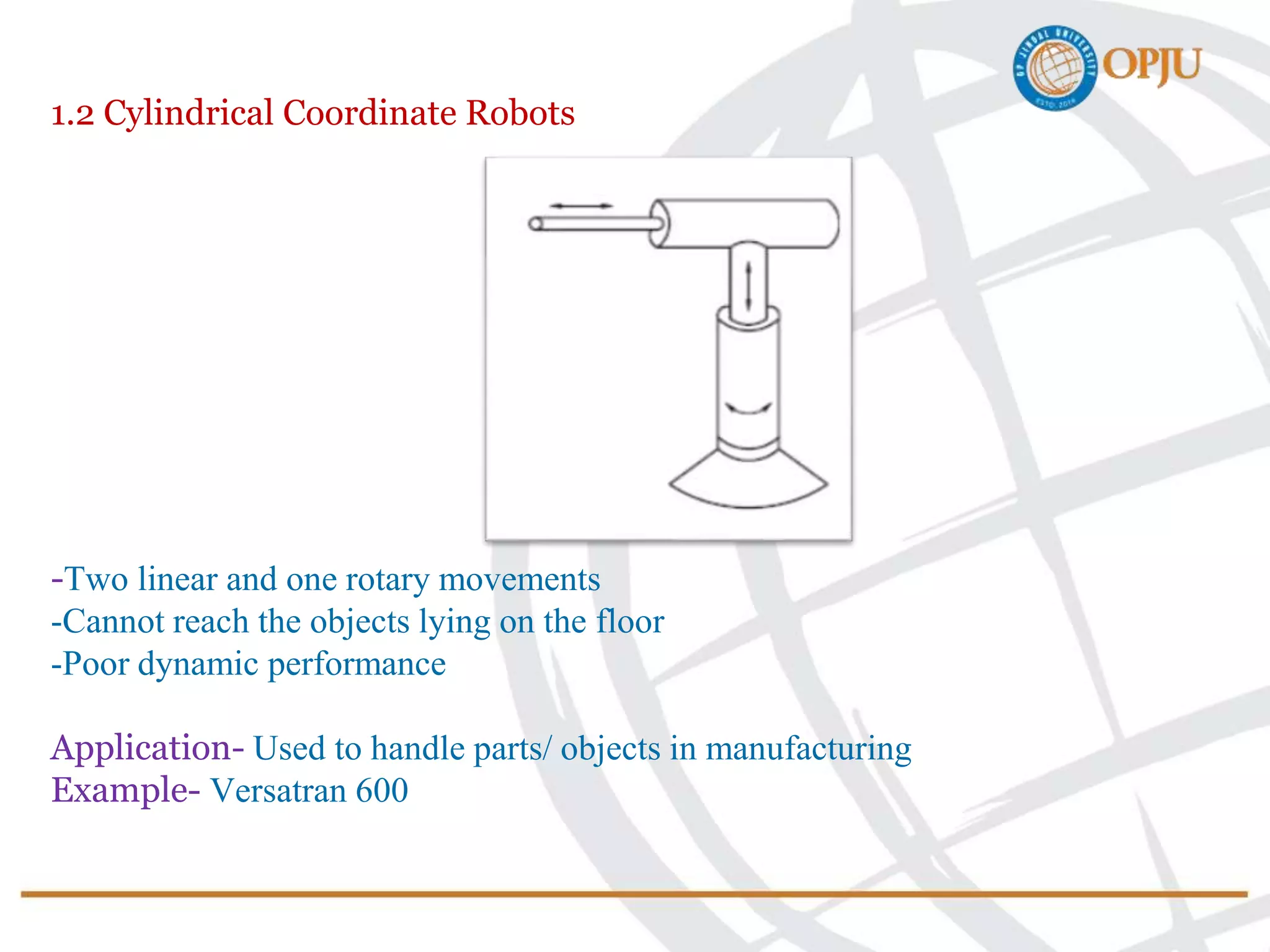
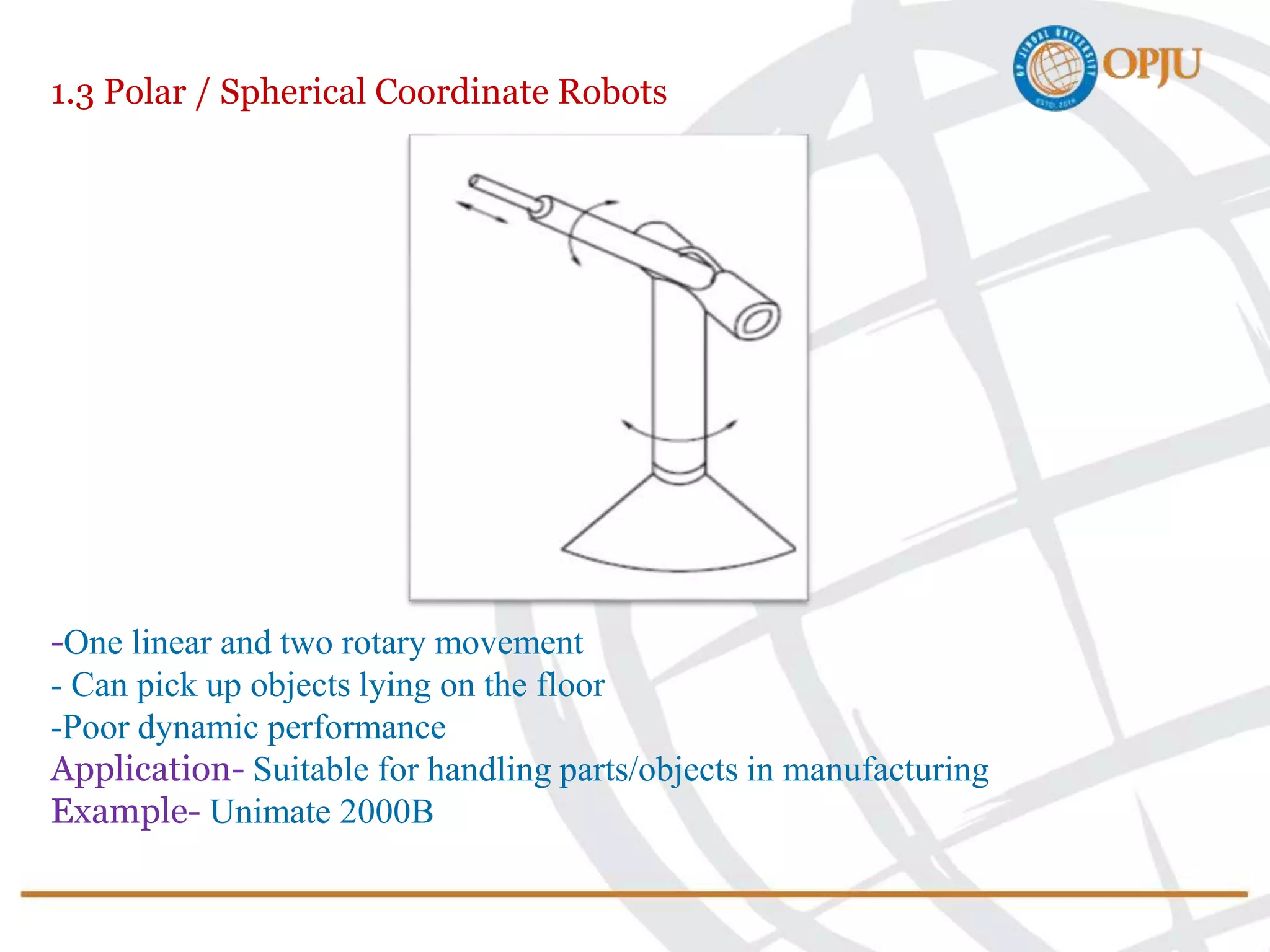
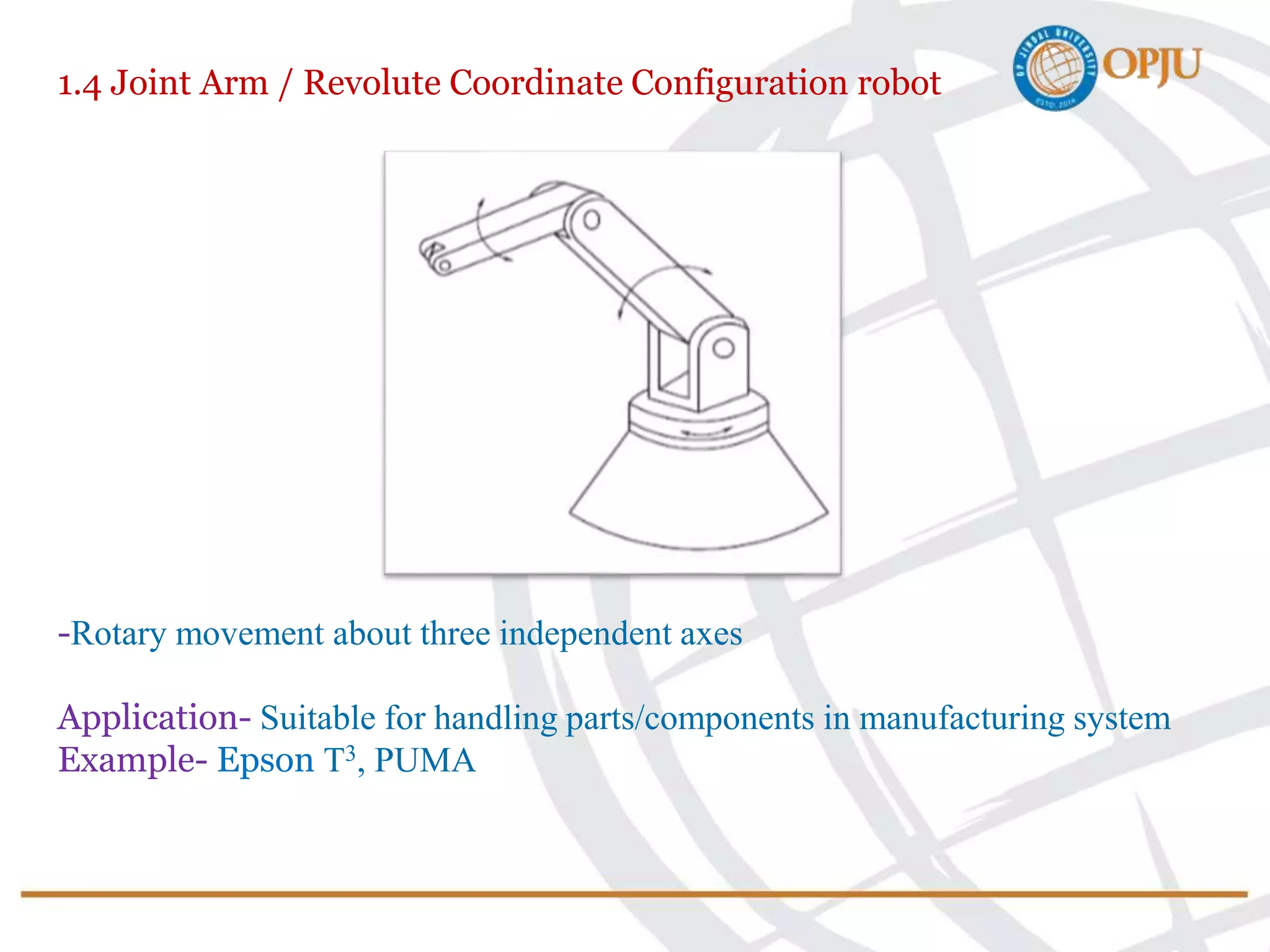
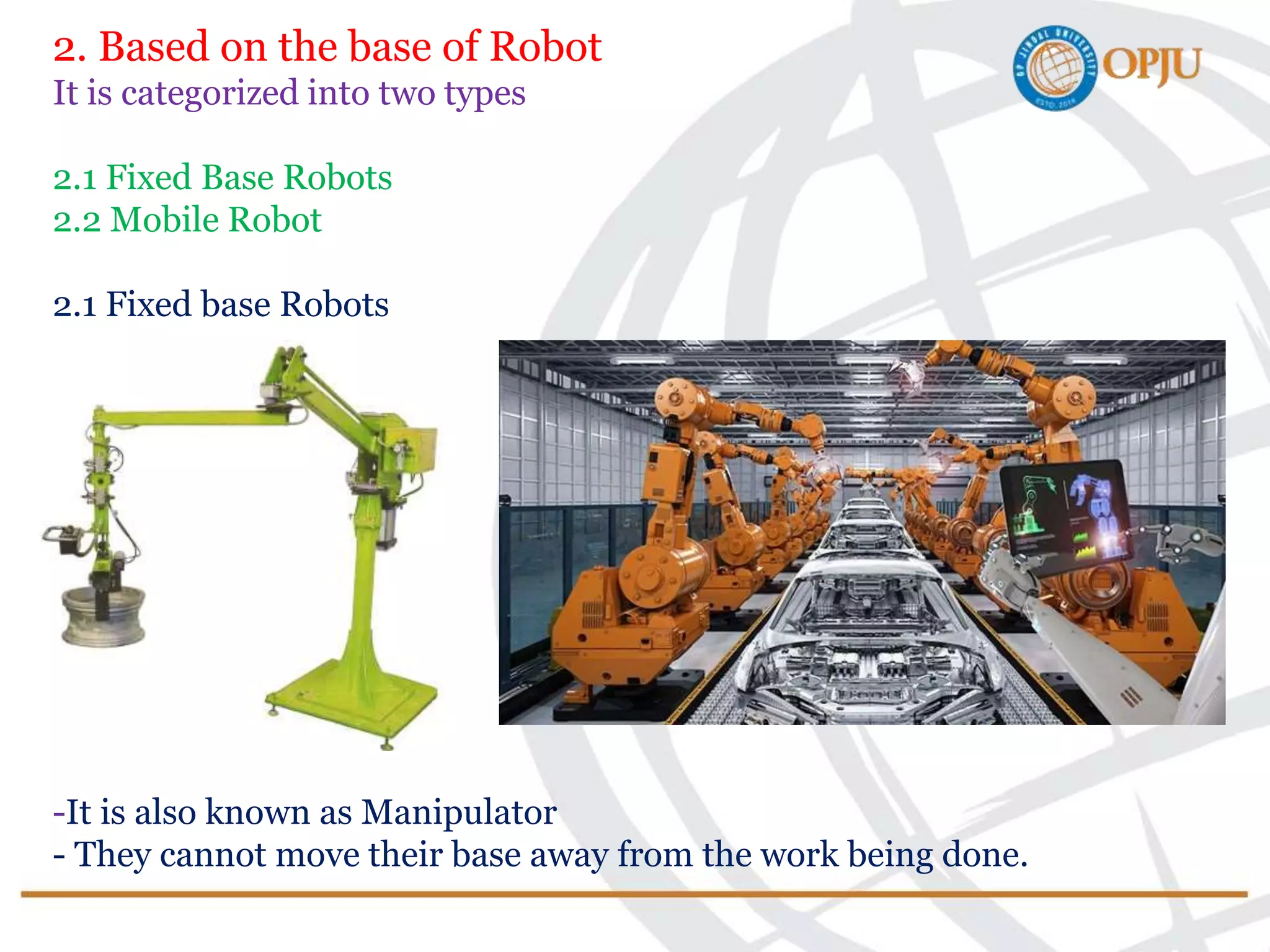
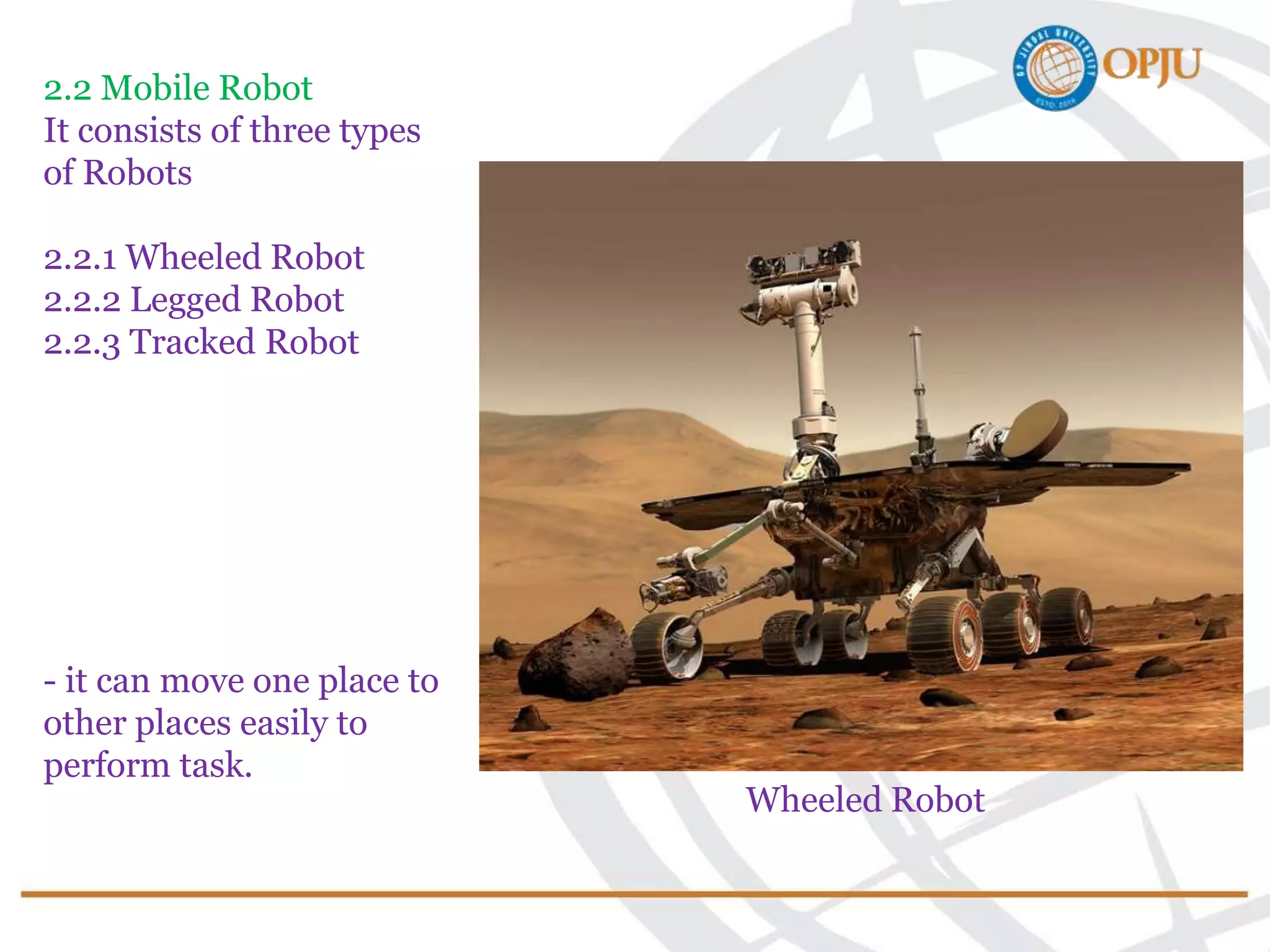
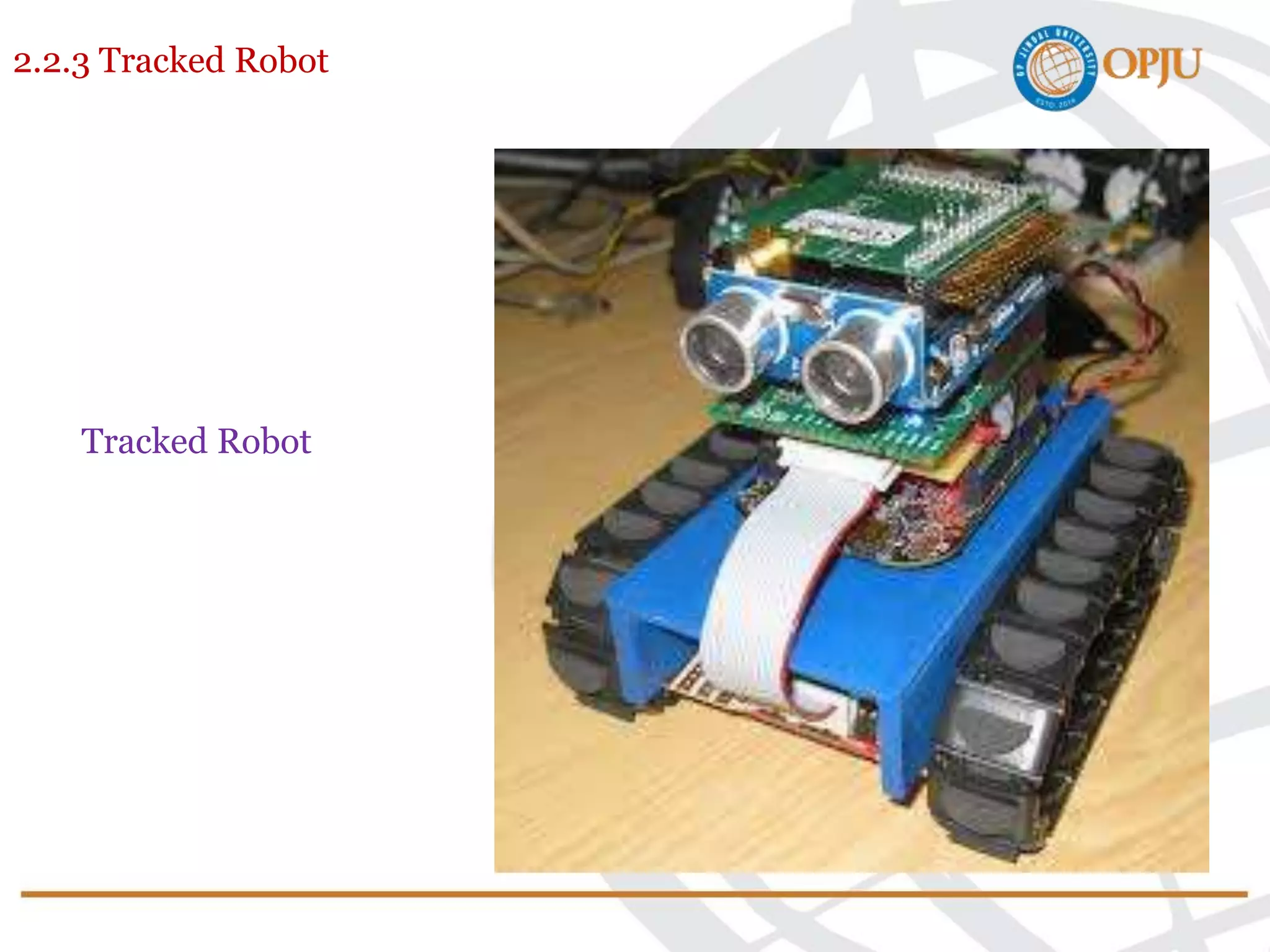
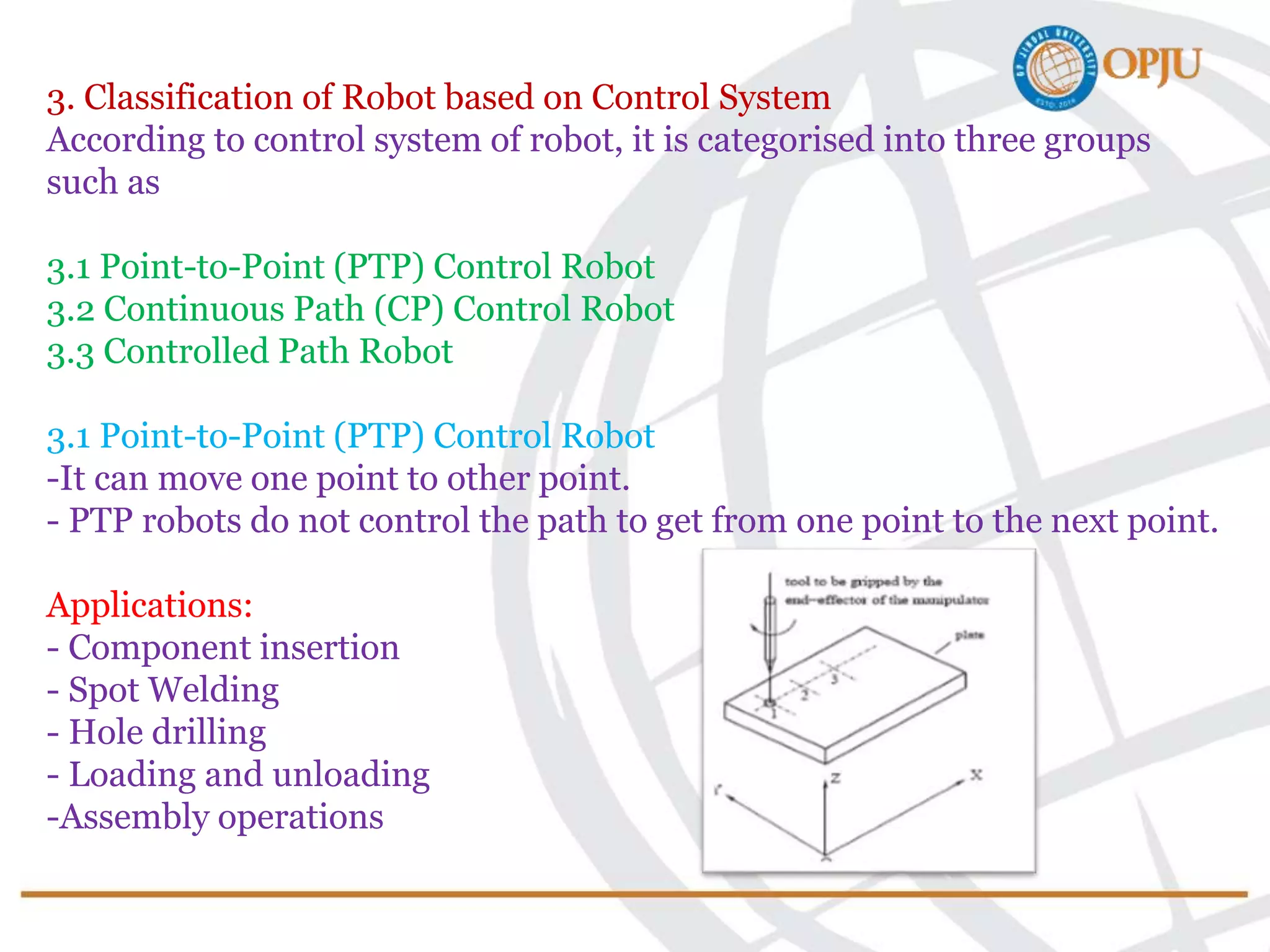
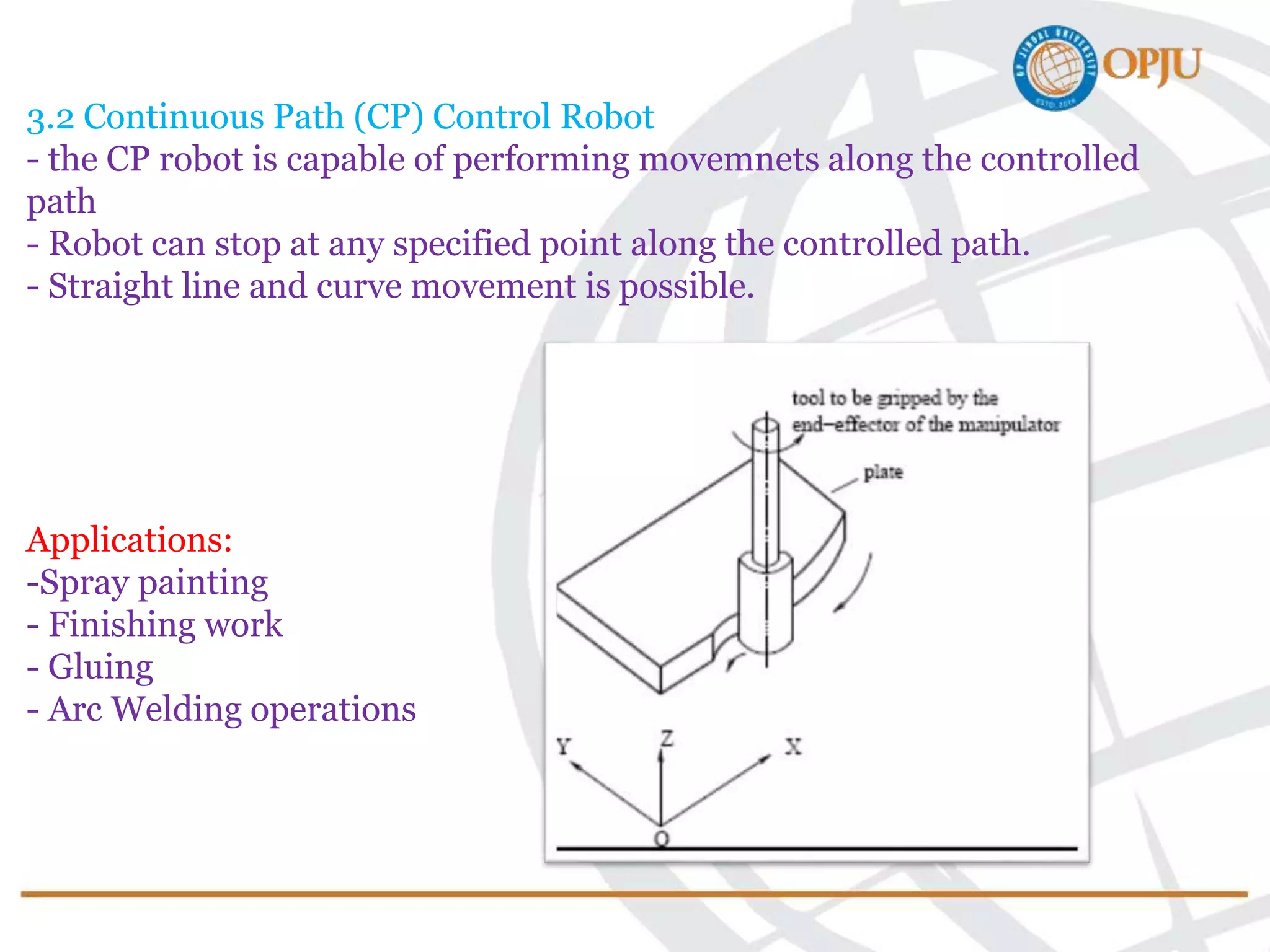
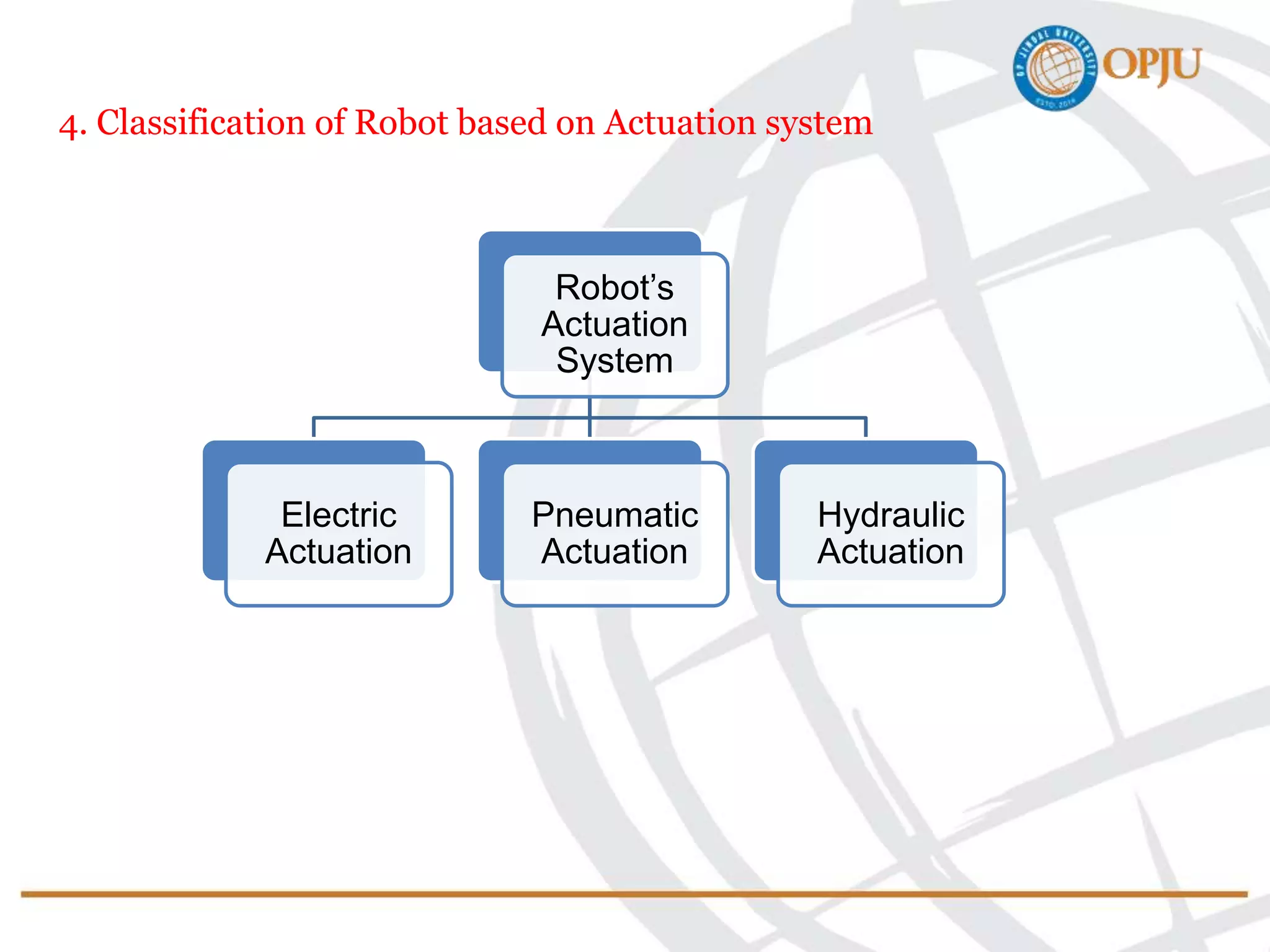
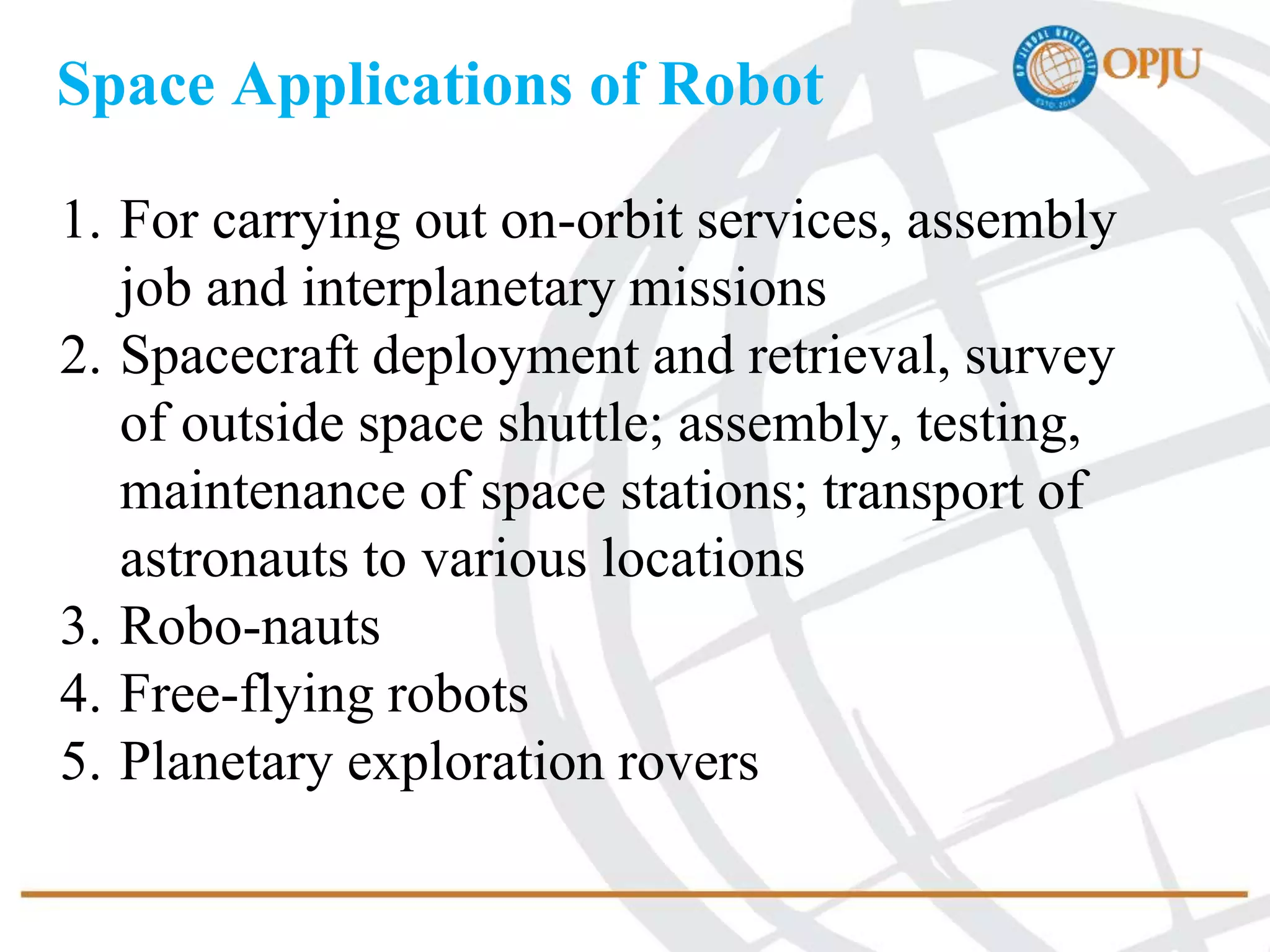
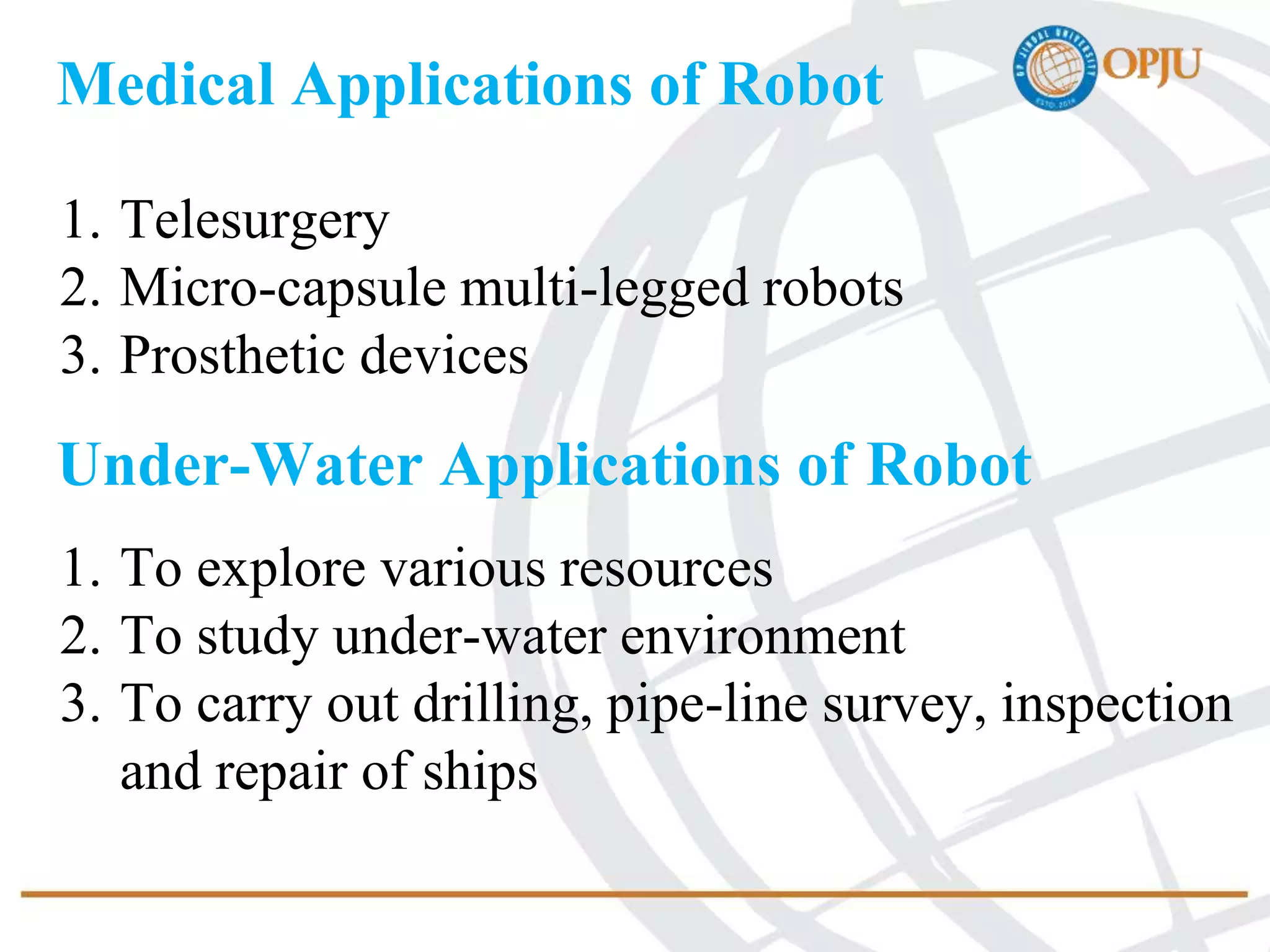
This document provides an introduction to robotics and robots. It defines robots as programmable mechatronic devices equipped with artificial intelligence. The document then discusses the historical development of robots from ancient times to modern examples. Robots are classified in multiple ways, including by physical configuration, mobility, and control system. The major applications of robots discussed are in manufacturing industries, space exploration, medicine, and underwater exploration. In each field, examples are given of how robots are used.
![Robot:
Robot has been defined by various organization
1. According to Robot Institute of America (RIA) [1979]
It is a reprogrammable multi-functional manipulator designed to
move materials, parts, tools or specialized devices through variable
programmed motions for the performance of a variety of tasks.
2. According to International Organization for Standardization
(ISO): An automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose
manipulator programmable in three or more axes, which can be
either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation
applications.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr-221212050259-c370a93e/75/Dr-S-K-Lecture-2-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
![Motivation Towards Robotics:
In the present scenario, to fulfill the gap between demand and supply
in the dynamic and competitive market with precision is the prime
motivation for the implementation of robots.
Another. In modern manufacturing systems, the following are the
essential requirements which also motivate towards robotics :
1. Quality improvement
2. Increment of Production Rate
3. Reduce production cost
Note: Automation can satisfy the requirement of modern systems
[Flexible and Fixed]
“Robotics is a type of flexible automation”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr-221212050259-c370a93e/75/Dr-S-K-Lecture-2-pptx-7-2048.jpg)